Better pictures taken by the James Webb telescope during its first year in space (14 photos)
It's been a little over a year since NASA's space telescope The $10 billion James Webb took off and during this time, he transmitted to Earth many amazing images of space from unprecedented detail. Here are the best images from the first year the telescope's stay in space, including a new image of the "Pillars creation", the rings of Neptune, the Cartwheel galaxy and the "cosmic dance" five galaxies.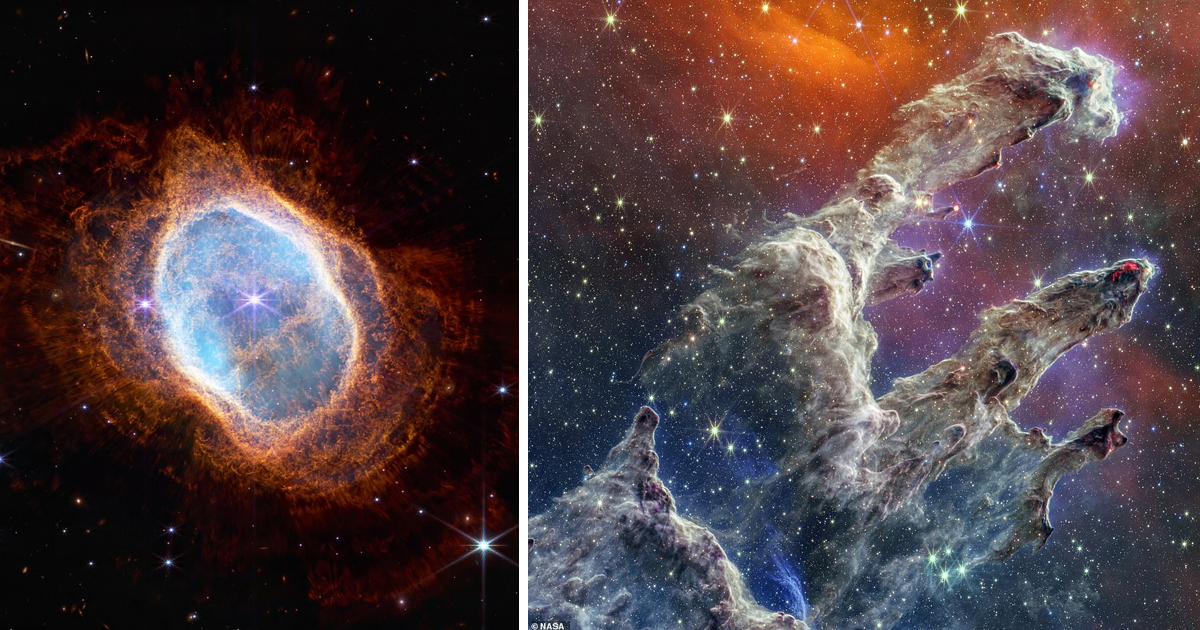 
southern ring nebula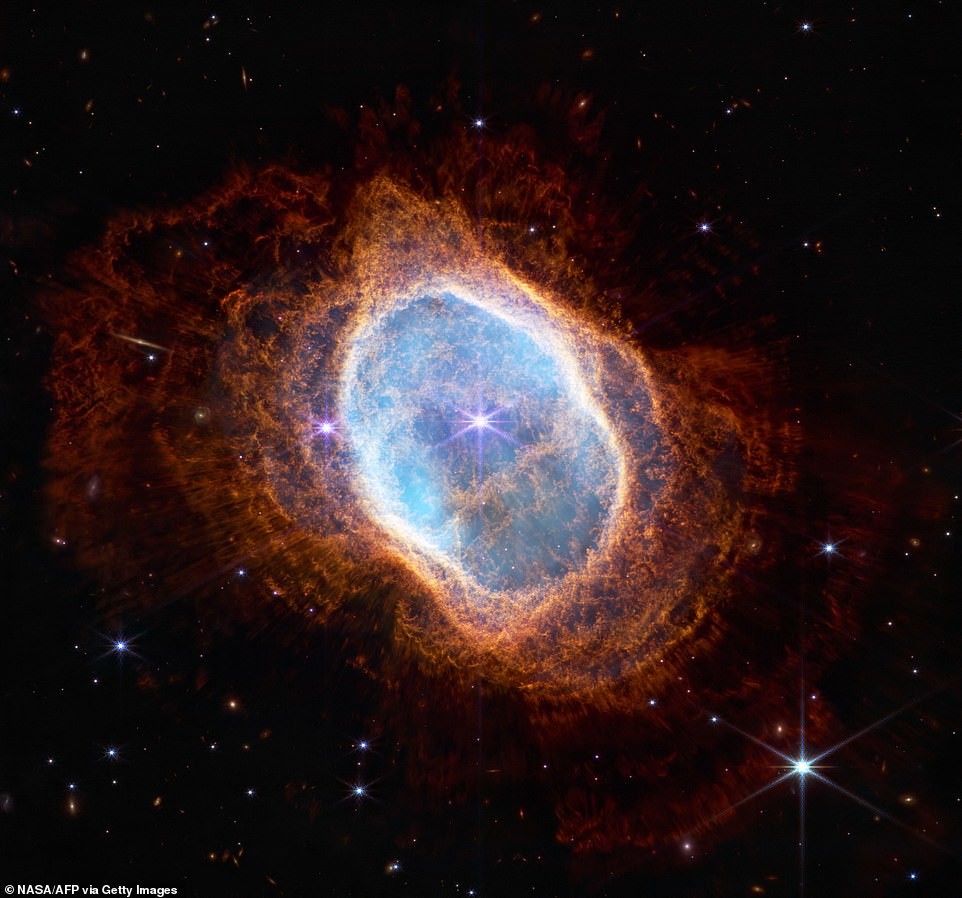 
In July, NASA released the first four photographs taken by James Webb, including the Southern Annular Nebula - an expanding luminous shell of ionized gas emitted by red giants at the end of their lives.
According to NASA, the Southern Ring Nebula has almost half a light year in diameter and located at a distance of about 2000 light years from Earth.
The dim star in the center of the image over the millennia emitted rings of gas and dust in all directions, due to which reminiscent of a bright glare on a precious stone.
A dying star shrouded in dust reveals its "last performance," as NASA put it, "that through which our Sun billions of years to go.
The southern ring nebula is shown almost completely frontal, but when rotated to view it edge-on, its three-dimensional shape resembles two bowls folded at the bottom, opening in different directions with large hole in the center.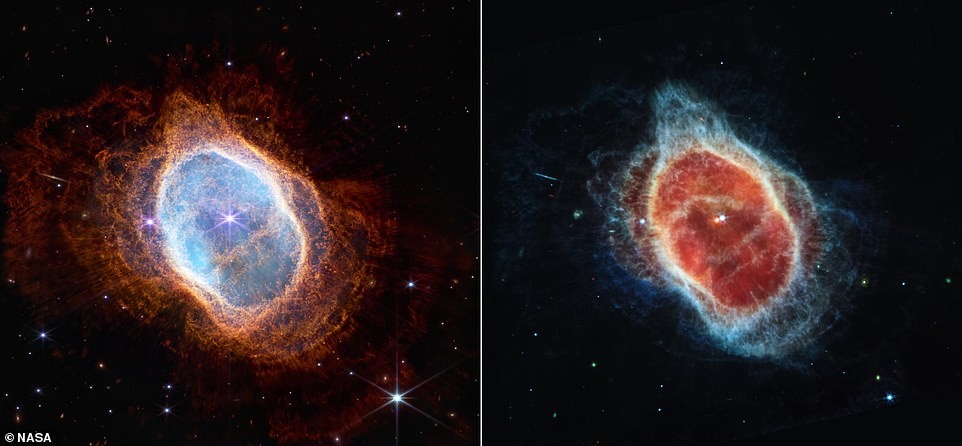 
"James Webb" sent two images of the Southern Ring Nebula, taken with two different instruments - a near-infrared camera range (NIRCam) and mid-infrared (MIRI) instrument, which sees light in the mid-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The stars and their layers of light are clearly visible in the NIRCam image, and the MIRI image showed the nebula's second star for the first time. NASA stated that a brighter star affects the appearance of the nebula, and when stars revolve around each other, they "stir" gas and dust, resulting in asymmetric patterns.
These two images also reveal a treasure trove of distant galaxies - not stars - in the background, which look like a lot of multi-colored glowing dots. The most attentive will also notice a bluish line on the left, which NASA astronomer Carl Gordon, according to him, originally mistook for part of the nebula. However, he later realized that it was galaxy photographed from the side. This perspective can tell more about how stars are distributed throughout the galaxy.
SMACS 0723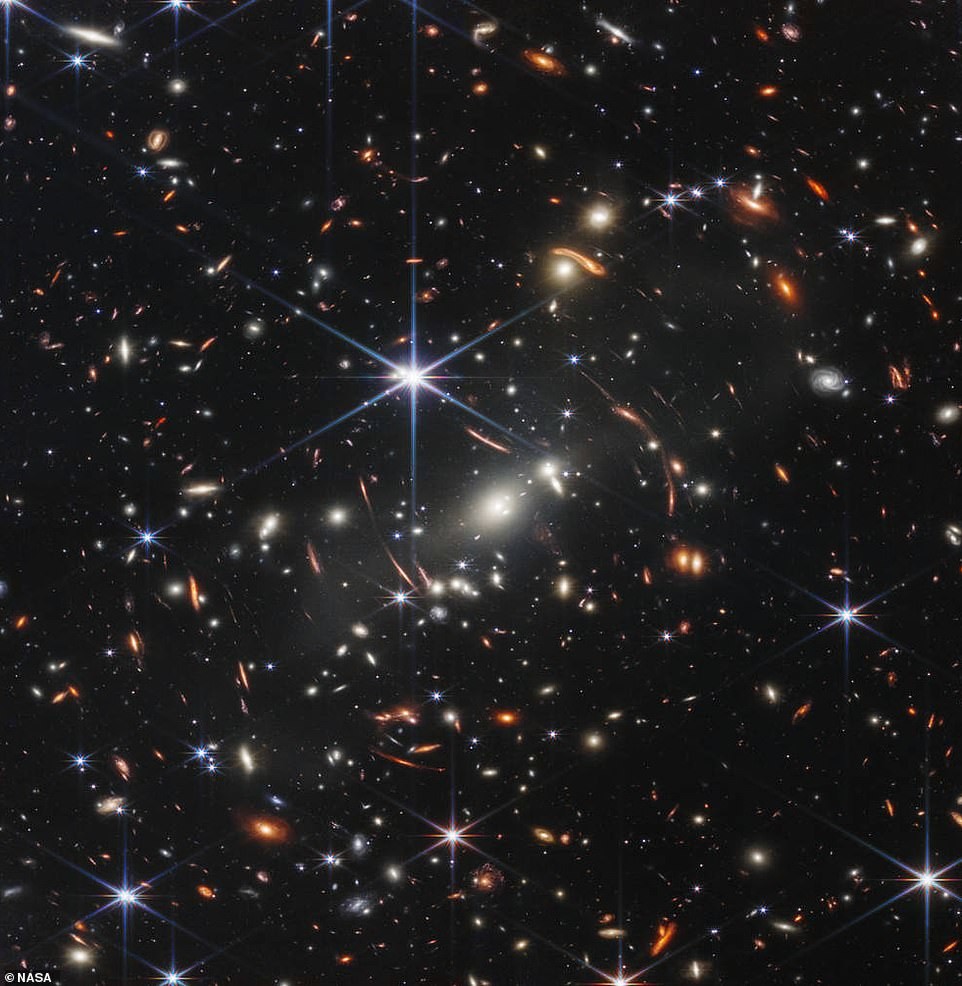 
Another shot from the first batch released in July shows galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 as it was 4.6 billion years ago.
Clusters of galaxies are the largest objects in the universe held together by their own gravity. They contain hundreds or thousands of galaxies, a lot of hot plasma and a large amount dark matter - an invisible mass that interacts with ordinary matter only through gravity and does not radiate, absorb or reflects light.
This SMACS 0723 image covers an area of sky approximately the size of a grain of sand that someone holds at arm's length, and shows thousands of galaxies in a tiny piece of the vast universe.
According to NASA, SMACS 0723 has such a powerful gravitational attraction that it distorts both space-time and and the path by which light subsequently travels through it. Because of this bright white galaxies distort and stretch light from more distant galaxies, causing them to appear elongated and almost "banana-shaped". 
The combined mass of SMACS 0723 acts as a gravitational lens and, according to NASA, "magnifies and distorts the light of objects behind them, providing a deep field of view of both extremely distant and faint by the nature of populations of galaxies."
NASA said the NIRCam camera, which captures light from edge of the visible to near-infrared electromagnetic spectrum, it was possible to catch distant galaxies in focus. Tiny, dull structures that have never been seen before, including stellar clusters - groups of hundreds to millions of stars that have a common origin, and they are all gravitationally bound by several billionyears.
Stephen's Quintet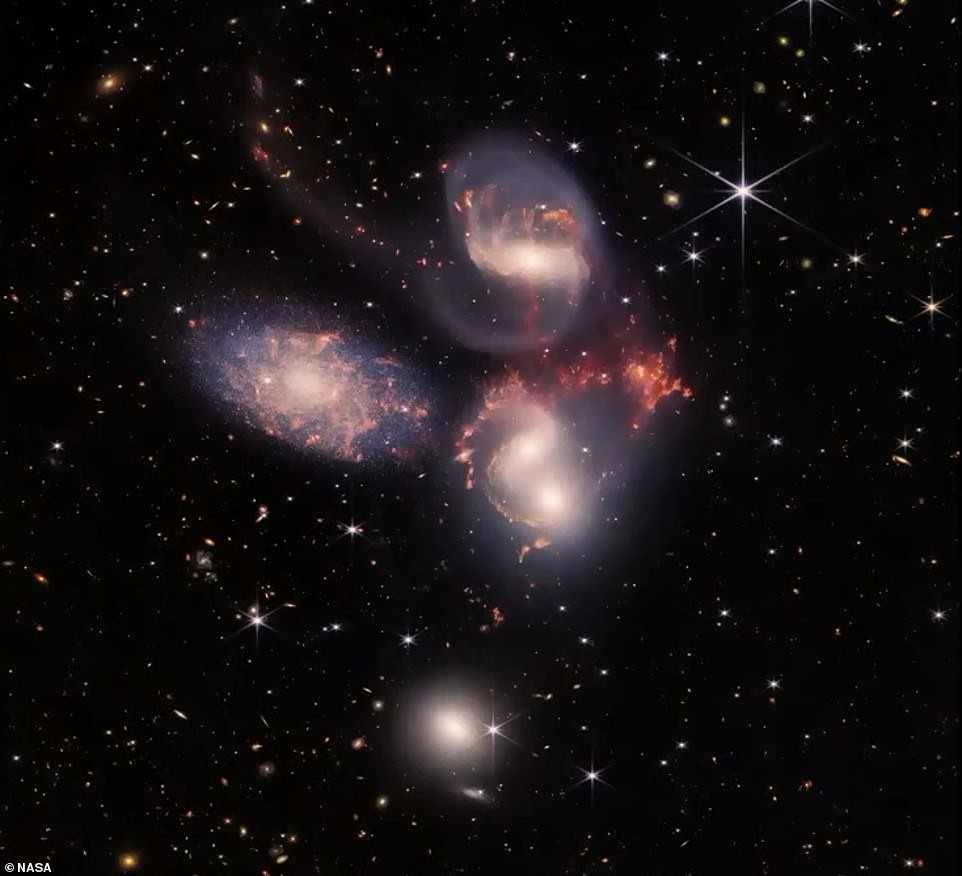 
The next photo is of Stefan's Quintet, a group of five galaxies in the constellation Pegasus, first discovered by a French astronomer Edward Stefan in 1877. Stefan would surely be shocked by the new James Webb image showing five galaxies "exquisite detail," as NASA puts it.
Four of the five galaxies in the quintet are involved in a "cosmic dance" of repeated close encounters.
"Dust lanes that cross galaxies, and long filaments of stars and gas, extending far beyond the central regions - all this indicates that galaxies are curved as a result of powerful collisions, the European Space Agency said. — Galaxies floating in space, distorted shapes shaped by tidal interactions, weave together into intricate shapes of the immeasurable cosmic dance choreographed by gravity.
Two of the five galaxies, NGC 7318 a and b, form a pair on the new The picture looks almost like one whole. The brightest representative of the five, spiral galaxy NGC 7320 on the left in the image, is closer the rest.
NASA said the image is a huge mosaic covering about one-fifth of the moon's diameter. It contains more 150 million pixels and consists of almost 1000 individual files images.
Stephen's Quintet is best known for appearing as angels at the beginning of the famous 1946 Christmas movie This Wonderful Life" starring James Stewart and Donna Reed.
Carina Nebula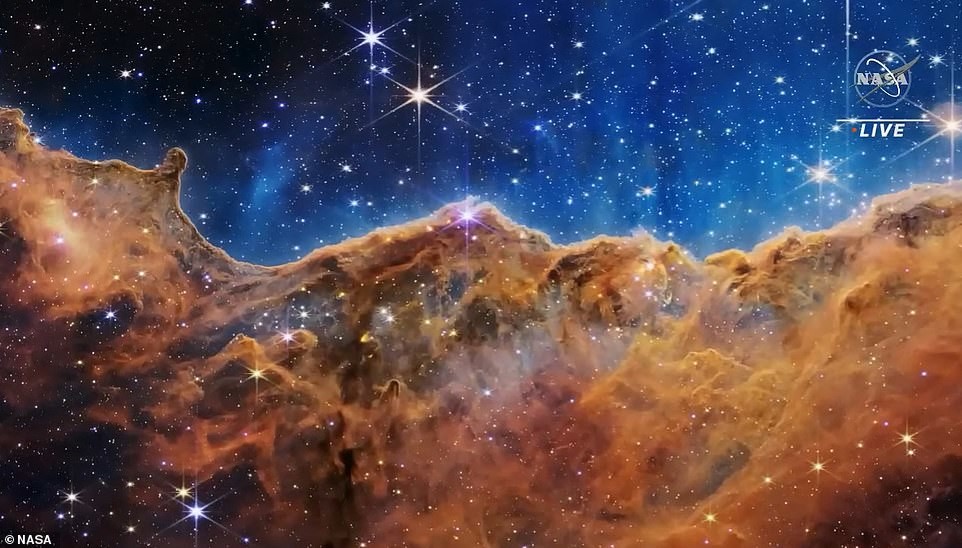 
The Carina Nebula is one of the brightest and largest nebulae in the world. space, located at a distance of about 7600 light years in the southern constellation Carina. Nebulae are "stellar nurseries" where stars are born, and it is this nebula that is home to many giant stars; some of them are even larger than our Sun. On a stunning photo the edge of a nearby young star-forming region called NGC is visible 3324.
At the bottom of the image is the western part of NGC 3324, and then, what NASA calls "Space Rocks" - orange-brown landscape "rocky mountains" and "valleys", strewn with sparkling young stars. Stormy ultraviolet radiation from young stars cuts through a wall nebula, slowly destroying it. The highest "peaks" in this picture are about seven light years high.
"Impressive pillars rise above the luminous wall of gas, resisting this radiation, according to NASA. - "Pair", which, seems to rise from the heavenly "mountains", in fact it is hot ionized gas and hot dust emanating from the nebula because of the inexorable radiation."
This is an image taken in infrared light by a space the James Webb Telescope, for the first time shows previously unseen areas the birth of stars.
“Today, for the first time, we see completely new stars that were completely hidden from our view,” Amber commented on the photo. Strawn, Deputy Space Telescope Project Manager "James Webb". - We see examples of bubbles, cavities and jets, blown out by these newborn stars. We even see some galaxies lurking in the background. We see examples of structures, oh we don't even know what they are."
Pillars of Creation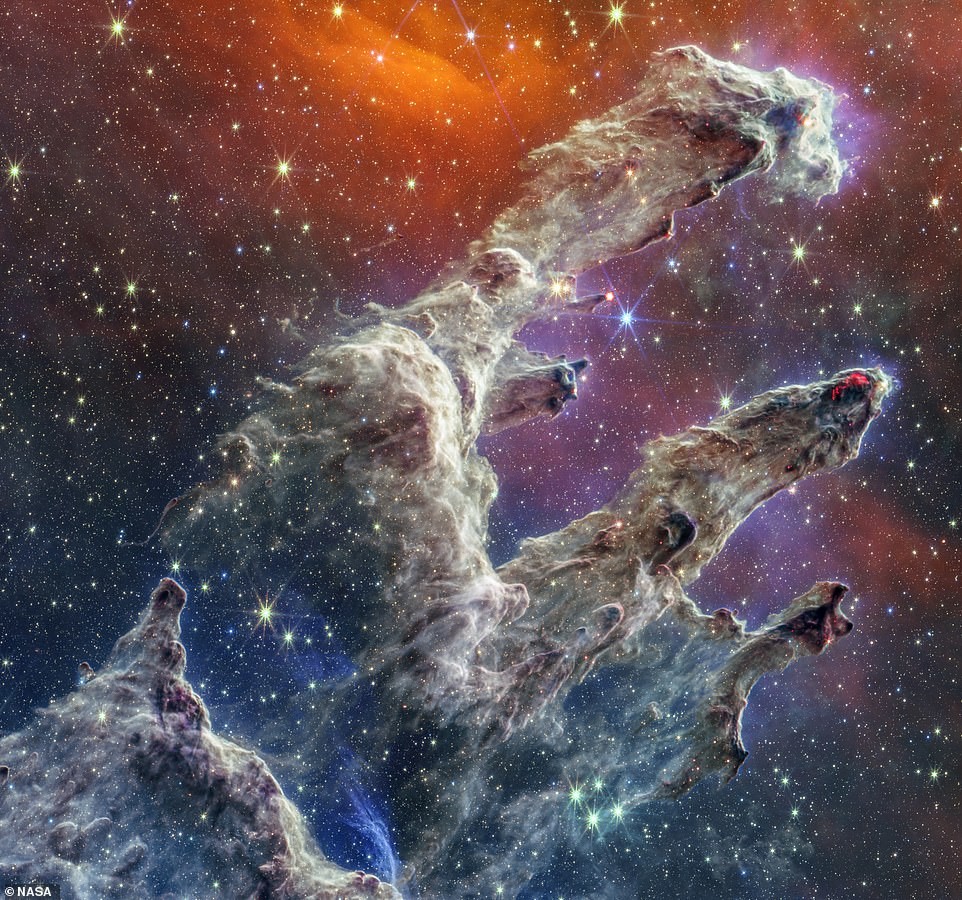 
Webb also allowed humanity to take a fresh look at spectacular "Pillars of Creation" - accumulations of interstellar gas and dust in Eagle Nebula. The first photograph was taken by Hubble in 1995. Webb's predecessor, but the new shot delivers an incredible level detail. It shows finger-shaped outgrowths of gas and dust, glowing edges of dust where young stars begin to form, and newly formed orange stars outside of the pillars.
The new image was taken in the mid-infrared range, which blocks the brightness of the stars and captures only the streams of gas and dust. This allowed a new way to study and understand the amazing education.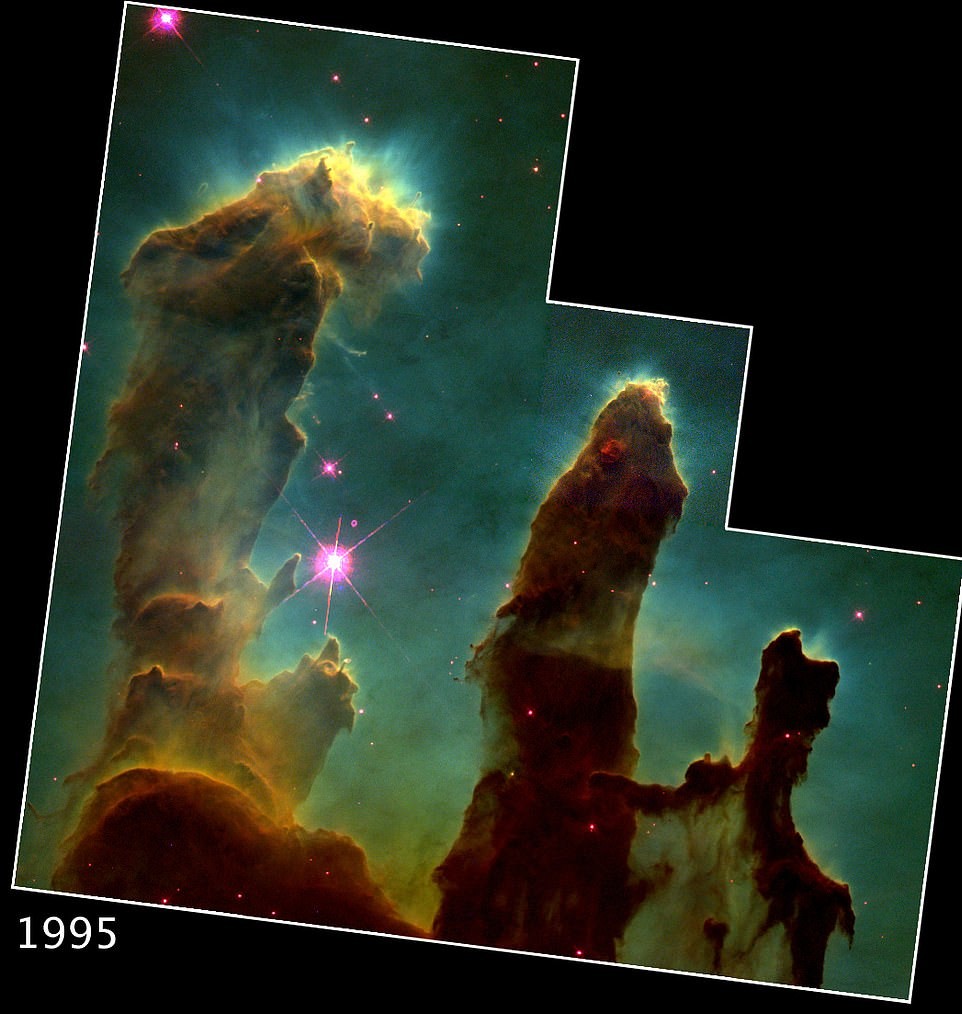 
Tarantula Nebula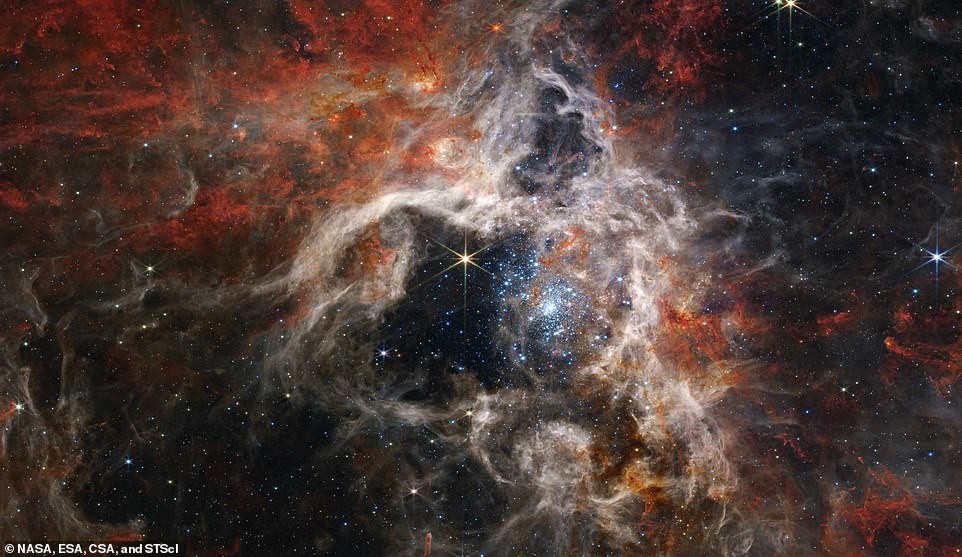 
Another picture of "James Webb", published by NASA in September, shows thousands of young stars in another "star manger" in the form spider. The Tarantula Nebula, also known as "30 Dorado" located at a distance of 161,000 light years in the Greater Galaxy Magellanic Cloud, which is the most blarge and bright area star formation in the Local Group - galaxies closest to ours Milky Way.
With the help of the NIRCam camera operating in the near infrared range, Webb was able to capture this nebula, which reminiscent of a tarantula dwelling, braided with silk cobwebs. Cavity nebulae, located in the center of the photograph, looks like hollowed out by the brilliant radiation of a cluster of massive young stars that twinkle pale blue in the image.
Exoplanet HIP 65426b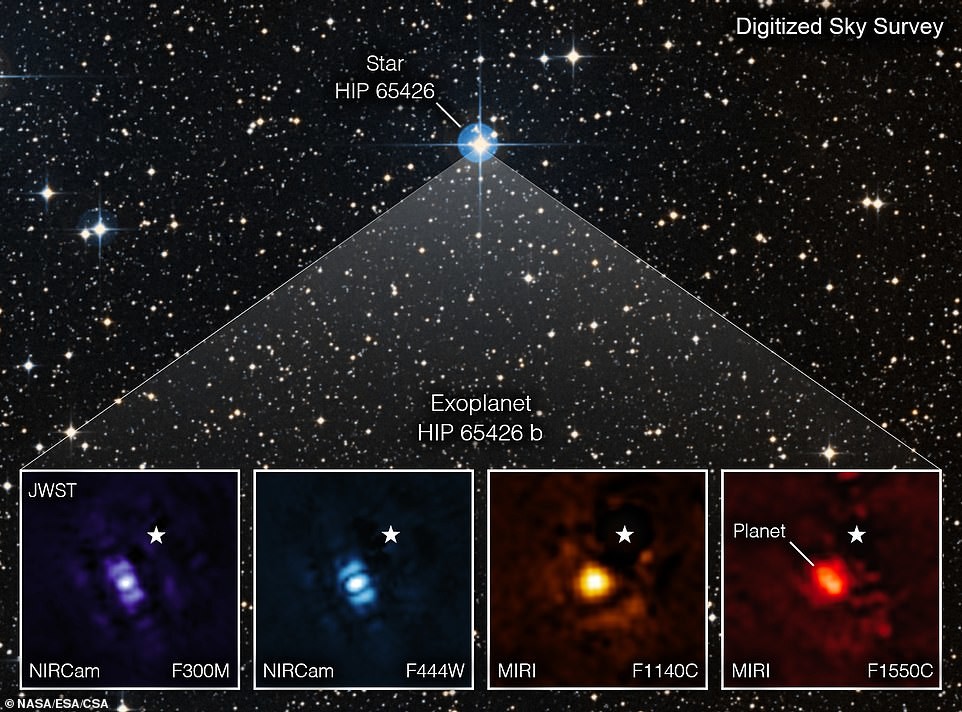 
"James Webb" also took his first photograph of an exoplanet - planets outside our solar system. Exoplanet HIP 65426b located 385 light years from Earth, and only 15 to 20 million years, which is much less than our Earth's age 4.5 billion years. The telescope used the NIRCam and MIRI instruments, which can block the surrounding starlight to make epic exoplanet shots.
The planet was first discovered in 2017 by the Very Large telescope of the European Southern Observatory in Chile, but the earth's atmosphere blocked long waves. However, since the Webb is floating in space, it was able to take direct pictures of the planet that astronomers can process, to remove the starlight and reveal the planet.
NASA has stated that this gas giant does not have a rocky surface, so life cannot exist on it.
Galaxies of the north ecliptic pole 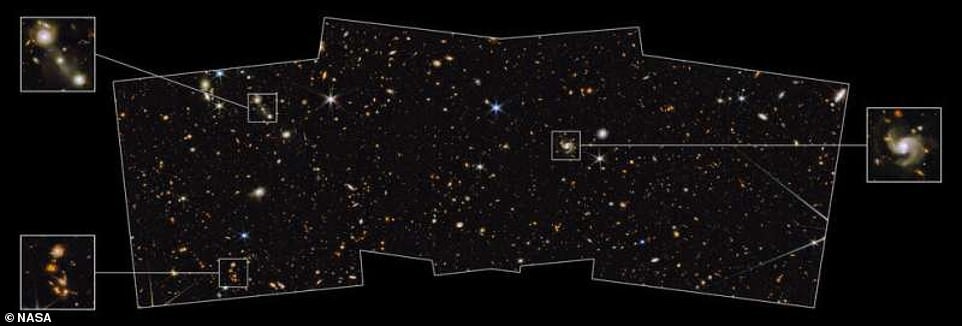
Another image posted earlier this month, shows the early universe with faint, distant light coming from newly formed galaxies in the region known as the North Pole ecliptic. These are thousands of never-before-seen galaxies that formed 13.5 billion years ago - about 200 million years after Big bang.
Space objects visible in the image, a billion times weaker than what can be seen with the naked eye, but the camera near-infrared (NIRCam) telescope fixed spectra of light coming from objects in the image.
The north ecliptic pole is located in the constellation Draco, one of the largest in the sky, which is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. This is one of the ancient Greek constellations, first cataloged Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century.
Galaxy Cartwheel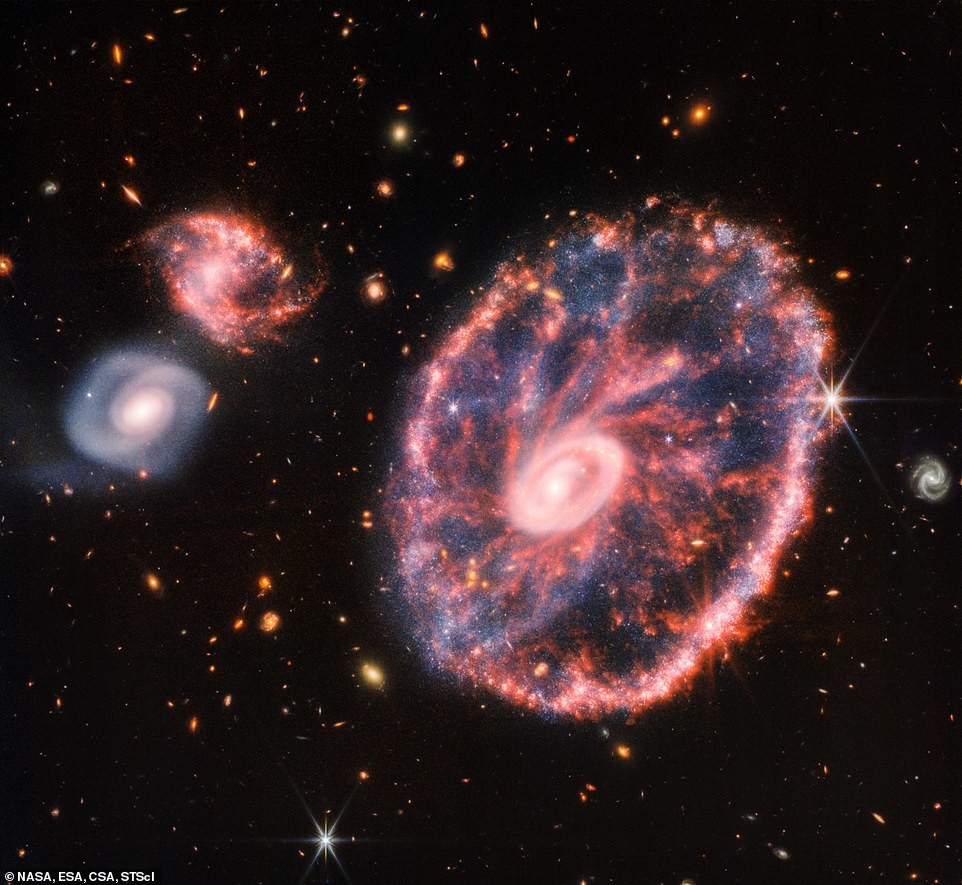 
James Webb took other pictures of spiral galaxies, one of which demonstrates the chaos of the Cartwheel galaxy, located on 489.2 million light-years from Earth.
Her cartwheel-like appearance is the result of extreme event - a high-speed collision between a large spiral galaxy and a smaller galaxy that is not visible in this image.
Other telescopes, including Hubble, have previously explored cart wheel. But the galaxy remained shrouded in mystery - perhaps literally, given the amount of dust that obscures the view.
The Cartwheel Galaxy has two rings - a bright inner ring and the surrounding colored ring. They expand outward from the center collisions are like ripples in a pond after a stone has been thrown into it.
Rings of Neptune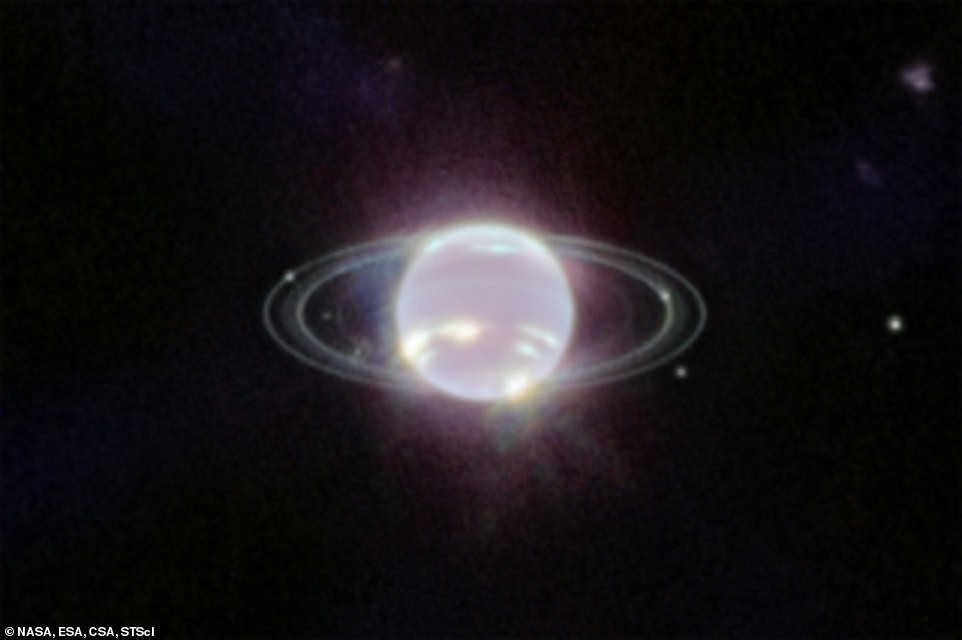 
James Webb took the clearest picture of Neptune's rings in more than in the 30 years since the Voyager 2 probe flew past the distant planets in 1989. In addition to several bright narrow rings, the image Webb, fainter dust lanes are clearly visible.
Behind the planet itself are seven of the giant's 14 satellites, the most the most prominent of which is Triton. He looks almost like a star because Neptune is obscured in the Webb's field of view due to absorption of methane in the infrared wavelength range. Triton, however, reflects on average 70% of the sunlight falling on its icy surface, so looks very bright.