American Aral (9 photos)
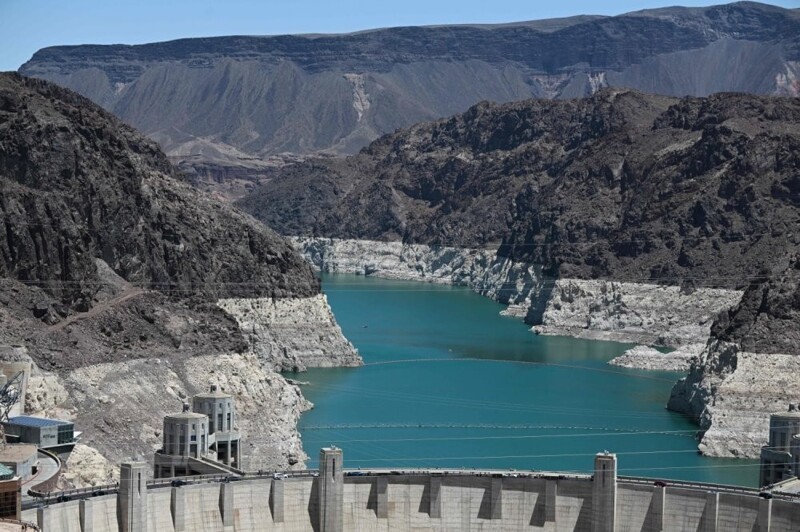
Man-made Lake Mead is formed by the Hoover Dam. Built in the 1930s, it was instrumental in defeating the Great Depression and the rise of cities like Los Angeles, and remains a symbol of American glory today. Now the lake has become catastrophically shallow.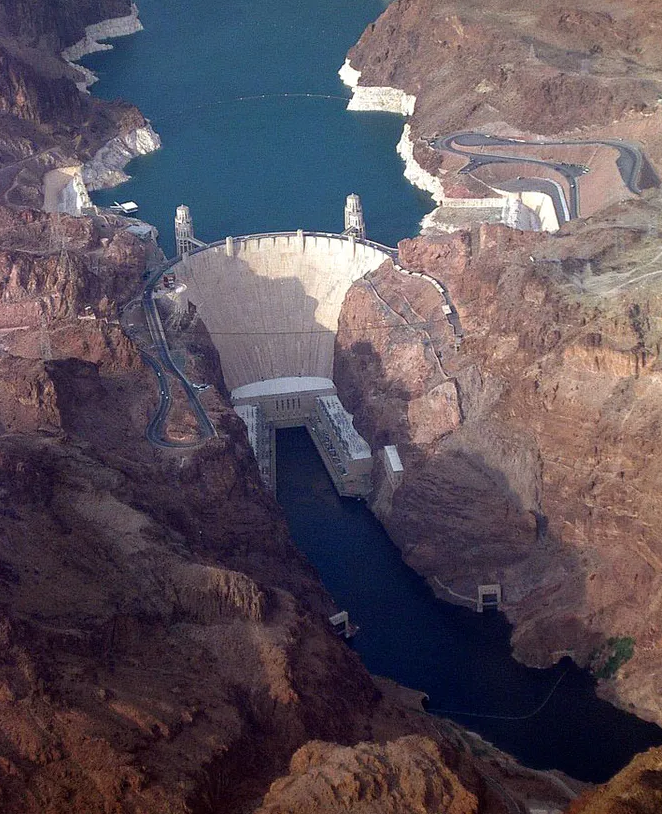 
The dam project is considered one of the greatest construction projects of that decade. He played an important role in defeating the Great Depression and settling the southwestern United States. The Hoover Dam also turned Las Vegas into the center of America's gambling business - the federal authorities gave the state of Nevada permission to open casinos in order to use the taxes collected from them to pay salaries to the workers who worked on the construction of the dam. It was named after then-President Herbert Hoover, who authored the so-called “Hoover Compromise” - an agreement between several states on who and how much water could take from the Colorado River.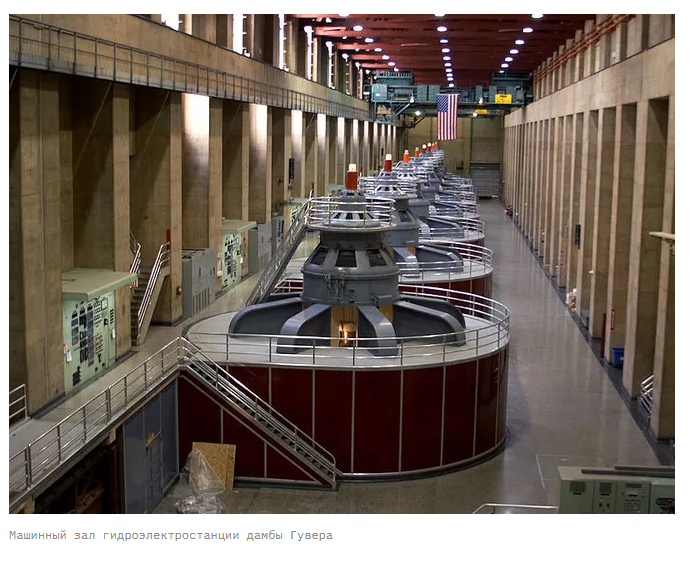 
Lake Mead, which generates just under 40 percent of Las Vegas's power through the Hoover Dam, is currently at just under 318 meters. It is less than 150 feet away from becoming a "dead pool," meaning there is no more water flowing through the Hoover Dam and no more electricity or water for every southwestern city that relies on this resource to live. . If Lake Mead levels continue to fall, it could be a couple of years until the danger zone is reached at 272 meters, which is the point where water will no longer flow through Hoover Dam to supply California, Arizona and Mexico.
Below 270 meters the lake will be considered a “dead pool”. At full capacity, Hoover Dam's 17 turbines can produce 2,074 megawatts of energy. As water levels have dropped over the years, this capacity has been declining and is currently down by about 33 percent.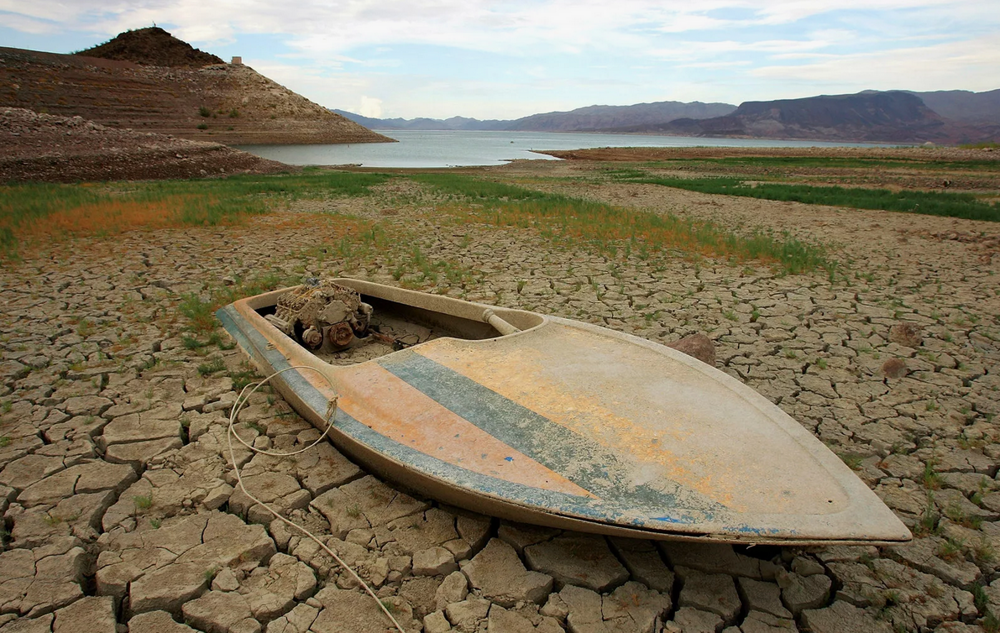 
Population growth in cities around Lake Mead has led to massive depletion of its waters since 1999. The depletion, along with other contributing factors, has caused the lake's water level to decline. In 2020, reservoir managers were forced to build and operate low-level pumps that pump out water during severe drought conditions.
According to July 2022 reports, Lake Mead retains just over one-fourth of the water it was originally filled with. Lake Mead and surrounding areas have been plagued by drought for the past several years. For example, 83% of Colorado is currently experiencing drought. 
Scientists estimate that 42% of droughts near Lake Mead are the result of climate change.
When temperatures rise in dry regions such as the Southwestern United States, water evaporates quickly. The lack of a wet warm arm in the southwest means the area is less likely to receive precipitation, leading to drought. Thus, as moisture evaporates faster and faster before reaching Lake Mead, the lake never replenishes. On top of this, the lake's water continues to evaporate and drought conditions are worsening.
The water level in Lake Mead has dropped so low that a white ring can be seen on the surrounding mountains. Many people call this coloring a “bath ring.” The ring shows what Lake Mead's water levels were in the past due to water erosion of the border mountains.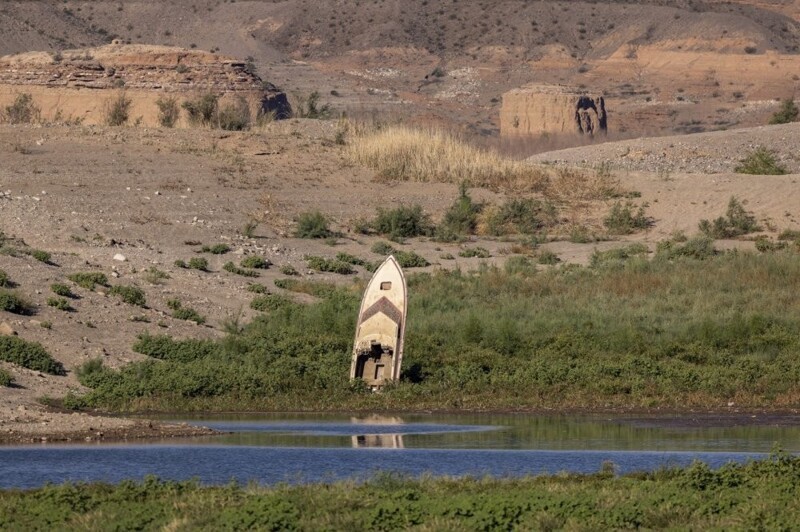 
Officials asked residents of Arizona and Nevada to reduce their water use by 18% and 7%, respectively. By many estimates, due to the prolonged drought in the southwest, the region is moving toward irreversible arilization. Most scientists believe drought conditions are unlikely to improve anytime soon. Thus, states have implemented water conservation regulations. The acts include reducing the amount of water used to water lawns and golf courses and possibly reducing water use for agricultural purposes.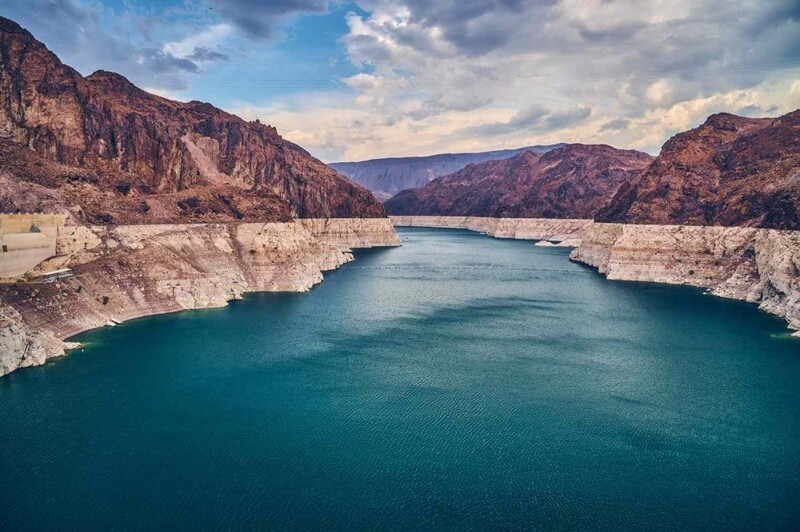
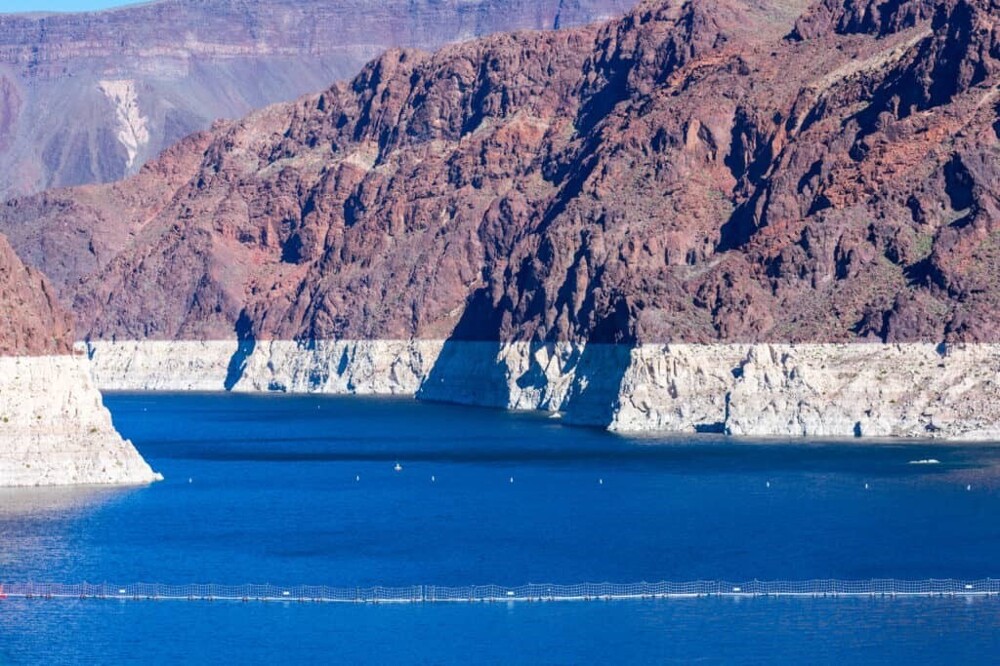

The "bath ring" shows what the water level was previously.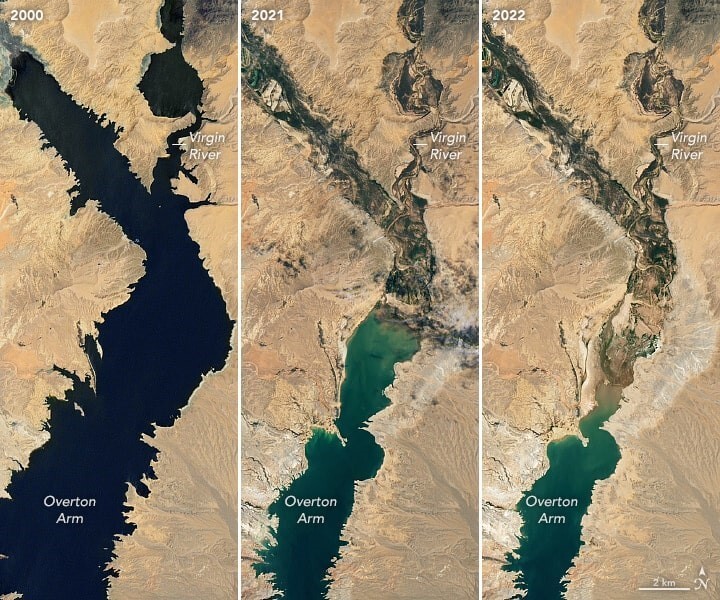 
Map of the lake's shrinking area.
Water consumption needs to be reduced by at least 30%, environmentalists say. Seven states in the United States and two in Mexico will have to agree on who is willing to reduce their needs and how much. The main reasons for Lake Mead's declining water levels, in addition to population growth leading to depletion, are drought and climate change.