Toothy monsters! Top 10 largest sharks on the planet! (11 photos)
When it comes to ocean predators, size matters. And sharks are a big part of that. While not all sharks are big, there are some that are incredibly huge. It's worth noting that some of these ocean giants are in danger of extinction due to overfishing, pollution, and climate change. 
Longfin Mako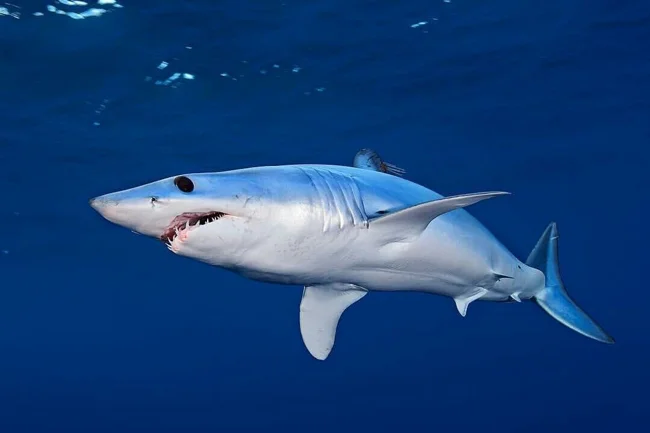 
Longfin Mako is a cartilaginous fish of the mako shark genus of the herring shark family. It is distributed in temperate and tropical latitudes. Some characteristics of the species:
1. A smooth, elongated shark with a long conical snout.
2. On average, it reaches 2.75-3 meters in length and weighs 120-135 kg. The largest specimen, 4.3 meters long, was caught in February 1984 near Pompano Beach in Florida, weighing 554 kg.
3. The teeth are large, very sharp, thin, without serrations along the edges, curved inward.
4. The eyes are large, equipped with a nictitating membrane.
5. The pectoral fins are equal to or longer than the head, the anterior edge is almost straight, the tips are wide and rounded.
6. The first dorsal fin is large, its base is located behind the base of the pectoral fins, the apex is rounded.
7. The second dorsal and anal fins are tiny, located opposite each other close to the caudal fin.
8. The caudal fin is crescent-shaped, there is a tiny notch at the edge of the upper lobe, the lower lobe is well developed and almost equal in size to the upper lobe.
Habitat: in the Indian Ocean - the Mozambique Channel, in the Pacific Ocean - the shores of Japan and Taiwan, northeastern Australia, numerous islands of the central Pacific region, northeastern Micronesia and southern California. It feeds on small bony fish and squid. They reproduce by aplacental viviparity, with a litter typically consisting of 2 young (one from each oviduct).
The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed this species as vulnerable due to its low reproductive capacity, small numbers, and susceptibility to intensive fishing.
Bluntnose Sixgill Shark 
The bluntnose sixgill shark is a species of combtooth shark, also known as the cow shark or bluntnose sixgill shark. Habitat: many areas of the World Ocean. It is found along the continental shelf of Europe, off the coast of North, Central and South America, off the coast of Florida and in the Caribbean. It is also found along the African coast, off the eastern coast of Australia and near New Zealand, in the Malay Archipelago, off the coast of Korea and the Japanese Islands.
This shark has a blunt, rounded nose, six pairs of relatively long gill slits on the sides of the head. The body is quite massive, the head is large, the eyes are small. Distinguishing features: fluorescent blue-green eyes with black pupils, six saw-like teeth on each side of the lower jaw and a characteristic position of the dorsal fin - it is shifted back and located close to the caudal fin.
Adult males usually average 3.1 to 3.3 m, adult females from 3.5 to 4.2 m. The average weight of an adult bluntnose sixgill shark is 500 kg. Large specimens can reach 4.5 m in length and 700-750 kg in weight.
It feeds on various fish, bottom organisms, including mollusks, crustaceans, sea worms and rays. It can attack marine mammals - seals and fur seals. It is a solitary predator, preferring deep-sea habitats, making daily deep migrations - at night, usually, it rises closer to the surface, before sunrise it dives into the depths. Juveniles are sometimes present in shallow water.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature classifies the bluntnose sixgill shark as "critically endangered". The species is an object of commercial and sport fishing. The meat and organs of these sharks are widely used in food and some other areas of human activity.
Thresher shark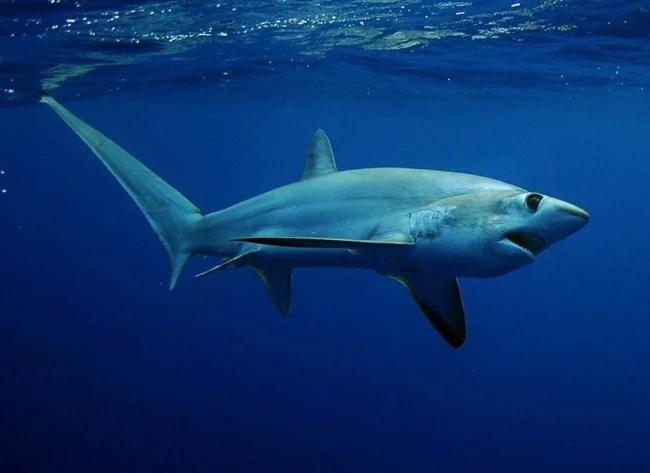 
The thresher shark is the largest species of cartilaginous fish of the genus Thresher shark of the family of the same name of the order Lamniformes. It reaches a length of 6.1 m, with a weight of 450-500 kg, with half of the length being the elongated upper lobe of the caudal fin. These sharks have a streamlined body, a short and pointed snout, and medium-sized eyes.
They live in all temperate and tropical waters, although they prefer cool temperatures. They are found both in the open ocean at depths of up to 550 m, and near the coast and usually stay in the surface layers of water.
They feed mainly on schooling pelagic fish (mackerel, horse mackerel, anchovies, etc.), squid, octopus, and sometimes seabirds. Reproduction occurs by placental viviparity. There are up to 4 newborns in a litter.
Despite their large size, thresher sharks are considered to be harmless to humans, as they are shy and have small teeth.
It is also worth noting that this species is an object of commercial fishing and sport fishing. Their meat and fins are highly valued.
Tiger shark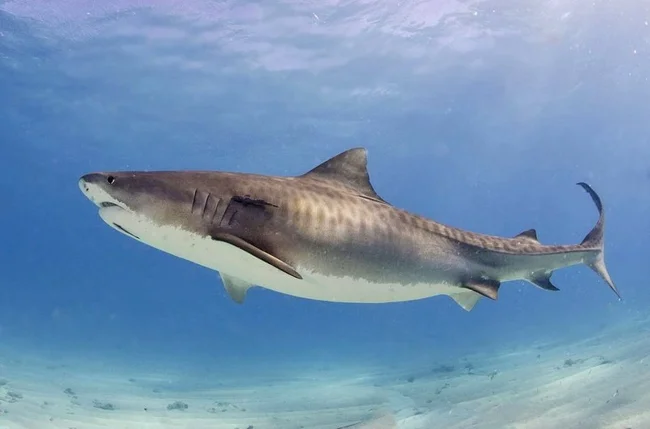 
The tiger shark is the only representative of the cartilaginous fish of the same genus of the family of gray sharks of the order Carcharhiniformes. One of the most common species of sharks on Earth. Some features:
1. The body is torpedo-shaped, tapering towards the tail, the snout is square, short and blunt. The shark has a large head with large eyes, a large mouth with many teeth with a beveled top and serrated edges.
2. The body length usually fluctuates between 3.5-4.5 m, but there are individuals of 5.5 meters, weight from 380 to 635 kg, and females are larger than males.
3. The body is gray, the belly is white or pale yellow, on the sides there are noticeable alternating stripes, reminiscent of tiger stripes (hence the name).
4. They live in the seas of the tropical and subtropical zones. They can be found at depths of up to 1000 meters, but are most often found near the surface of the ocean or in shallow waters.
5. The diet includes various animals, including fish, birds, snakes, crustaceans, mollusks and dugongs.
6. Tiger sharks are ovoviviparous, a female can give birth to 10 to 80 sharks at a time.
Tiger sharks are considered one of the most dangerous sharks for humans due to their omnivorous nature and curiosity
Giant hammerhead shark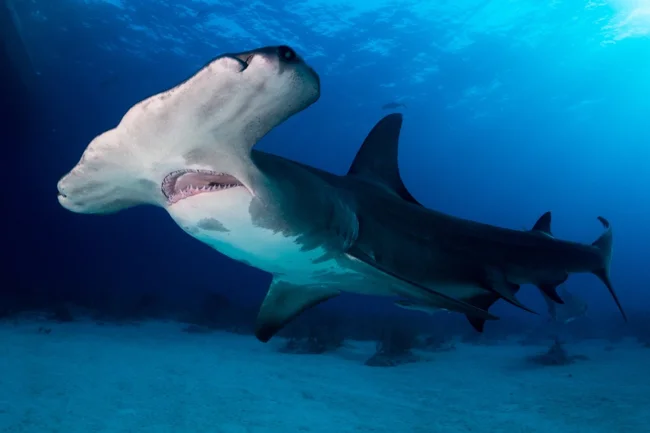 
The great hammerhead shark is a species of the genus Sphyrna from the hammerhead shark family. Some characteristics:
1. The maximum recorded length is 6.2 m.
2. The front edge of the "hammer" is almost straight, which distinguishes these sharks from other hammerheads.
3. The high dorsal fin is shaped like a sickle.
4. The teeth are triangular with strongly serrated edges, and have an increasingly greater slope towards the corners of the mouth.
5. The body is light gray or gray-brown on the back, turning white on the belly.
6. The shark's skin is covered with closely spaced placoid scales.
It lives in tropical and warm temperate waters. In the Atlantic Ocean, it is found from the coast of North Carolina to Uruguay, including the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, and from Morocco to Senegal, as well as in the Mediterranean Sea. Giant hammerhead sharks lead a solitary lifestyle, actively hunting for various crustaceans, cephalopods, bony and cartilaginous fish, including sharks. They reproduce viviparously, females give birth every 2 years, with a litter of up to 55 newborns. It should be noted that, although potentially dangerous, these sharks rarely attack people.
Giant hammerhead sharks are the object of targeted commercial fishing. Because of it, from 1978 to 2003, their population decreased by 73%. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assigned this species the status of "endangered".
Pelagic megamouth shark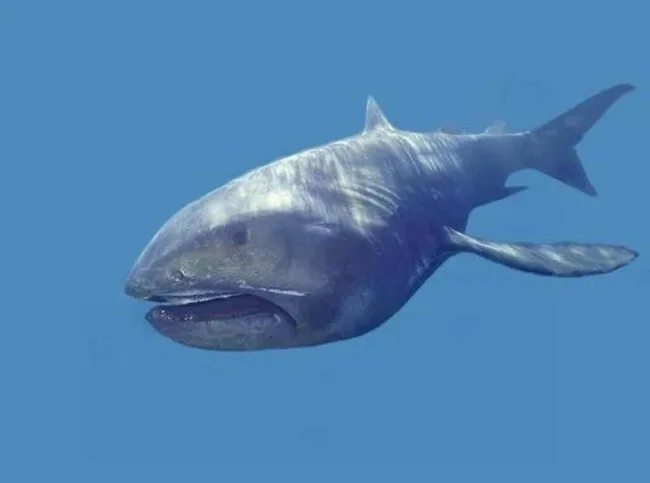 
The pelagic megamouth shark is one of the most unusual and little-studied inhabitants of the ocean depths. Some features of the species:
1. It got its name due to its huge mouth, which takes up almost half the length of its head.
2. Adults can reach a length of 5.5-5.7 meters and weigh 1.2-1.5 tons.
3. The shark's body is streamlined, which helps it move effectively through the water.
4. The coloration varies from dark brown to gray, which helps the animal blend into the environment at great depths.
5. The skin is covered with small placoid scales, which reduce water resistance when moving.
It leads a solitary lifestyle and makes vertical migrations. During the day it stays at depths of 150-1000 meters, and at night it rises closer to the surface, following the migration of zooplankton, which makes up the main part of its diet.
Habitat: tropical and subtropical waters of the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Prefers open ocean spaces and rarely comes close to the coast. It is considered ovoviviparous, and the female carries several developed embryos, which are born fully formed. Sexual maturity occurs when the body length of about 4 meters.
Studying the megamouth shark helps to understand the evolutionary adaptations of deep-sea animals and the mechanisms of filter feeding in sharks.
Great White Shark 
The great white shark is a species of cartilaginous fish of the herring shark family. One of the largest predatory fish on Earth. Some features:
- adults usually reach 4.5-5 meters in length, and some females grow up to 6 meters and weigh up to 2 tons;
- the body is streamlined, cigar-shaped;
- coloring - the back and sides are gray with a bluish tint, which makes the shark invisible against the background of dark depths. (the white belly camouflages the predator under the bright light of the surface);
- jaws - they contain three rows of serrated teeth up to 7 cm long, which are constantly renewed;
- the bite force reaches 18,000 N, which makes it easy to crush bones and tear flesh;
- sensory system - ampullae of Lorenzini, these are microscopic pores on the snout that detect electromagnetic impulses from the movements or heartbeat of living creatures, allowing it to detect prey hundreds of meters away;
- thermoregulation - thanks to a complex circulatory system, the shark heats up its muscles, which gives it an advantage in cold waters where other fish become sluggish;
Habitat: prefers coastal zones with a temperate and subtropical climate, where the water temperature ranges from 12 to 24 °C. It is found in regions such as South Africa, South Australia, the west coast of the United States, cold regions off the coast of Canada, the Mediterranean Sea and certain areas of the Pacific Ocean.
The basis of the menu is marine mammals (seals, sea lions) and large fish, such as tuna or even other sharks. Young individuals often feed on squid and small fish, switching to high-calorie prey as they grow older.
It is considered the most dangerous shark species for humans. At the same time, it is on the verge of extinction: there are about 3,500 individuals in the world.
Greenland polar shark 
The Greenland polar shark is the northernmost and cold-loving species of shark. It lives in the cold waters of the Arctic and the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean. Some features:
1. Habitat - off the coast of Greenland, Iceland, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Norway and the USA. It is found on the continental and island shelves and in the upper part of the continental slope from the surface of the water to a depth of 2200 m.
2. The maximum recorded length is 6.4 m, and the weight is about 1 t. The largest individuals can reach 7.3 m and weigh up to 1.5 tons.
3. This shark has an elongated head, a short and rounded snout, a massive, cylindrical body. The color ranges from pale gray-cream to black-brown.
4. The average lifespan is 250 years, but according to scientists, some individuals can live up to 500 years.
5. They feed on fish and carrion.
The Greenland shark is a rare species threatened by climate change and poaching.
Giant shark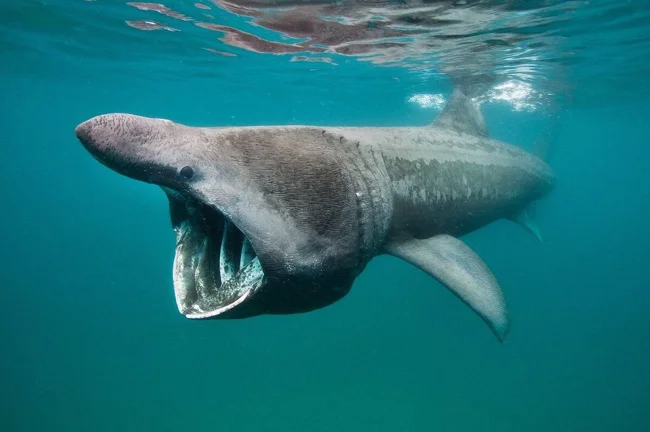 
The basking shark, or giant shark, is a large pelagic shark from the order Lamniformes, the only modern species of the family of the same name. Some characteristics:
- the maximum recorded length of males is 9 m, females 9.8 m (according to unconfirmed data, there are specimens up to 15 m);
- the maximum recorded weight is 4 tons;
- the body is massive, loose, with a conical snout, a huge mouth and large gill slits that can swell;
- the color is gray-brown with specks;
- the caudal peduncle has pronounced lateral keels, the tail is sickle-shaped;
- small conical teeth with one point bend back, in one row there can be more than 100 teeth.
The giant shark feeds on plankton, but does not suck in water, but simply swims with an open mouth, filtering through the gills everything that gets into it. In this way, the giant shark is able to filter up to 2000 tons of water per hour.
It is found in the temperate waters of all oceans. In the Barents and White Seas. They live in small schools and alone. It is worth noting that giant sharks do not pose a danger to humans. For a long time they were valuable commercial prey, but overfishing led to a reduction in the population to a vulnerable level.
Whale Shark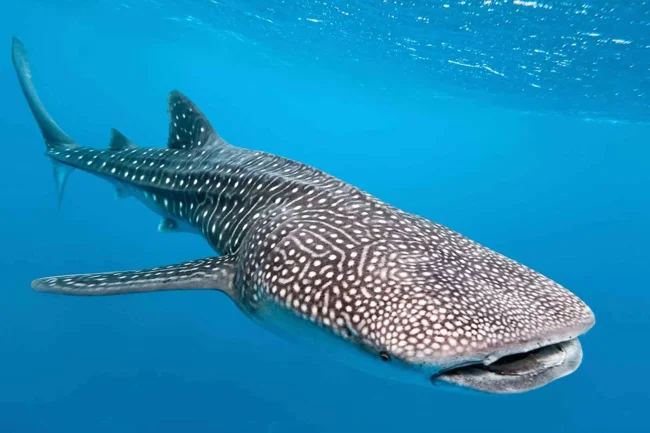 
The whale shark is a large pelagic shark of the rhyncodontidae family, or whale sharks, of the Wobbegongiformes order. Some features:
1. The largest of the currently existing shark species, as well as the largest of the modern fish. The usual size reaches at least 12 meters with a weight of 14 tons, but there were individuals up to 18 meters and weighing up to 20 tons.
2. A powerful body covered with thick skin with tiny pointed scales. The head is relatively small, somewhat flattened, and turns into a flat muzzle with a wide mouth. The eyes are small and deep-set.
3. The back and sides of the body are dark gray, with yellowish or dirty white longitudinal and transverse stripes. The belly is light gray.
4. It feeds mainly on plankton, straining food from the water with the help of a special straining apparatus formed by gill arches.
It stays near the surface of the water most of the time. It swims very slowly, usually no faster than 5 km/h, and does not pose any danger to humans.
It lives in warm waters of tropical latitudes throughout the World Ocean. It is usually found in small scattered groups, less often alone, and occasionally, in places where food is abundant, it forms large clusters of hundreds of individuals. Life expectancy, according to the latest data, is 80-130 years. Since 2016, the whale shark has been classified as an endangered species.