Biologist showed how human body tissues look like when you look at them with a microscope (11 photos + 1 video)
This article will be a selection with various biological structures and tissues of the human body, taken with electron microscope. 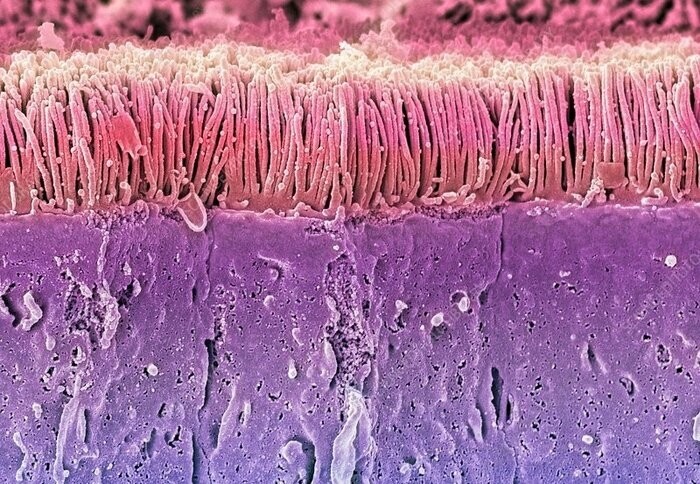
I will try to leave a clarification for each image description so that even people far from biology and medicine can understand what is shown in the picture.
Important point: due to features of the electron microscope, all source images are obtained in black and white and only then are painted on a computer for visibility. Therefore, the colors seen in the pictures may not match with real.
1) Skin surface
The top layer of human skin is made up of dead skin cells. that perform a protective function. In addition to keratinized cells on the photo shows the sweat gland (left, bottom), and the hair shaft, the bulb of which is located in the lower layers of the skin (right). Magnification: x2000 times. 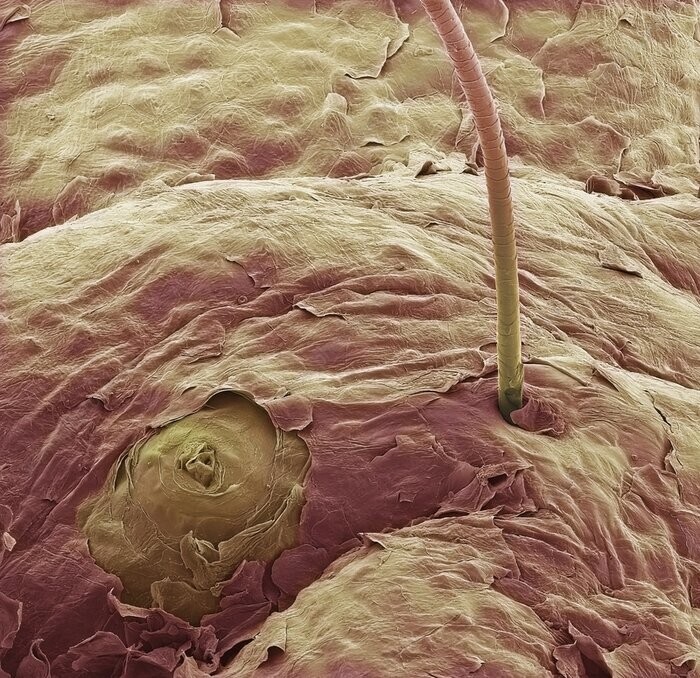
Skin surface
2) Skeletal muscles
Skeletal muscle tissue is made up of many individual dark red muscle fibers that have a striped appearance due to contractile filaments called myofibrils (purple).
Each fiber is surrounded by endomysial connective tissue. (gray), which contains nerve cells and capillary blood vessels vessels (beige color) feeding muscle tissue. Inside the capillary in the center the erythrocyte (red) can be seen. Top left - cell nucleus (yellow). Magnification: x5000 times. 
Skeletal muscles
3) Blood cells
Blood consists of two main components: liquid plasma and formed elements (cells).
The photo shows the formed elements of blood:
1) erythrocytes - participate in gas exchange, carry oxygen (red);
2) lymphocytes - cells of the immune system (pink);
3) neutrophils - cells of the immune system (large cream cells);
4) macrophages - cells of the immune system (green);
5) platelets - provide the formation of blood clots and blood clotting in case of damage to the vessel (small cream cells); 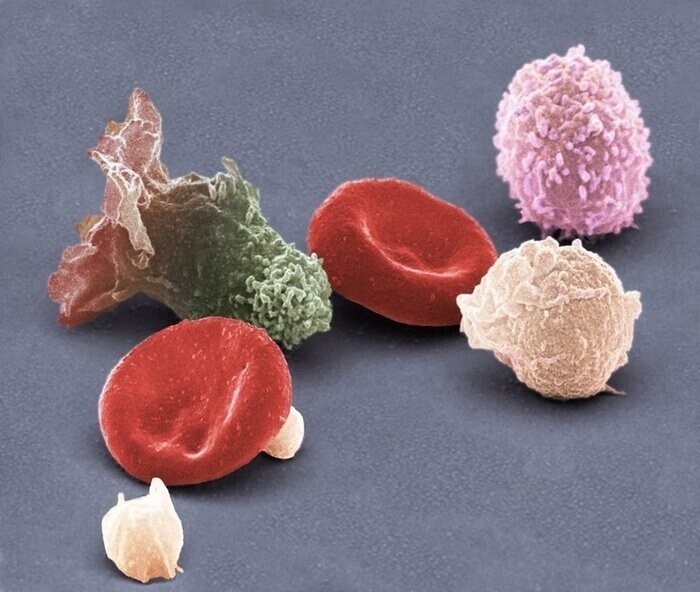
blood cells
4) Artery (arteriole)
Blood in the body moves through the vessels (veins, arteries and capillaries). Arteries carry oxygenated blood to the tissues under the large pressure, so they have thick walls (highlighted in blue) and a special lining that prevents them from being squeezed and damaged.
There are many blood cells inside an artery. (erythrocytes, highlighted in red), which are involved in gas exchange and carry oxygen to tissues and organs. Magnification: x1600 times. 
Artery
5) Nerve
With the help of nerves, the CNS collects information from receptors body and gives orders to tissues and organs and generally coordinates body work.
The photo below shows a bundle of peripheral nerves. (in the center). Inside the bundle, individual nerve fibers are clearly visible (blue color) surrounded by a protective myelin sheath (pale blue). The myelin sheath is formed by Schwann cells (red). also in the composition of the nerve bundle includes reticular fibers (gray) and others connective tissue cells.
The nerve bundle itself is surrounded by perineural cells (yellow color). At the bottom, you can see the cell nucleus, it is labeled orange (just below center). 
Nerve
6) The surface of the tooth enamel
The photo shows the surface of an erupted tooth. grooves, that you see previously contained ameloblast cells that secreted minerals that form enamel. Magnification: x600 times. 
Tooth enamel
7) Testicles (testes)
The testicles are the male reproductive organs where maturation of germ cells (spermatozoa). Tails are clearly visible inside spermatozoa (white) and progenitor cells (blue). Magnification: x2000 times. 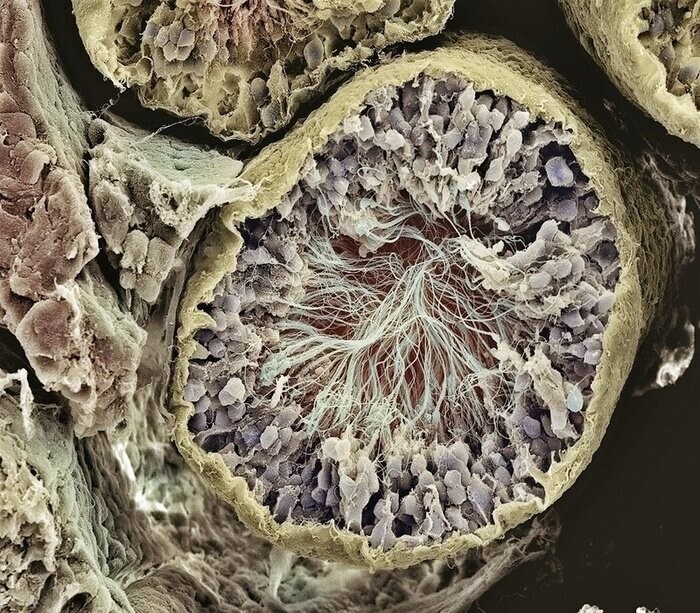
testicles
8) Ovaries
The maturation of the egg (female germ cell) in the ovaries. After maturation, the egg (red color)vt) exits the ovary into the uterus pipe as a result of rupture of a mature follicle and the woman begins ovulation. Magnification: x1600 times. 
ovaries
9) Adipose tissue
Adipose tissue consists of cells - adipocytes (red). They are a reservoir filled with triglycerides. Textile braided with an extensive network of blood vessels (beige). Under hormones, fat cells can both store fat and excrete them into the blood so that the body converts them into energy in case of nutritional deficiency. Magnification: x2200 times. 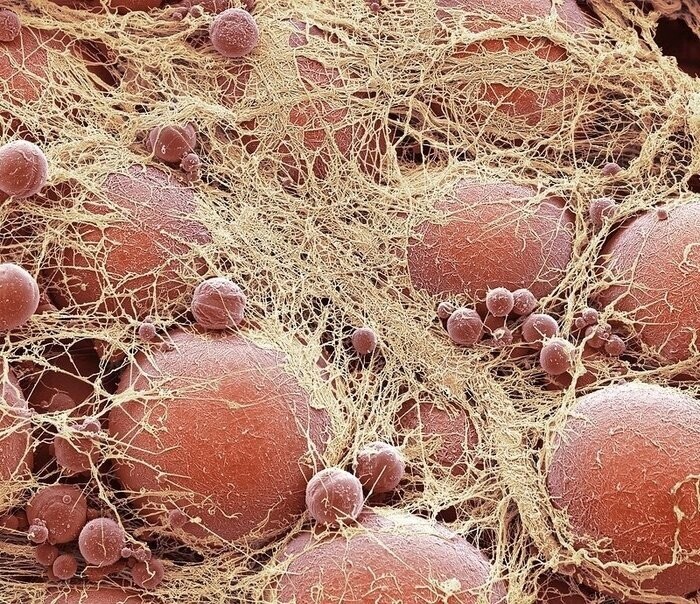
Adipose tissue
10) Intestinal villi
Cells that form intestinal villi line the surface intestines and thus increase the usable area of absorption nutrients from food. The intestinal villi themselves are associated with blood vessels, through which nutrients are further transported to all tissues and organs. Magnification: x1200 times. 
intestinal villi
Bonus: Some More Human Tissue in Video Format