12 photos of incredible things, creatures and phenomena (13 photos)
Our world is full of amazing things and phenomena. 
If you look closely at the most ordinary objects, you will notice how incredible they are. Here are 12 photographs of rare phenomena, from strange creatures and objects to bizarre natural wonders, that will make you reconsider your established views of the world.
1. Salpa - "glass fish"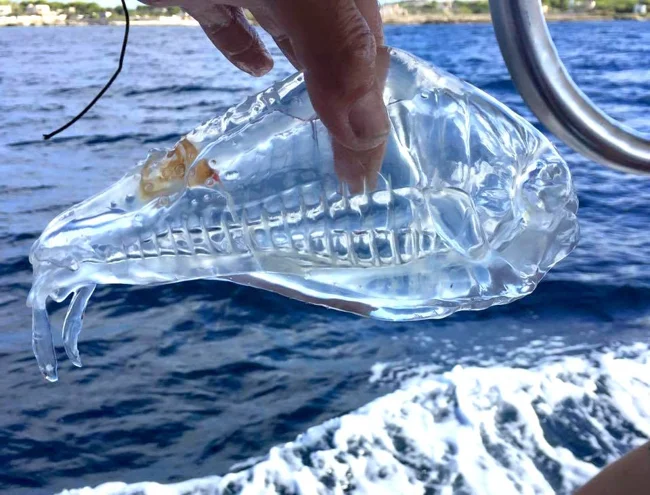 
These marine invertebrates are some of the most unusual creatures on Earth. Glass-transparent, barrel-shaped organisms look more like fantasy creatures than real ocean dwellers.
2. Frozen Lake Michigan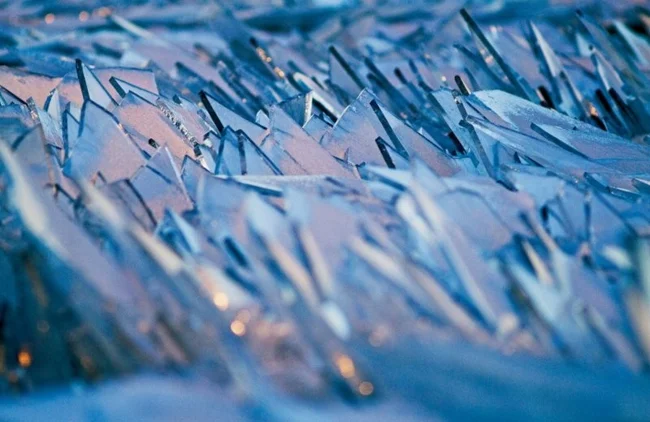 
This isn't broken glass, a crystal castle, or shards of ice. This is what the surface of the largest freshwater lake in the United States looks like in the dead of winter, when temperatures drop to -30°C.
3. Baikal Zen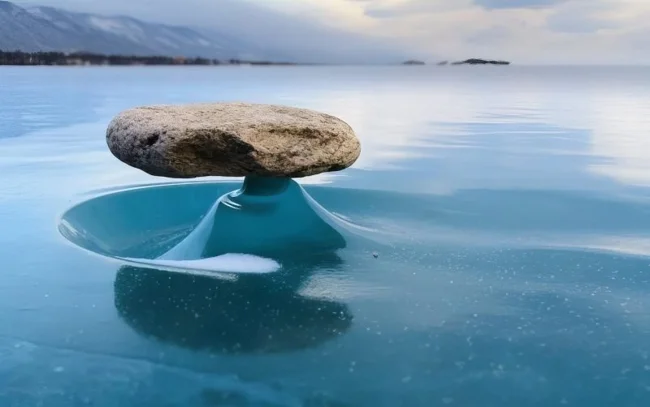 
Stones floating on ice legs are a unique phenomenon on the deepest lake on the planet. It is found only on Baikal, where winter temperatures reach -40°C, and the ice becomes transparent as glass.
4. American Bashkir Curly Horse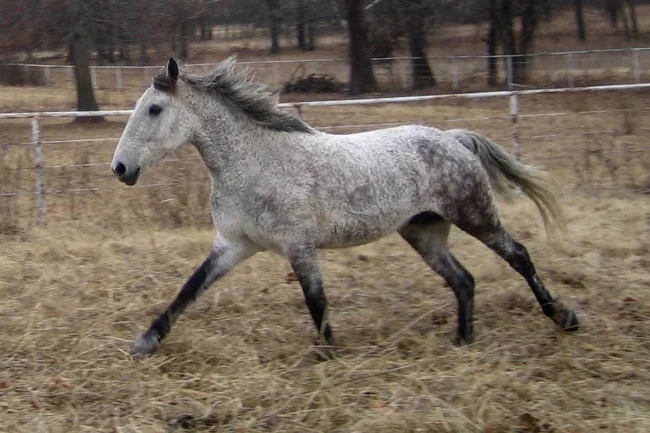 
These unusual horses wear astrakhan fur coats in winter and curls like a lamb in summer. Their origins remain a mystery. Presumably, the breed originated from American horses of Iberian origin, among which there are sometimes individuals with curly hair.
5. Giant dinosaur footprints in France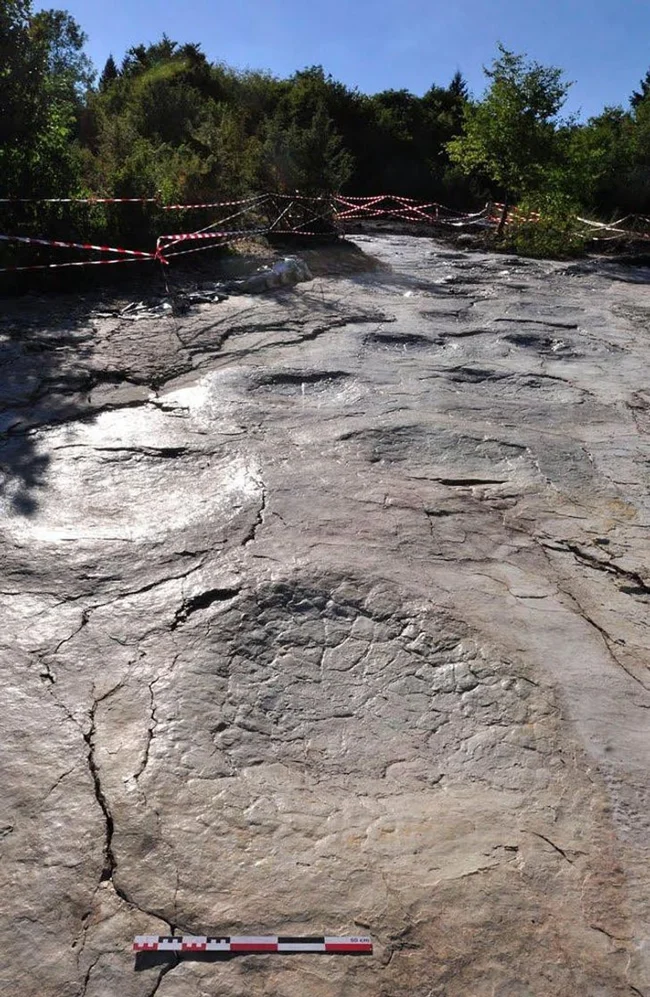 
These are not craters, but sauropod footprints that are 145 million years old. They were accidentally discovered by two amateur paleontologists who noticed ripples in the limestone. Excavations showed that this was not erosion, but 110 footprints stretching the length of a football field. They are located in the commune of Plagne (eastern France). This is the longest chain of dinosaur footprints in the world.
6. Music Typewriter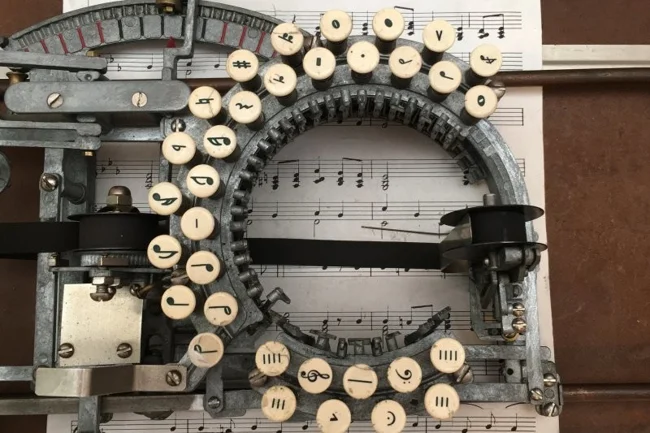 
The Keaton Music Typewriter is the only machine in the world designed exclusively for printing music sheets. It was invented in 1936 by Robert Keaton from San Francisco, tired of copying scores by hand.
7. A Gigantic Find 
A dinosaur femur weighing half a ton was unearthed in France. These are the remains of a sauropod that roamed the Earth 150 million years ago. The fragment was discovered in 2019 at the Angeac-Charente paleontological site in southwestern France. The region is known as the "dinosaur El Dorado."
8. A giant living ball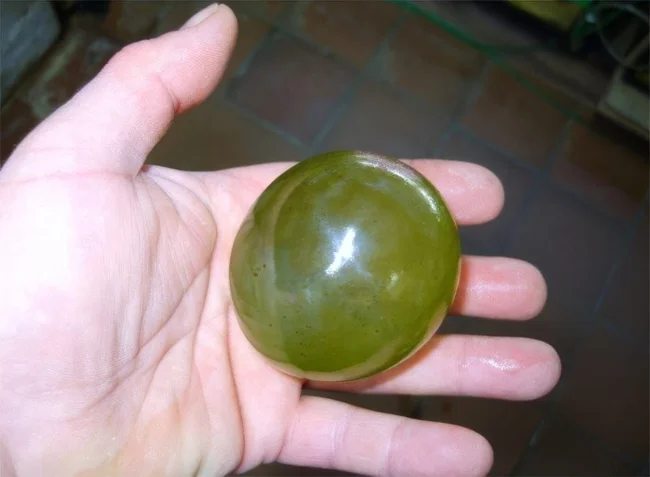 
Valonia ventricosa is a grape-sized alga that is a single cell. It is also called "bubble algae", "cursed grape" and "sailor's eyeball". Valonia ventricosa is an organism that forces us to reconsider the idea of the microscopic nature of single-celled organisms. It is one of the largest single-celled organisms.
9. The "Face" of an Ant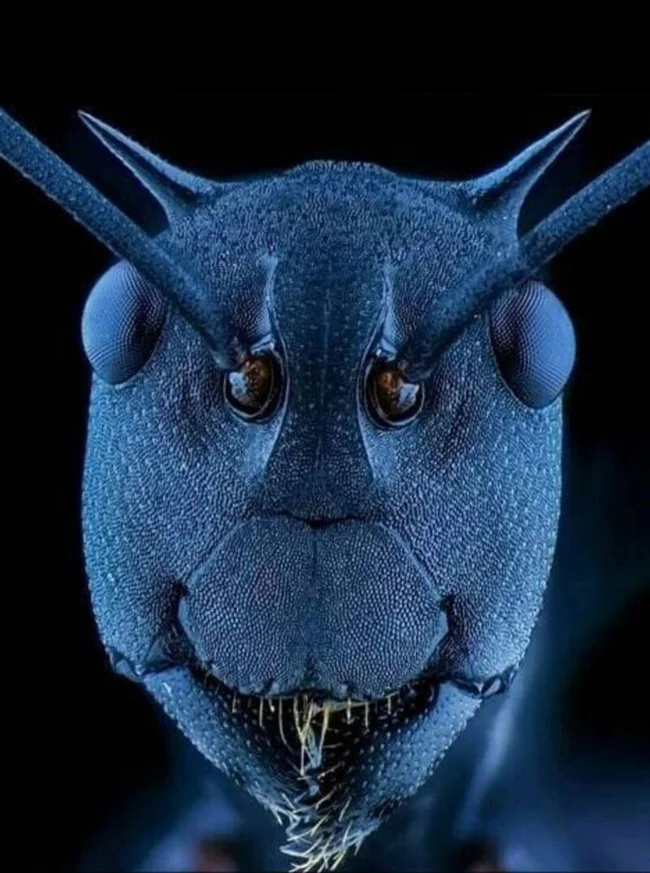 
At first glance, this image appears to be quite creepy, as the holes for the ant's antennae look more like eyes. The image was taken using electron microscopy, which is a method of producing high-resolution images with much greater magnification than a conventional light microscope. It is used in biomedical research to study the structure of biological materials in depth, along with various other objects.
10. A sea slug that became a "plant"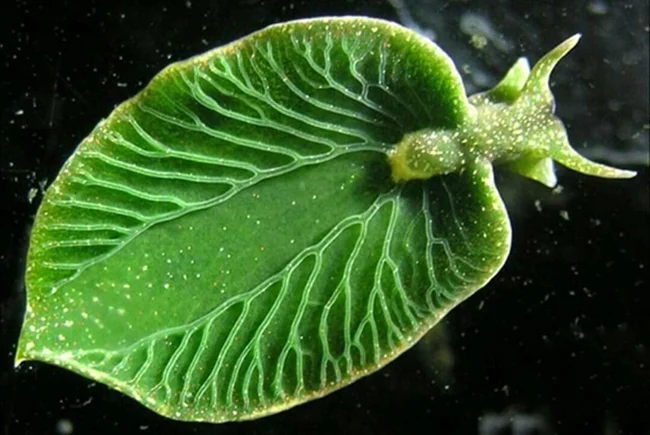 
Elysia chlorotica is a marine mollusk, a species of small marine gastropods from the Plakobranchidae family of the Heterobranchia subclass. This is the first animal known to scientists that is capable of independently, like plants, carrying out the process of photosynthesis without the use of symbiotic algae. The slug integrates algae plastids into its cells, lives for 6-8 months at the expense of sunlight and uses algae genes to maintain the "stolen" chloroplasts.
11. Bisexual lobster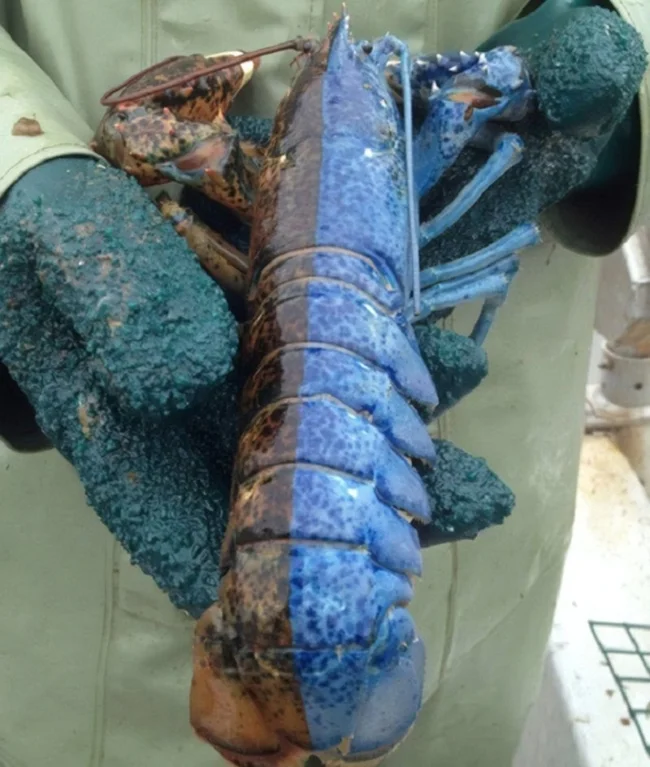 
The gynanthromorphic lobster is a rare genetic phenomenon in the crustacean world. The left side is female (blue), the right is male (brown). The internal organs are gender-specific. Occurs in 1 in 50 million individuals.
12. Symphony of Fire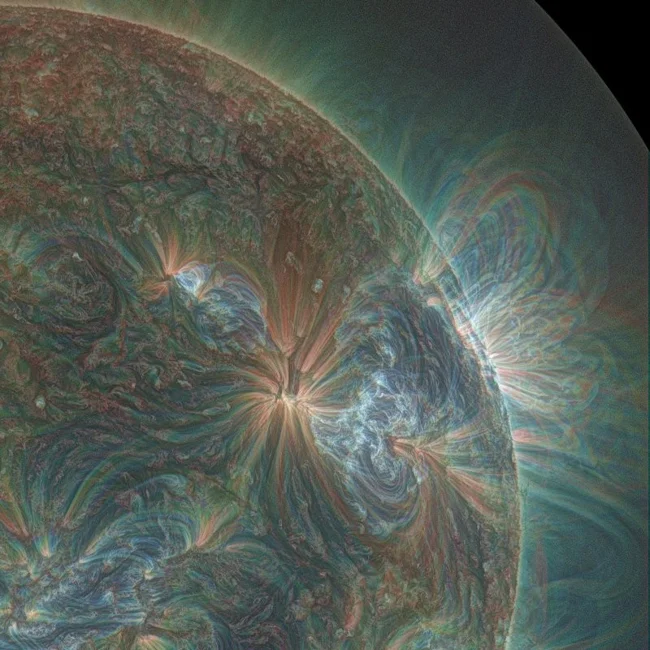 
A view of the sun through a NASA ultraviolet lens. The image looks like a painting. However, it is actually a series of unusual eruptions in the outermost layers of the sun's atmosphere, which were recorded by a team of astronomers using three NASA solar observation spacecraft in 2013. A series of rapid explosions that occurred over three days caused a slow release of huge amounts of plasma from the Sun's atmosphere, the team said.