A diet of meat and cheese brought a Florida resident to the point that cholesterol began to appear on his skin (2 photos)
Doctors in Tampa, Florida, reported an unusual case: a man on a “meat-eating diet” had cholesterol levels in his blood so high that they began to accumulate under his skin in the form of yellowish nodules. 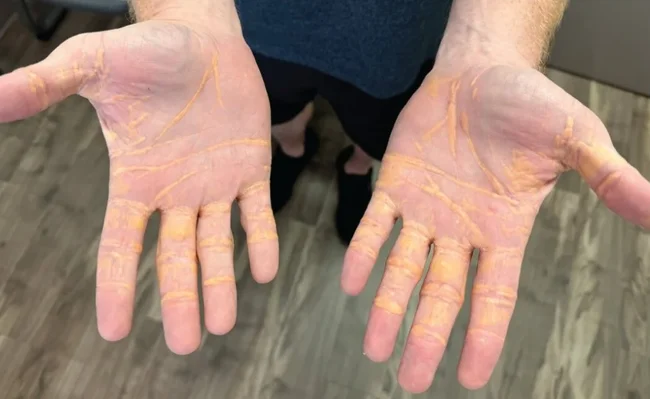
The man sought medical attention after developing painless but noticeable yellowish nodules on his hands and elbows. Doctors diagnosed the patient with a rare but known complication, xanthomatosis, caused by extremely high cholesterol levels in the blood.
A man in his 40s had been on a “meat-eating diet” for about eight months before his symptoms began. His diet was high in fat, with lots of cheese, lots of butter, and hamburgers with added fat every day. Despite this diet, the patient noticed weight loss, increased energy, and improved mental performance. However, side effects were not long in coming.
His blood cholesterol level was over 1,000 mg/dL (normal is less than 200 mg/dL, and high is 240 mg/dL). This caused cholesterol to accumulate under the skin, causing the nodules. 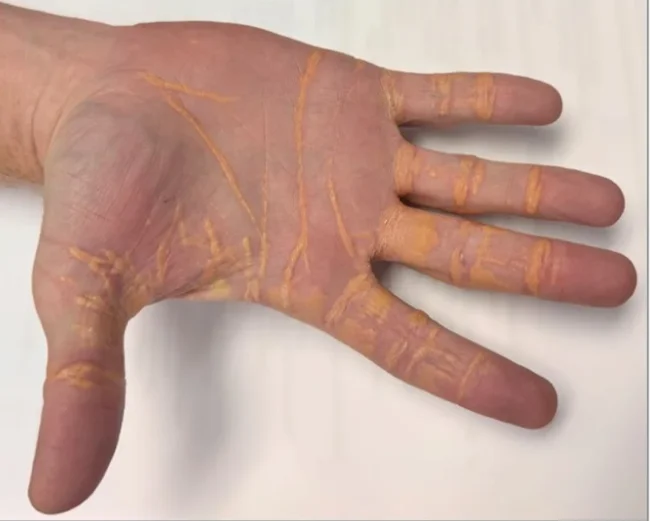
Xanthomas (cholesterol deposits under the skin) form when white blood cells responsible for removing excess fat fail to do their job. As a result, they turn into "foam cells" overloaded with cholesterol, which are deposited under the skin.
Xanthomas usually appear around the eyelids due to weak blood vessels in that area. However, in rare cases, like this patient's, they can occur on other parts of the body. Studies show that xanthomatosis occurs in about 1% of women and 0.3% of men.
Although the nodules themselves are harmless and can be surgically removed, high cholesterol levels significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
The authors of the article emphasize the importance of controlling cholesterol levels to prevent complications.