Another version of the origin of man (11 photos)
Once upon a time, at the dawn of youth, being deeply dissatisfied with the official theory of the emergence of man, due to the fact that it only asked more questions than it gave, an understanding of this material came to them. Later it turned out that such a theory, the aquatic appearance of man, has a right to exist. And it was already announced quite a long time ago. Forced to reconsider previously compiled material. 
Forced to reconsider previously compiled material. By including existing evidence of the theory and related materials.
The issue that I want to highlight is very controversial and I repeat that it contradicts official history. And it relates to the emergence of man. According to the official theory, it is believed that man arose from a monkey at the moment when, due to another cataclysm, the climate changed. As a result, trees disappeared in the area where human ancestors lived. And the monkeys ended up in the steppe region. Covered with tall bushes and grass. As a result, the monkeys stood on their hind legs to rise above the grass and bushes. And in order not to cling to thorns and small branches, human ancestors lost hair on their bodies. At the same time, they picked up sticks to defend themselves. Although where in the savanna are sticks suitable as weapons? They became omnivores, starting to hunt other animals. What gave impetus to the appearance of speech. As the need for more complete transmission of information. And this was the impetus for the emergence of man. But even now there are monkeys living in similar conditions. These are baboons. But for some reason they are not drawn to stand on their hind legs. To better survey the surroundings, while freeing the forelimbs. And somehow they don’t really pick up sticks. Although it’s possible they just can’t find it. And they don’t particularly hunt for antelopes. They're probably not catching up. And for some reason the fur doesn’t come off from them, so they run around covered in hair. Except for the bright red spots under the tails. Necessary, as I understand it, for orienting young animals in tall grass. And I don’t even mention speech development. Although, perhaps, after looking at us, they simply do not want to become human. But in any case, if there are no questions about the thesis of the cataclysm, then there are questions about the thesis that the forest was replaced by the savannah. 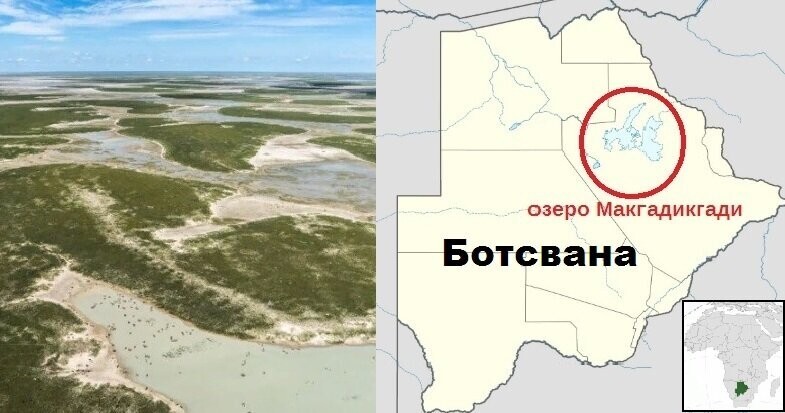
Landscape and location on the map of Lake Makgadikgadi.
Moreover, modern research shows that even before our species could evolve, our ancient ancestors faced almost complete extinction. A study published in the journal Science found genomic evidence of a stunning demographic collapse in the numbers of an unknown human predecessor that occurred 900,000 years ago. The results show that after some event, only 1,280 breeding individuals remained. Compared to a maximum of 100,000 individuals previously available. And that number won't rise for another 117,000 years. And here it is believed that in order for proto-humans to survive for so long, they probably 'occupied a very localized territory with good social cohesion'. “If this is true,” he continued, “then it would require a stable environment with sufficient resources and low system load.” If our ancestors had lived together in a small area, it could have wiped out up to two-thirds of genetic diversity, leading to the emergence of distinctive human features such as a large brain, the researchers say. Therefore, of course, it is interesting - what kind of catastrophe was it, after which 1280 survivors remained, gathered literally in one place and socially united?
And here the theory that man is the only crown of creation, even if he descended from monkeys, then through a purposeful chain of successive species, competing with others, is perhaps incorrect. There were many species at all stages of evolution, and they lived simultaneously for millions of years. The proximity of a Cro-Magnon man and a Neanderthal man is not a funny sensation, but a norm. Moreover, starting from 6 million years ago, all types of people had 46 chromosomes in their karyotypes and therefore could interbreed. Even our own species, Homo sapiens, could arise from such crossing. In any case, the age of his supposed ancestors, ‘Adam’ and ‘Eve’, calculated by geneticists, differs by tens, if not hundreds of thousands of years. And from the bone remains of proto-humans, it is clear that the torso and limbs became human millions of years before the head. Australopithecus had an even smaller brain than chimpanzees. However, if you don’t look at the head, they can easily be mistaken for clumsy people. And the face was the last to change, and even today people’s faces are not the same among different races. Comparison of the genomes of humans and monkeysconfirms this. The second human chromosome is the result of a merger of two apes, in which the work of the genes for the proportions of the torso and limbs has changed. Their structure has changed much more than the structure of the brain, and very quickly, literally in just a few generations. The human body ‘suddenly’ changed from adapting to life in the trees to adapting to something. The dogma about adaptation to the dry savannah is untenable. It is much more comfortable there not for two-legged, slow and thirsty people, but for fast and agile four-legged baboon monkeys. Which, unlike us, do not need at least two liters of water per day. And only because in us, a layer of subcutaneous fat, which is absent in monkeys, prevents the body from cooling down. And let me remind you that this is water, a particularly valuable resource, literally critical, for savannas. But easily accessible on the shore of a reservoir. 
In addition, two links are missing in the chain of human development. Precisely the transition from ape to ancient man. And from ancient man to modern man. It seems that they are simply looking in the wrong place. Although the localization of the place where the person appeared was determined quite accurately. This is the southern part of East Africa. And here the more preferable theory is that man emerged from ape on a vast and shallow coastline. That is, climate change occurred as a result of natural processes. As a result, a vast shallow-water region was formed in the habitat of human ancestors. Possibly with decent beaches and low vegetation on the shore, and a very large shallow water area. As a result, our ancestors were forced to live in conditions of transition, from land, having lost trees, to the shore. When land predators appear, hide in the water. And when aquatic predators appear, run ashore. At the same time, the nutritional structure has also changed. Without fruit from the trees, the monkey had to make do with new food. First with algae, and then with other gifts from the reservoir. Perhaps starting with shellfish. Mistaking them for nuts. This is what made the human ancestor an omnivore. In addition, only mammals living in water lose their fur. But man, unlike seals and cetaceans, did not become a completely aquatic animal. Content with gathering in a vast shallow area. In addition, in such conditions it might be necessary to stand in the water on the hind limbs for a long time. Waiting for the lion, or the same terrible enemy the baboon, the leopard, and for us psychologically, actually a cute pussy, to get tired of roasting in the sun. Which seems to have made man upright. Well, standing, safe, neck-deep in water, our ancestors could well have had fun while throwing all sorts of stones, branches and other things found at the bottom at the cats. They fought the crocodiles in exactly the opposite way, jumping onto land and throwing at them what had previously been thrown at the lion. Although it is worth recognizing that there is another species of primates, besides humans, that are not afraid of water. Hokkaido's harsh weather conditions drive local macaques into hot springs. Where they warm themselves between feeding and sleep. At the same time, having met a Japanese in “their” pond, these macaques drive people away. Throwing stones and branches at them.
At the same time, our species has many features that would not have given it advantages if our ancestors had lived in a dry savannah. But at the same time providing huge benefits for a semi-aquatic lifestyle. So our wide foot is not the best organ for running, especially with flat feet. But it is more convenient for standing and walking on two legs on a loose surface - in a swamp, silt or sand. Especially at the bottom, against the waves and current. A wide, short foot is beneficial for walking on loose sand, silt at the bottom when entering a body of water, through a swamp (or for standing steadily in a body of water, especially in the presence of waves), but not for running on a hard surface. Human feet are closer to a flipper than to the hooves of fast-running digitigrade land animals, and cases of flat feet may be atavisms of aquatic life. At the same time, the elongated legs, compared to the limbs of monkeys, are more convenient for swimming. Everyone who has artificially lengthened them with flippers knows this. At the same time, the shape of our hand, with the rudiments of swimming membranes, which monkeys do not have, is similar to an oar. Wide human palms, in contrast to the long and narrow palms of monkeys, allow excellent swimming, scooping water with their hands. Of the primates, only humans have rudiments of swimming membranes between their toes. This rudiment is especially noticeable between the thumb and index fingers. And the characteristic wrinkling that appears on the fingertips after a long stay in water can be explained by the fact that it is easier to grasp food, such as shellfish. Besides humans, among primates, only the Japanese macaque has such an adaptation, which obtains and washes food in water. 
And in general, the list of characteristics of aquatic animals in humans is very long. So, long hair is only on the head, it does not submerge in water, and it is more convenient for swimming children to hold on to something. Staying on the surface. A thick layer of subcutaneous fat and the absence of wool are characteristic only of aquatic mammals now, or in the past, such as pigs, mammals, since wool in water cannot be a heat insulator due to the loss of air layers. And subcutaneous fat, in this sense, replaces it. We have 10 times more fat cells than other primates, and only our children are born with a layer of fat. Moreover, it appears only immediately before birth. Rapidly thickening in the first months of life. This fat is useful not only for thermal insulation, it also helps to float on the water, like dolphins, seals and hippos. Let me remind you that a person, due to his constant thermal insulation by subcutaneous fat, needs to consume at least two liters of liquid per day. Since he has many active sweat glands, which save him from inevitable overheating on land. At the same time, monkeys do not drink, content with liquid obtained from fruits and leaves. And they do not have a high need, like humans, for iodine and sodium chloride. There are a lot of these substances in sea water, and therefore they are quickly eliminated from the body only by marine animals, and monkeys use them more sparingly. The skin of monkeys is dry, since lubrication with abundant secretions of the sebaceous glands, which protect it from water and facilitate swimming, is not needed. A large amount of adipose tissue on the mammary glands is characteristic only of humans. This can be explained by the fact that the milk had to remain warm in cold water. Female monkeys have small mammary glands without fatty tissue. Long, strong hair on women’s heads that does not fall out with age allows children to hold onto it firmly in the water, especially during breastfeeding, when the mother’s hands are busy swimming. Of all primates, humans have the longest penis and the deepest vagina. When copulating in water, this ensures fertilization without exposure to water. Moreover, only in humans, unlike all primates, there is no priapic bone in the penis, which makes it retractable and therefore does not lose heat in water. Sex in a face-to-face position is typical only for cetaceans other than humans, since otherwise the lower partner could not surface to breathe.
In addition, bipedalism, a method of moving on a hard surface with the help of two paired limbs, in our case legs, with undeveloped curves of the spine and back/leg muscles, is not beneficial in the savannah. As the example of baboons proves. But the water pushes the body, making it easier to stand on two legs. The vertical position of the body allows you to go further into the water and travel in it on foot along the shore. At the same time, without swimming, but keeping your head above the surface. But man did not become a completely aquatic animal, did not lose contact with land, because he lived on the coasts of drying up reservoirs and therefore had to change them often. And when land animals catch prey in the water, they always stand on their hind legs. Examples are bears, for example, in Kamchatka, raccoons, Japanese macaques. Now give me at least one example of a land mammal running well on its hind legs. Not jumping, and even with the help of a tail, but running like a human being. This is the weakest point of criticism of the water theory of the origin of man. All birds are bipedal, but only waterfowl have legs located not closer to the center of the body, but at its rear end. And of these, only penguins can not only swim well, but also walk, precisely due to the vertical position of the body. The formation of the human musculoskeletal system took millions of years, and before that, in the conditions of the savannas, they faced a quick death, but they had to live here and now! The water pushed and supported the body in an upright position, giving evolution time to gradually improve the new ability. And when people then broke away from the saving reservoirs, they became better prepared for this. Subsequently, after the transition to the savannah, upright walking in humans was preserved, since the body had already adapted to it by that time.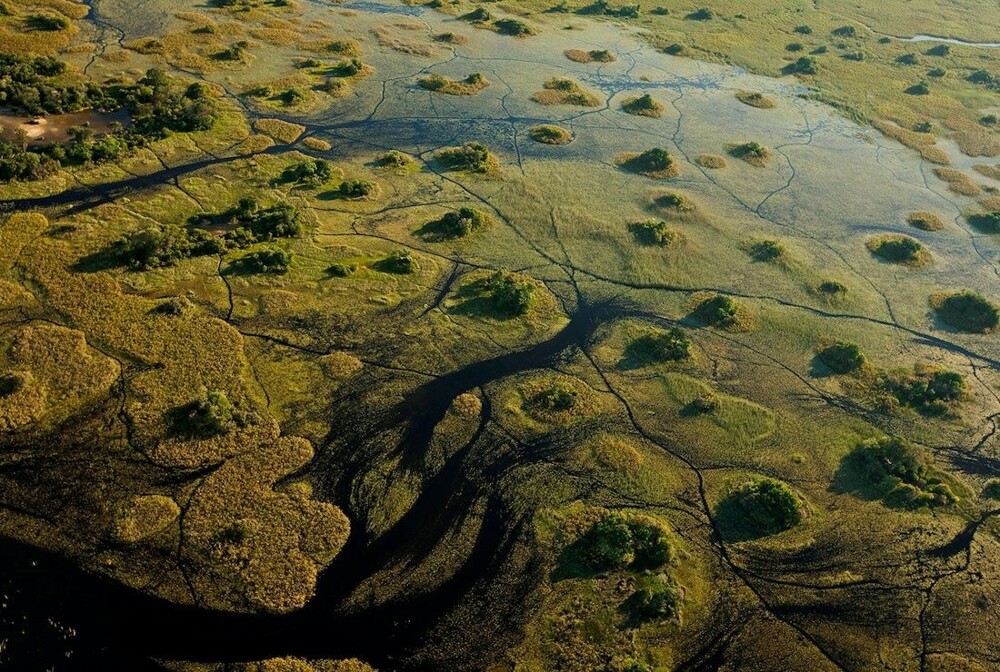 
Humans have nostrils that open downward, preventing water from entering the nose, while monkeys have nostrils that point forward and upward, losing air when immersed in water. That's why they drown where we can swim and dive. Humans have a rather weaker sense of hearing and smell than other primates; this is typical for aquatic animals, but is deadly when living on the savannah. And the greater refraction of light by the eyes, which allows us to see better under water, like all aquatic animals, often leads to myopia in the air. And so that you don’t have problems with myopia, in the savannah, you should have aplection and character of a hippopotamus or rhinoceros. Monkeys do not have myopia; it was fixed by selection only in humans, since its carriers were better at collecting food at the bottom. We have a low larynx, and this allows us to hold our breath. And only in humans, of all primates, does breathing automatically become blocked when the face is lowered into the water. In general, people can voluntarily control their breathing processes, like marine mammals and birds. The human windpipe is not distant from the esophagus; it is the so-called 'low larynx'. A similar design is found only in aquatic mammals, such as seals. It allows you to control your breathing, hold it and dive. And the development of the ability to make articulate sounds is associated precisely with the ability to retain air in the lungs. A person can do this because it was required for diving, but other primates are not capable of this and therefore cannot develop speech.
In addition, all the smartest mammals either live in water (dolphins), or their ancestors lived there (elephants), since life in such an environment hostile to land animals requires very complex behavior. If only because life on the border of two environments required an increase in signals that have different meanings. It was not enough to simply sound the alarm. There was a need to clarify exactly what danger was threatening. And not just from which side. After all, a tiger is one thing, but a snake or a pack of wolves is another. The crocodile, at the same time, is something completely opposite in terms of the reaction to its appearance. Which was supposed to promote the development of muscles and bones responsible for speech. And, in the end, it led to its appearance. And the need to open a shell, pull a crab out of a crevice, or finish off a fish caught on the sand required picking up a stone or a stick. And at the same time it could turn out that it is easier to open shells with a stone of a special shape. And no crevice could save the crab from a stick with a hook. Which is possible and ultimately stimulated the creation of tools. In the form of specially chopped stones and branches, the shape of which was adjusted to the desired one. Fortunately, the upper limbs were really freed. And such a semi-aquatic life made a person more graceful and elegant. Firstly, due to the lower gravity in water. Secondly, for the sake of the opportunity to go deeper into the water while remaining on your feet. Which contributed to the increase in growth. Fortunately, the diet became more protein-rich, which, in turn, served as a material basis for brain development. Brain development is impossible on a vegetarian diet. And only later, when this habitat changed as a result of another cataclysm, did people move to the steppe. But it didn't appear there. 
Studies have shown that the greatest fear among people (even among hereditary residents of the Far North) is caused by images of crocodiles, or predatory dinosaurs, sharks and snakes. But the reaction to images of lions, leopards, bears, and in general any modern land predators, is rather neutral. The instinct of fear was shaped by the environment. By the way, our children can swim right from the moment they are born, sit up only after three to four months, and begin to walk even later, while baby chimpanzees do the opposite. Finally, let us remember that small children, when they see a puddle, will always try to climb into it. Baby monkeys, well, except for Japanese macaques, will never go into the water of their own free will. People prefer to live or relax on the banks of water bodies. If a person is offered to build a house or spend a vacation in the savannah, jungle, deep forest or on the shore of the sea, river or lake, the vast majority will choose the shore of a reservoir. And gorillas, for example, avoid stepping into even small puddles. Although they live in the jungle, on the southern coast of the Congo. We are still drawn to water. The ideal of our vacation is by the sea, and not in the steppe, forest or desert... And the ancient adaptations to the amphibian lifestyle remain. We can only add that the fingertips of our hands are an order of magnitude more sensitive than those of chimpanzees. Deaf-blind people can even read with their help! Such sensitivity appeared precisely in order not to remain hungry when searching for food in the bottom silt. And the use of fire also determined our aquatic formation of humanity. All land animals are mortally afraid of him, but aquatic animals never are.
Moreover, if we understand by the word ‘man’ only our species, Homo sapiens - Homo sapiens, then he, both according to bone remains and according to the calculations of geneticists, is no more than 200 thousand years old. If we take this concept as the entire genus Homo, as a group of related species, then it is approximately 2 million years old. If you start counting with the most ancient species, for example Homo habilis. If we take the entire evolutionary line that separated from monkeys and led to us, the genera Ardipithecus-Australopithecus-Humans, then it is from 6 to 7 million years old. Species don't live that long, unless they're 'living fossils' like lathiMeria and Gutteria! So the statement that man has always been one species is completely false. It is enough to recall the Neanderthal, who was close to us and lived tens of thousands of years in parallel, but belonged to a different species. Which also arose from those proto-people who lived near reservoirs. But who simply left Africa a little earlier than our ancestors. 
Parallel existence of human ancestral species.
Brief chronology of human evolution:
55 million years ago - the first primates arose and developed.
15 million years ago - hominids - apes - arose
7 million years ago - gorillas appeared. A little later, the genus Chimpanzee arose and it was then that the evolutionary branches of the ancestors of primates and the ancestors of humans diverged. Moreover, the closest relatives of people living below are the bonobo species, a species of the chimpanzee genus. But not the great chimpanzees themselves.
5.5 million years ago - Ardipithecus arose - an early “proto-man”, similar in skeletal structure to both gorillas and chimpanzees.
4 million years ago - Australopithecus arose, the first creatures more similar to humans than monkeys. Their brains were larger than those of chimpanzees.
3.9-2.9 million years ago - Australopithecus afarensis arose, confidently walking on two legs.
2.7 million years ago - Paranthropus arose - “fat” australopithecus, living in forests and eating mainly plant foods.
2.6 million years ago - Australopithecines began making stone axes.
2.3 million years ago - Homo Habilis arose, making various stone tools.
1.85 million years ago - Homo Habilis "acquired" a hand similar to the hands of modern people.
1.8 million years ago - Working Man arose. 1.5 million years ago - Homo erectus (Pithecanthropus, Sinanthropus) arose.
800 thousand years ago - early people learned to make fire and make hearths. Their brain size has increased greatly. And this is the end of the 100 thousand-year era of the “bottleneck” defined by a sharp decline in population.
400 thousand years ago - Neanderthals arose and began to quickly spread throughout Europe and Asia.
300-200 thousand years ago - Homo Sapiens - Homo Sapiens - modern people arose. Estimated lifespan of 'Eve' - the single foremother of humanity.
50-40 thousand years ago - Homo sapiens began to conquer Europe and displace the Neanderthals. Estimated lifespan of 'Adam' - the only forefather of humanity.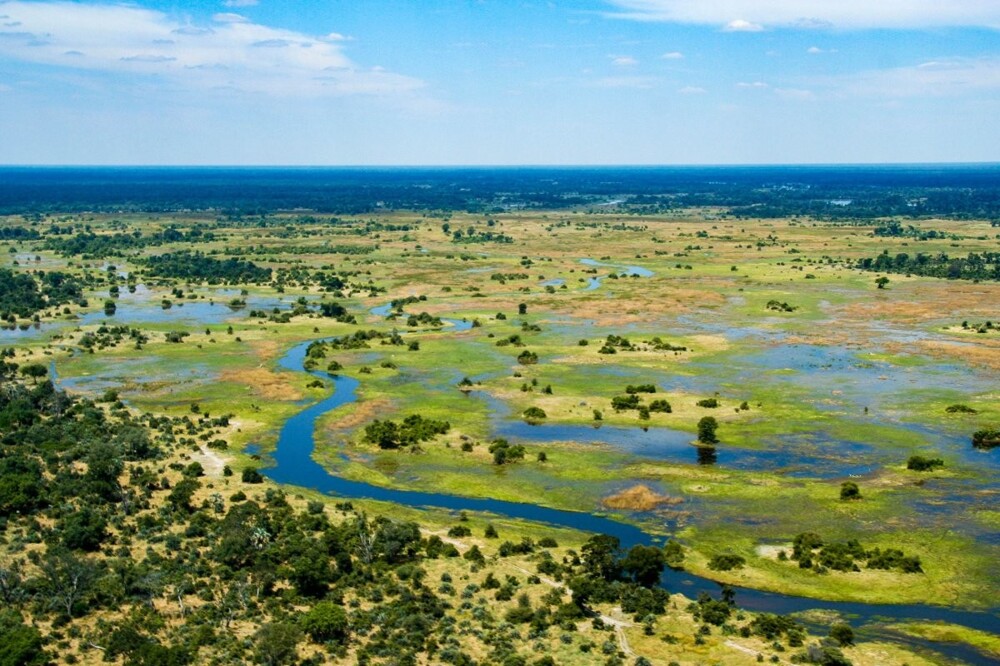 
The birthplace of humanity.
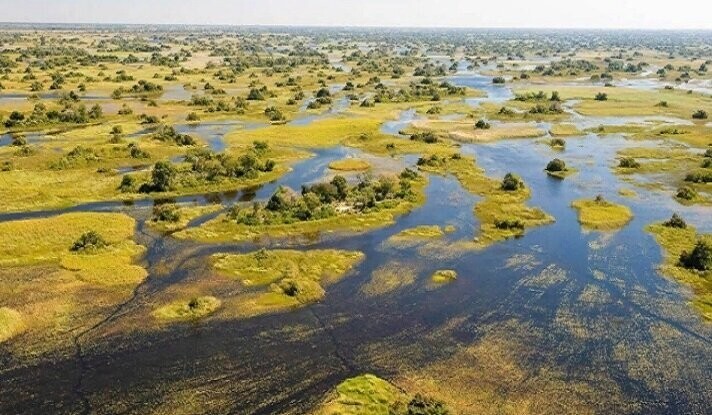
And let me remind you that exactly 900 thousand years ago, humanity consisted of only 1280 reproducing individuals. And this figure will remain at this level for another 117 thousand years. Moreover, these people lived along the banks of a cluster of small, shallow and sometimes drying up, but at the same time very numerous reservoirs of the savannah. And such a place existed in Africa. Northeast of Africa's Kalahari Desert and southeast of the Okavango Delta lies a concentration of literally the largest salt flats in the world. Moreover, they are located precisely in one of the two places where the most bone remains of australopithecines and ancient people are found. This is where the closest relatives of bonobos settled in waves - Australopithecus, people (Homo), including Neanderthals, and us (Homo sapiens). Once upon a time, this place was home to one of the largest lakes on Earth. And now it is a system of drying lakes and swamps of the Makgadikgadi of the world's largest inland delta of the Okavango River. Located in Botswana. And which the DNA genealogy of humanity independently points to.
Scientists, having studied the DNA of more than a thousand Africans, from the most ancient people, discovered that they all came from one particular swampy area of Botswana (South Africa). This place is located next to the Zambezi River and is called Makgadikgadi-Okavango in the local language. In past millennia, there was a large lake here, on the shores of which Homo sapiens apparently arose about 200 thousand years ago. It was from here that modern people began and spread throughout Africa, and then moved to Europe and displaced the Neanderthals from there. Those who were unlucky enough to leave the warm shores of the lake a little earlier. But in that era it was very warm here, it was almost subtropical. And here the plants bloomed luxuriantly, fruits grew, and there were a lot of fish in the waters of the lake. There was a real Garden of Eden here. According to scientists, perhaps it was these conditions that created Homo Sapiens, since here he developed in several directions at once, caught fish (and possibly knew how to swim), hunted animals, ate fruits. All this involves different principles of thinking and different motor skills of the limbs. Everything changed about 130 thousand years ago, when the climate became aridyom and people went to other places, looking for more suitable places to live. The direct descendants of this group still live in the Kalahari Desert. These are the people who did not go far with a large group to the north and did not reach Europe, they also did not go further to the south, but decided to settle in these places.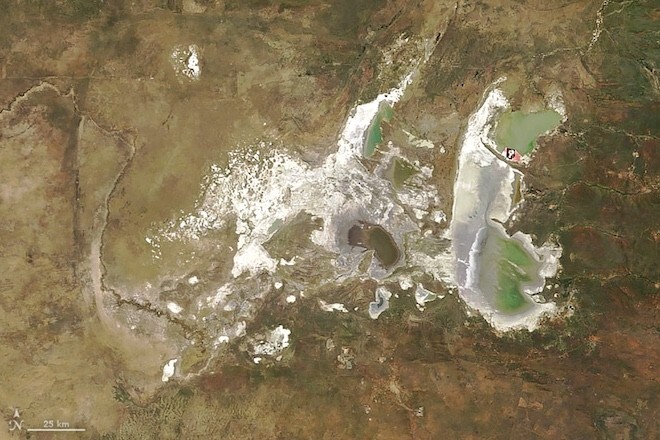 
Makgadikgadi salt lakes in Africa, satellite photo. The Makgadikgadi Salt Flats in Botswana mark today's remains of the lake.
The salt marshes are the salty remains of the ancient Lake Makgadikgadi. Scientists estimate that it once stretched over an area of 80,000 to 275,000 square kilometers and was up to 30 m deep. The Okavango, Zambezi and Kwando rivers probably flowed into this lake until tectonic shifts changed the terrain , and climate change has not led to the drying up of the lake. Its remains can be seen in the Makgadikgadi salt reservoirs, one of the largest salt reservoirs in the world. And about 2 million years ago, a fault blocked the drainage route to Limpopo. The blocked flow allowed the formation of Lake Makgadikgadi. After many millennia, the lake was filled with water to capacity. But, due to climatic conditions, it began to overflow only about 20,000 years ago, choosing the lowest point of the watershed in the northeast as its new outlet. This led to the formation of Victoria Falls. Now that water has been able to flow out of the basin, Lake Makgadikgadi has partially drained and its average level has dropped. A drier climate period followed, which increased evaporation and reduced the flow of rivers that fed the lake. Thus, the water of the Okavango River spread over a much larger land area than it had previously, forming the fan-shaped inner Okavango delta characteristic of this time, which further reduced the amount of water flowing into Lake Makgadikgadi and accelerated its drying out. About 10,000 years ago Lake Makgadikgadi reached its present stage. And sediments and wind-blown sand gradually filled the space previously occupied by the lake. Forming a desert.
But research shows that it is the Makgadikgadi Lake region that is the homeland of Homo sapiens. That this is where humans first evolved as a distinct species around 200,000 years ago, before spreading to other parts of Africa around 70,000 years later. So that in another 80,000 years we could enter Europe and Asia. 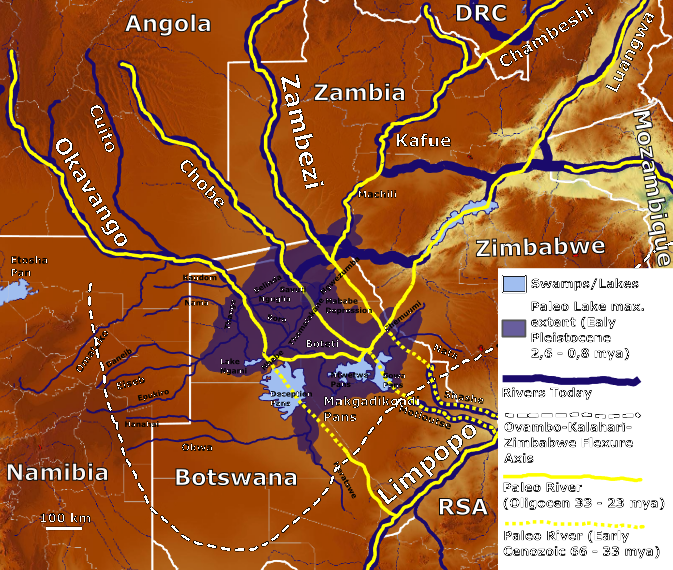
The extent of the former Lake Makgadikgadi that existed in what is now the Kalahari Desert in Botswana. Between 2,000,000 BC and 10,000 AD.
At the same time, people recently became mobile predators at the top of the food pyramid. Before that, they were shallow-water shellfish gatherers and scavengers. Because the oldest stone tools are no more than about 2 million years old, and they were still imperfect for a long time. People began to use fire about 1-1.5 million years ago. But on their own, without weapons and fire, they were still small and weak. Even modern man is weaker than any animal of the same weight, all hunters know this. And a person always loses in hand-to-hand combat with any large ape, which all trainers and zookeepers know and take into account. And the man was also stupid. Even the first australopithecines had no larger brains than chimpanzees. And only the fact that, as a result of the cataclysm that led to the appearance of Lake Makgadikgadi, a small group of proto-humans found themselves isolated in a small space for survival, led to the emergence of our species. A smart and skilled predator. At the top of our planet's food chain.
Of course, this, like any theory, does not claim to be completely correct. And it requires a thoughtful approach. But, at least, it is able to explain a number of points that are not explained by other theories of the emergence of man.