Mars as art images obtained by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft (8 photos)
Scientific experiment HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science) Experiment) helped photograph hundreds of target surface areas Mars in unprecedented detail.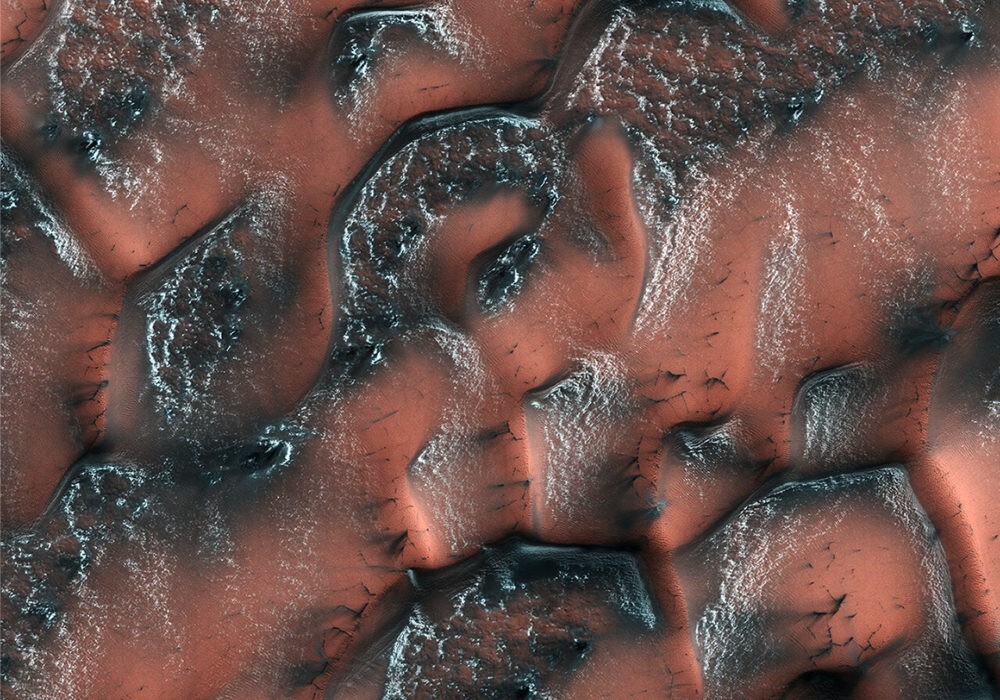 
Unlike Earth, this snow and ice are made of carbon dioxide. gas, better known to us as dry ice. When in the spring it begins to the sun is shining, the ice on the smooth surface of the dune is cracking, and the gas carries away the dark sand from the dune below, often creating beautiful patterns.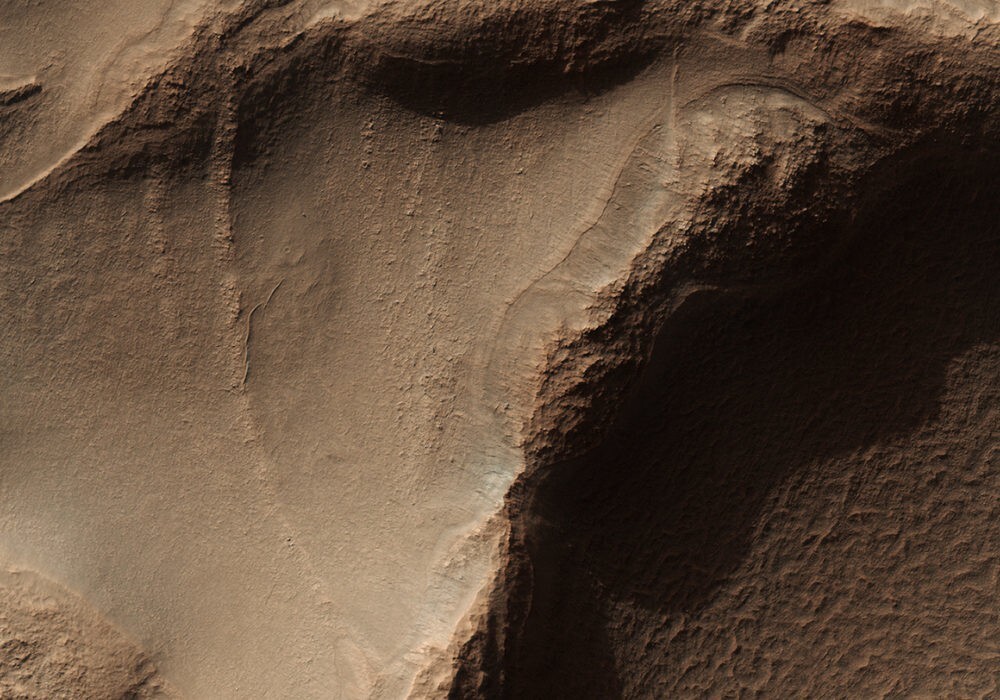 
This photograph shows part of a group of relief forms with cellular structure in the northwestern part of Hellas-Planitia, which is part of one of the largest and oldest impact basins on Mars. 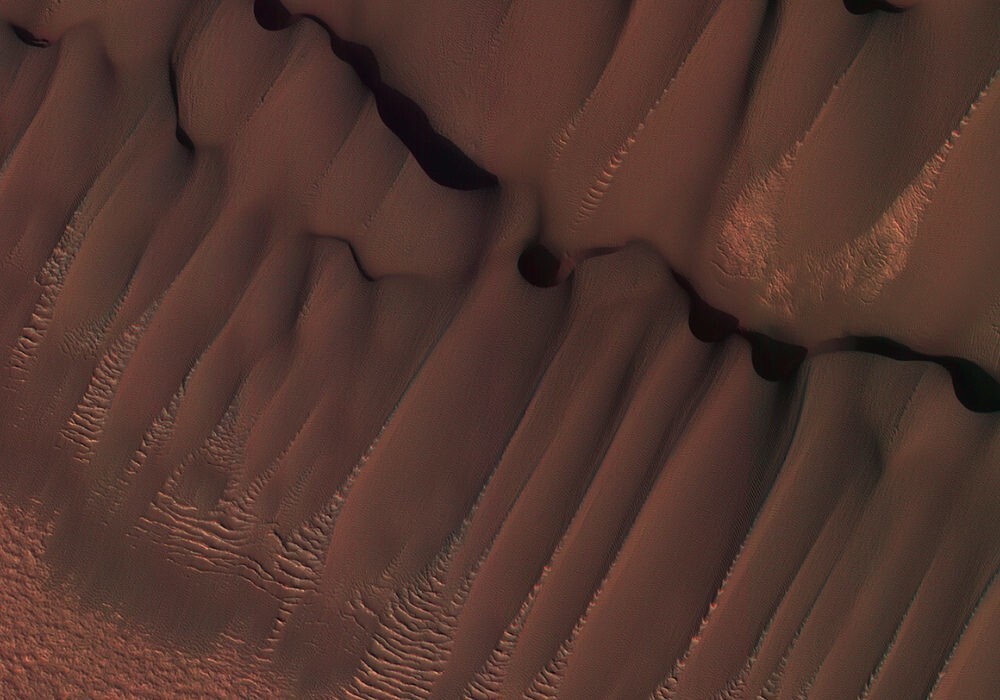
This image was taken during the Martian northeast summer, so there is no frost on the dunes. Dunes closest to the base of the polar caps, long and parallel, indicating strong winds from the direction hats. As they move away from the polar cap, they begin to form all more crescent-shaped dunes called barchan dunes.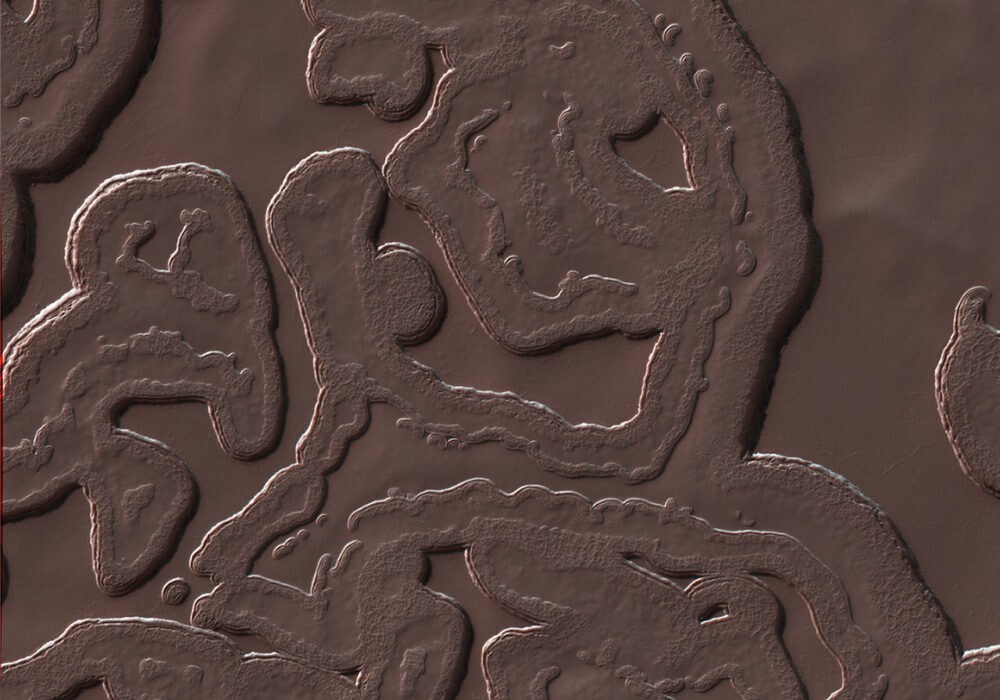 
Many Martian landscapes contain features familiar to those that we find on Earth, such as river valleys, rocks, glaciers and volcanoes. However, Mars also has an exotic side, with landscapes that alien to earthlings. This photo shows one of these exotic places at the South Pole. The polar cap is made of carbon dioxide (dry ice), which does not occur naturally on Earth. Round pits are holes in this layer of dry ice that expand several meters every Martian year. 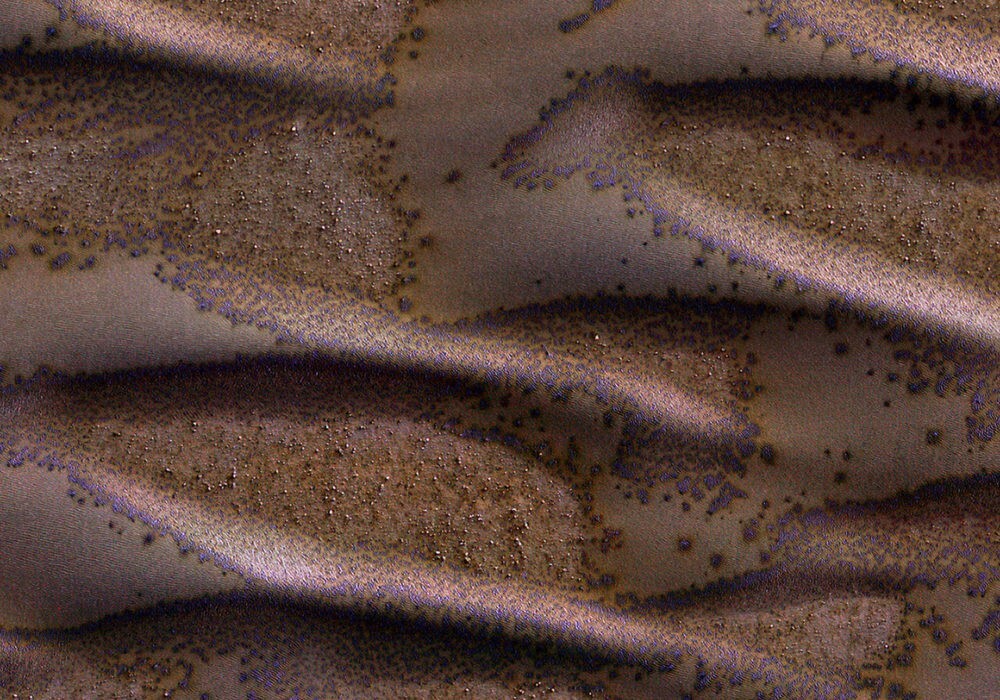
Sand dunes cover much of this area, with large boulders lying in the flat areas between the dunes.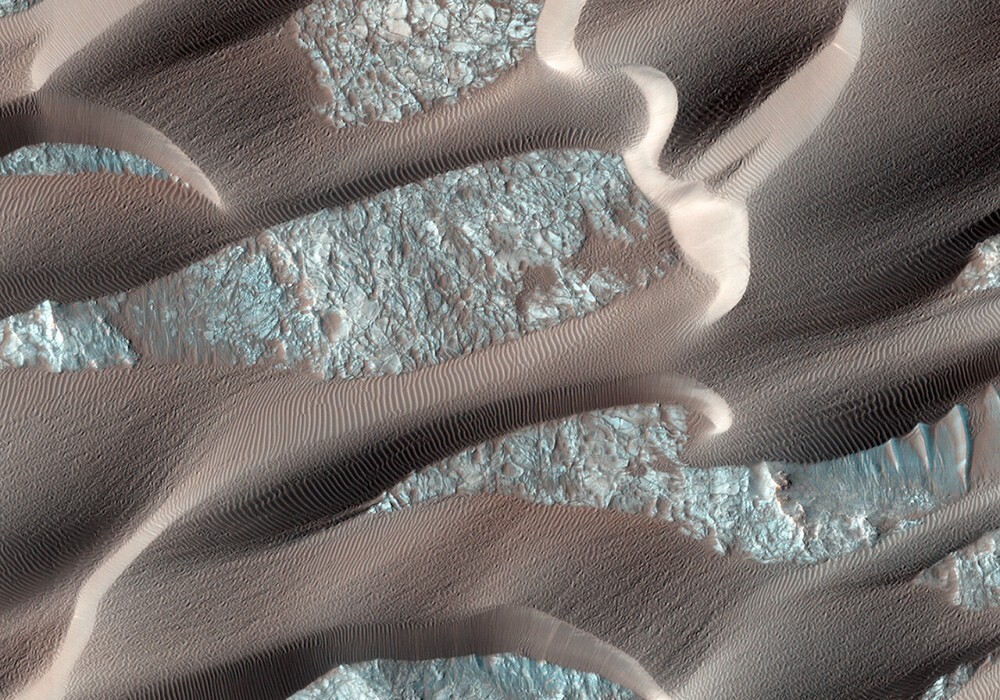 
Nili Patera is an area on Mars where dunes and ripples. HiRISE continues to monitor this area every couple months to see changes in seasonal and yearly times scale. 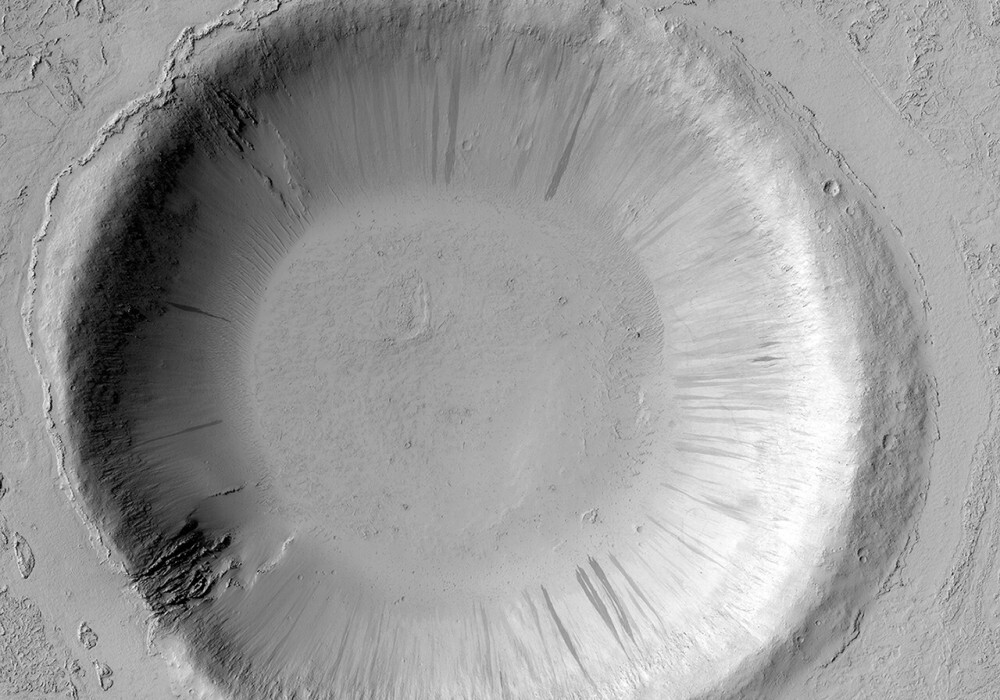
This image shows an impact crater about 3 kilometers (1.8 miles) in a region that was flooded by lava.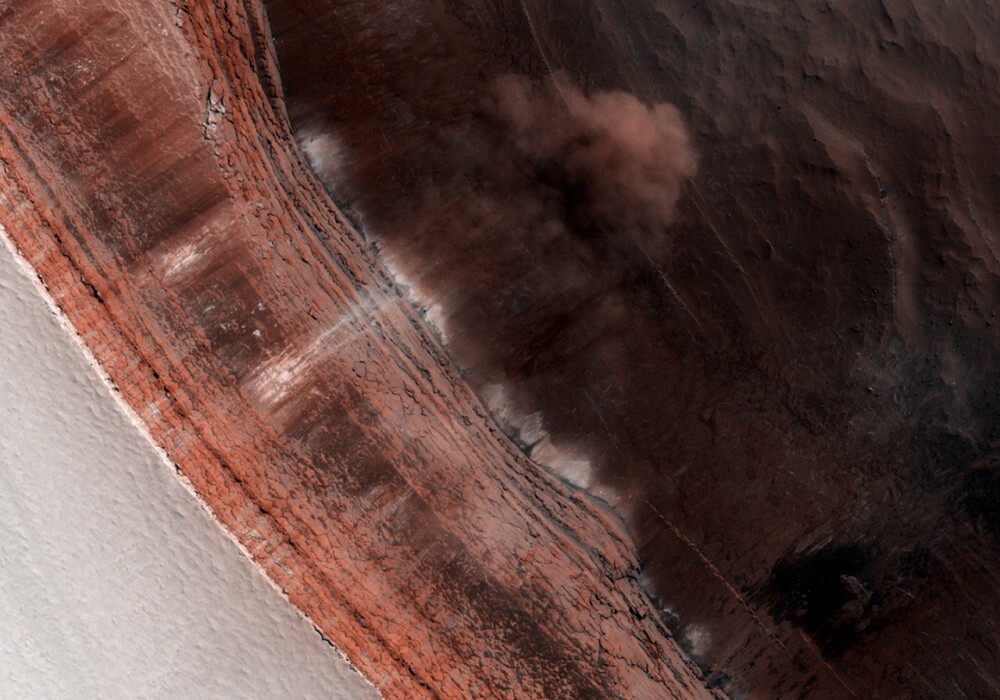 
Ice avalanches on steep ledges