Horseshoe crab: an ancient inhabitant of the planet who helps people (11 photos)
Horseshoe crabs are one of the most ancient representatives of the animal world of the earth. I suggest you learn about these interesting creatures that survived to the present day.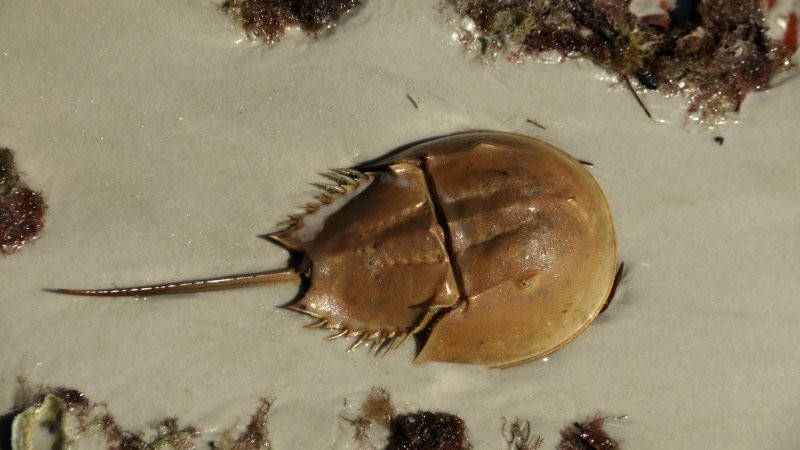 
“Shining to others, I burn myself” - this phrase fits not only to doctors who risk their lives to save others, but also horseshoe crabs. Only in contrast from the medical staff, the animals have no choice. Because their blood not only saves lives, but also sells remarkably well. She costs up to $13,000 per liter!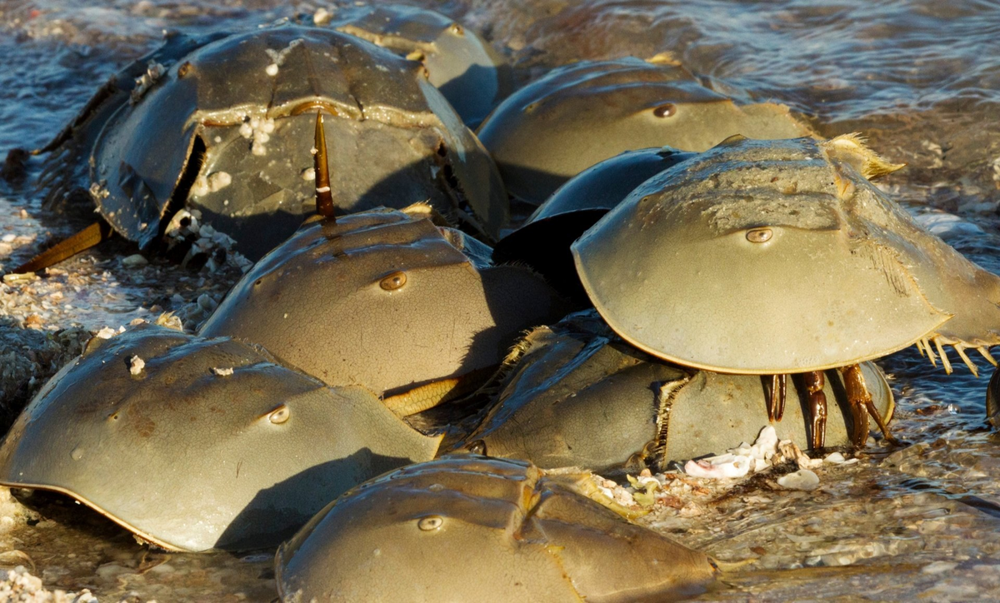 
Horseshoe crabs are unhappy that you look at them like bags of money.
Horseshoe crabs are real living fossils. They appeared simultaneously with the first centipedes, snails and teleosts fish as far back as 420 million years ago. For this period their peers have come a long evolutionary path, but here horseshoe crabs have not changed much. Except for a couple of notable modifications are all the same animals that crawled along the bottom in the distant past.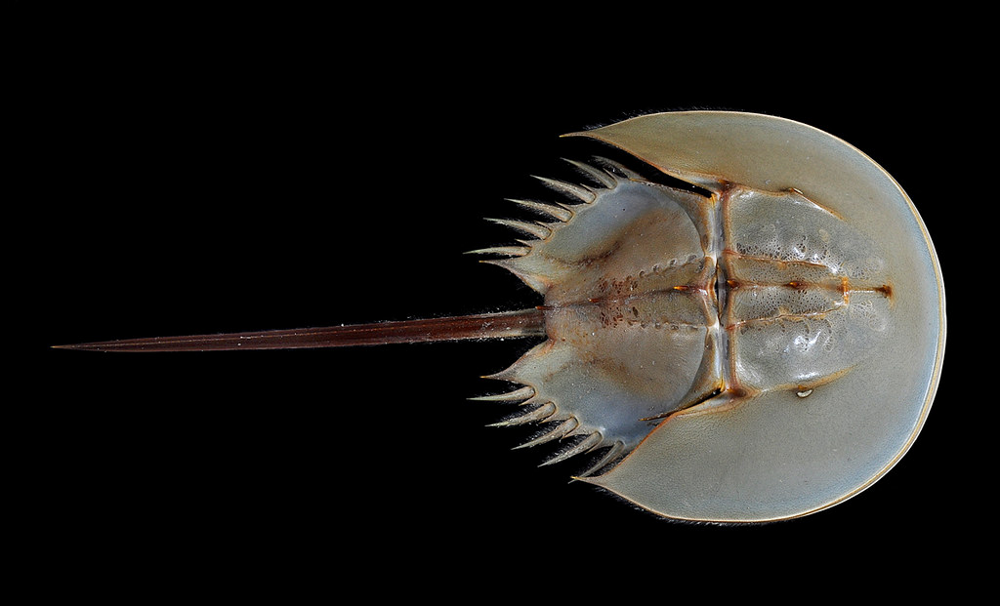 
The abdomen of the first horseshoe crabs consisted of separate segments, and they were 2-3 times smaller than modern ones.
The closest relatives of horseshoe crabs are arachnids. But since the spiders did not score on evolution, they have in common left a little. And in both the body is divided on the cephalothorax and abdomen. Both of them have chelicerae. This is where the similarity ends.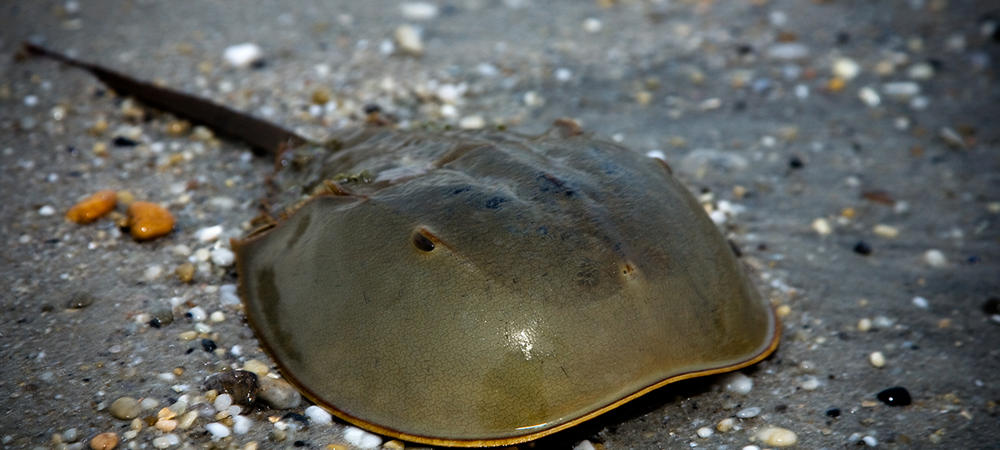 
By the number of legs, horseshoe crabs are clearly closer to crabs than to land relatives: they have as many as 24 paws. The first 5 pairs sit on the front section body. They are used for locomotion and food capture: snails, worms and bivalves hiding in the sand. Another 7 pairs stick out from the abdomen. The first two pairs are used for reproduction, and the rest turned into plates with gill books located on them. read they will not work, but use for breathing - as much as you like.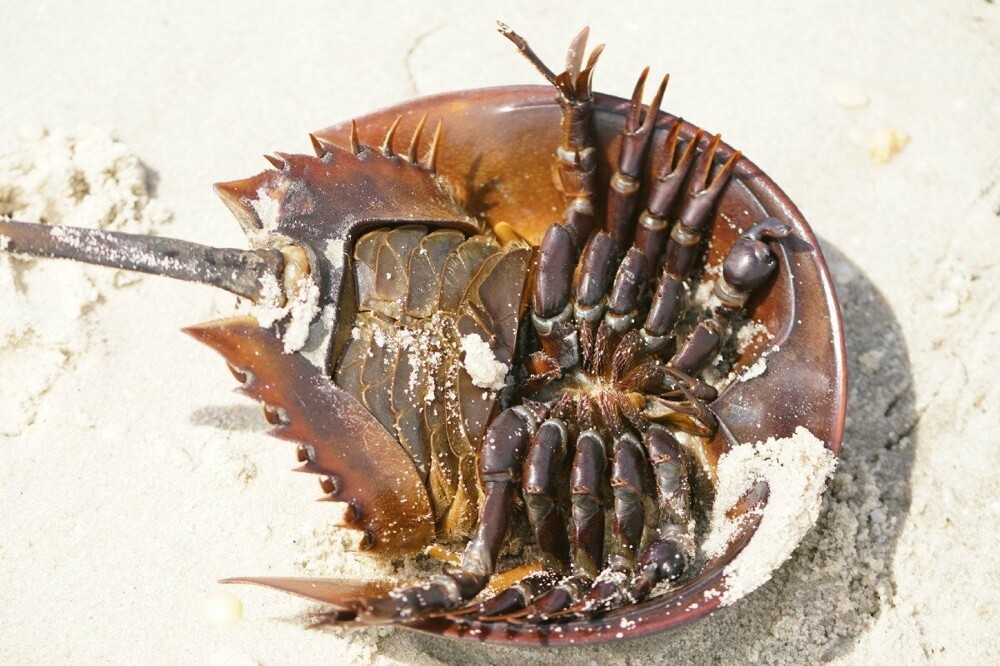 
Yes, those flat things are also legs.
And if the limbs perform their function well, then with the eyes of the horseshoe crab came out a clear crap. Arthropods have 2 pairs of them, and each eye consists from several small eyes covered with a common chitinous film. The result was a poor copy of the compound eyes of insects. organs of vision ancient arthropods are able to distinguish between distant shadows and close objects, but no more. 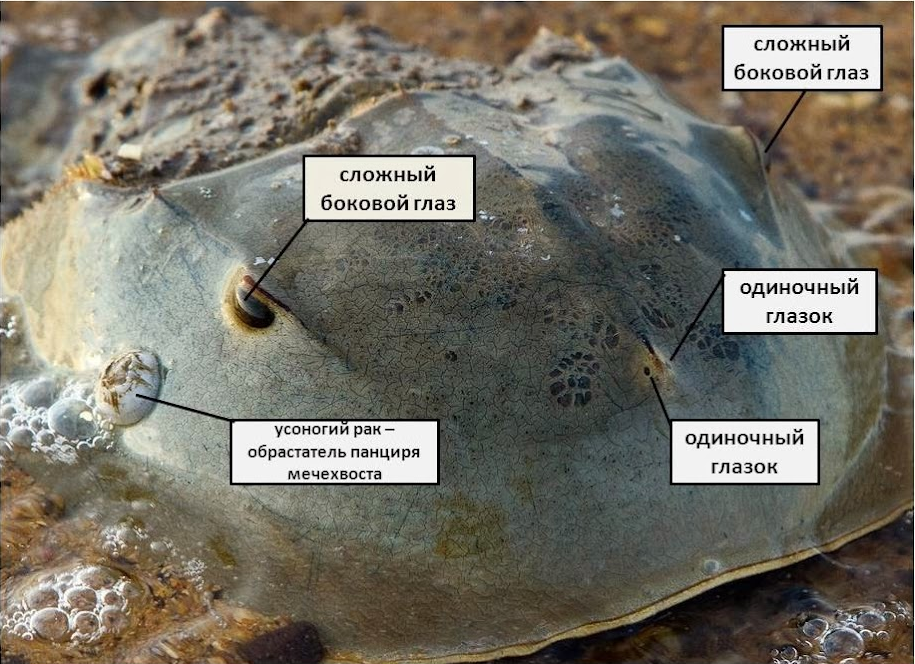
Memo about the location of the eyes on the horseshoe crab. Eye and barnacles.
Therefore, arthropods have to hold on in sunlit shallow waters. They prefer depth up to 40 meters. From the good: food in shallow waters in abundance. From the bad: it is very easy for people to get to to horseshoe crabs. In Southeast Asia, ancient pseudocrayfish caught for eating or for making feed additives for animals. In the USA, they are treated more humanely - they are drained blood and set free.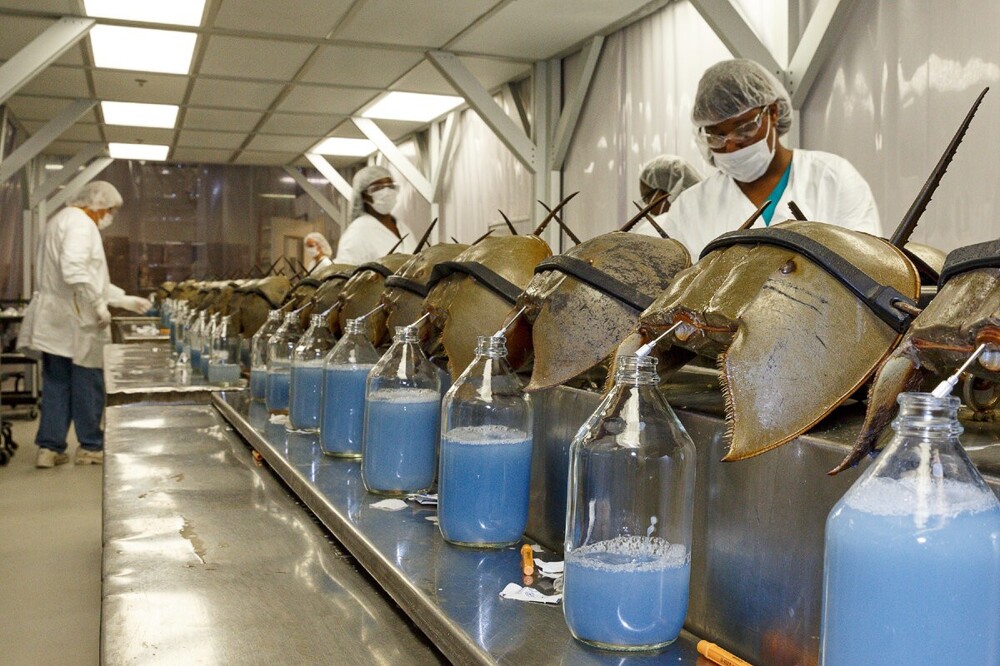 
Point of involuntary blood donation.
Horseshoe crab blood looks weird. She looks more like on chemose lemonade than on the red liquid we are accustomed to. And all because our blood is colored red due to oxidized iron contained in hemoglobin. And horseshoe crabs made a bet on copper, which is part of hemocyanin, protein analogue of hemoglobin.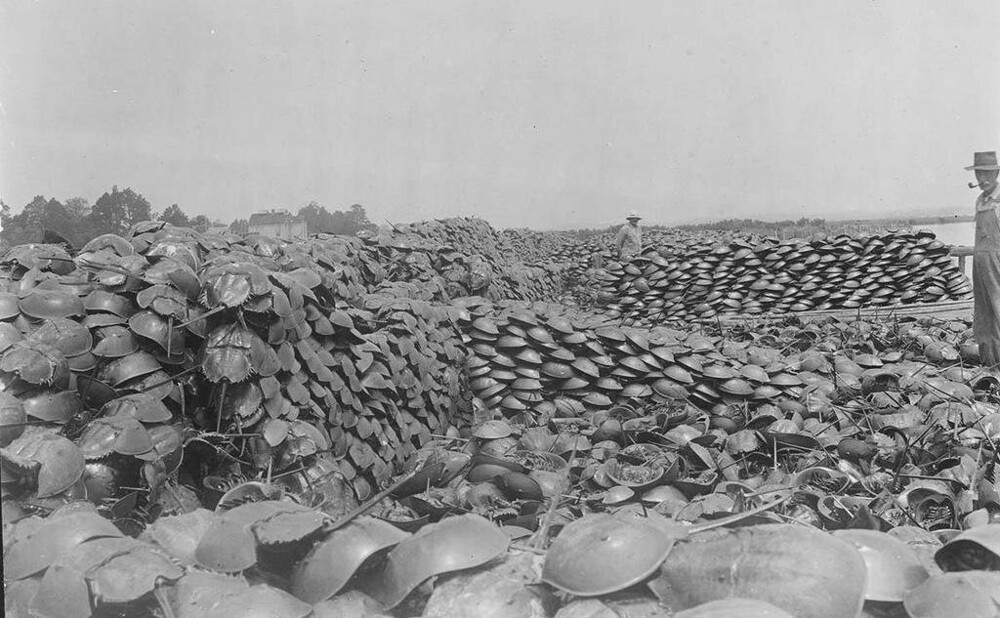 
Until 1930, horseshoe crabs were used to produce fertilizers, but when their population was greatly reduced, this genus activities were banned.
And no, it is not collected in order to boil the copper out of it. The blood of horseshoe crabs contains a unique protein - coagulogen (not to be confused with collagen!). When in contact with bacteria or toxins, it coagulates and blocks foreign particles inside itself. Thanks to this feature our heroes almost do not suffer from infectious diseases.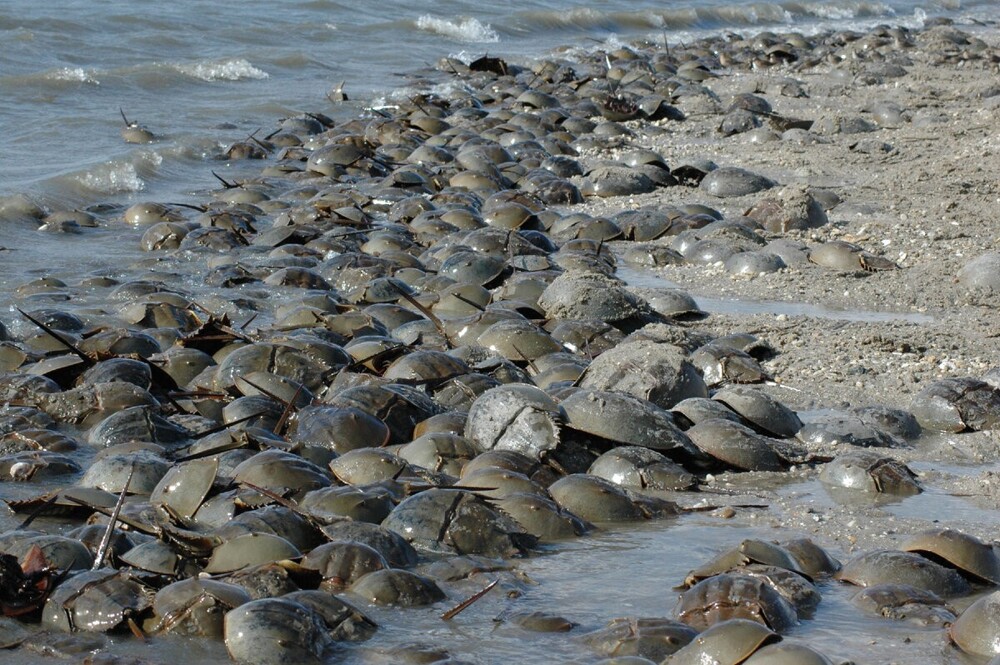 
We humans have found other uses for it. Tests based on coagulogen, LAL tests, used to check sterility of laboratory equipment, medical instruments and operating rooms. The "swordtail" test is more accurate than synthetic analogues and orders of magnitude faster than microbiological studies. Thanks to him, tens or even hundreds of thousands of people on time popali on operating tables and avoided dangerous complications from bacteria that enter the body. 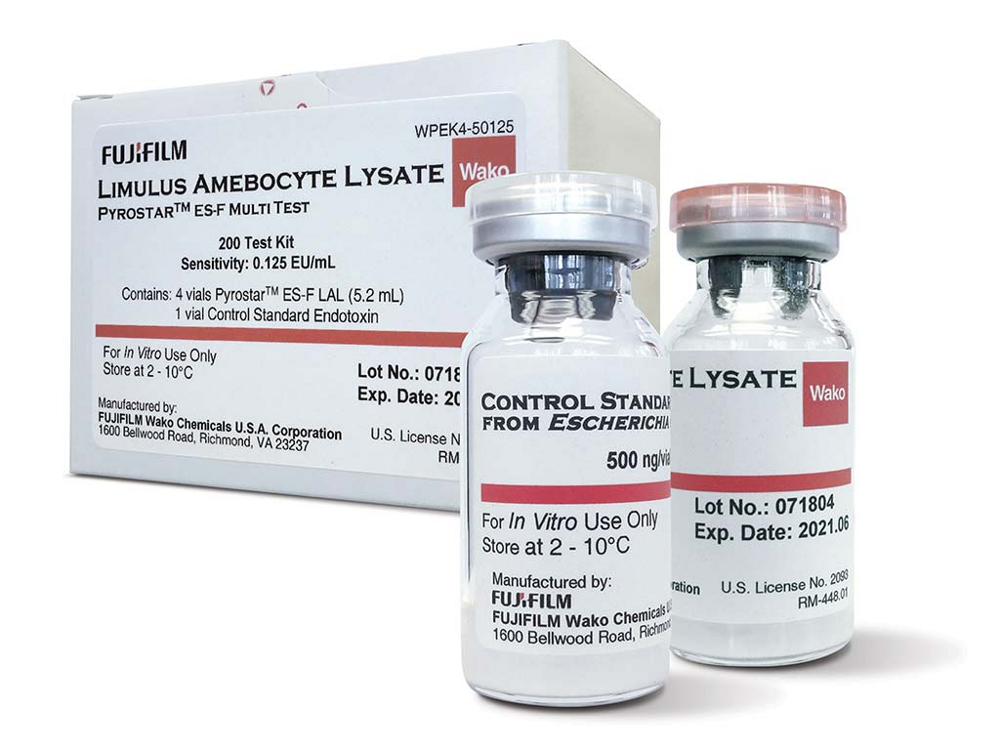
Despite the fact that LAL tests are not produced, they are actively used in laboratories.
Only horseshoe crabs themselves are not happy about this. About a third of the total supply is expressed from each of them. blood. According to various estimates, from 10% to 30% of animals unable to survive such blood loss, and many of the survivors skip the mating season. Load too big for their bodies. Therefore, populations gradually are shrinking.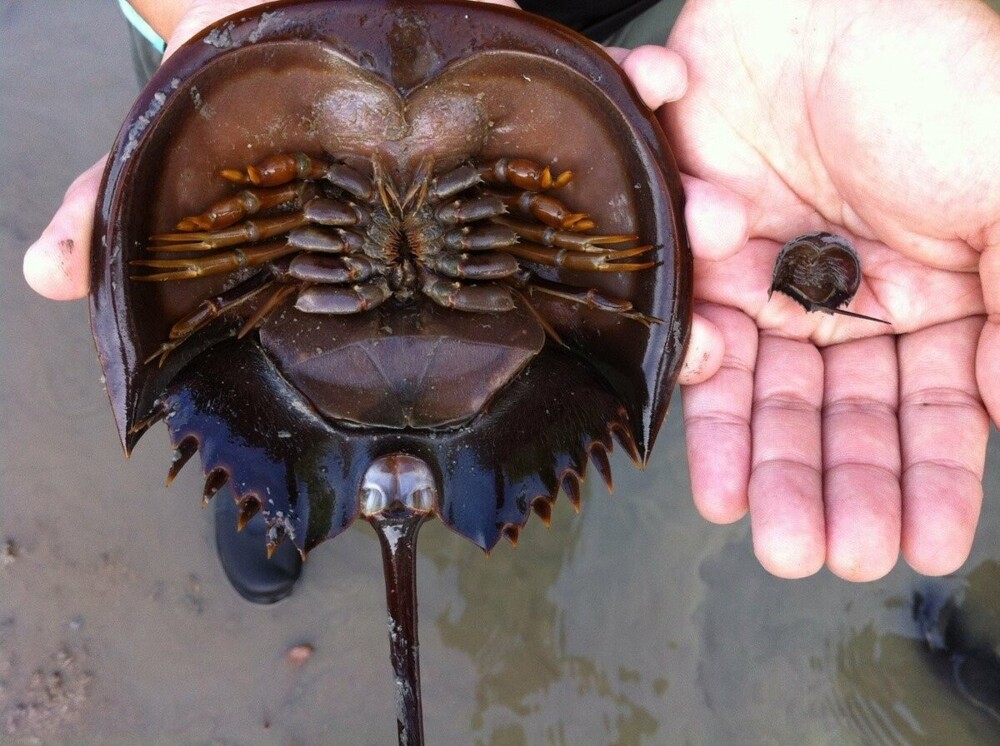 
Size difference between juvenile and adult horseshoe crabs quite significant. But to reach such sizes, they need from 8 up to 10 years old!
Fortunately, in recent years there have been nurseries for horseshoe crabs. Their employees catch ready for breeding animals, collect eggs from females, and from males - genetic material, after which they grow larvae under controlled conditions and released into the wild. In the wild, from a clutch of 1-2 thousand eggs survives no more than 1% of animals, while in nurseries this number reaches 80%!