The evolution of the spacesuit: how the clothes of NASA astronauts have changed over the years (14 photos)
Once-futuristic "foil suits", space suits NASA has changed significantly over the years to allow astronauts to survive in the vacuum of space and eventually skip walk on the moon. Now the space agency has unveiled a spacesuit the next generation, which is expected to be mission-ready Artemis III in 2025. 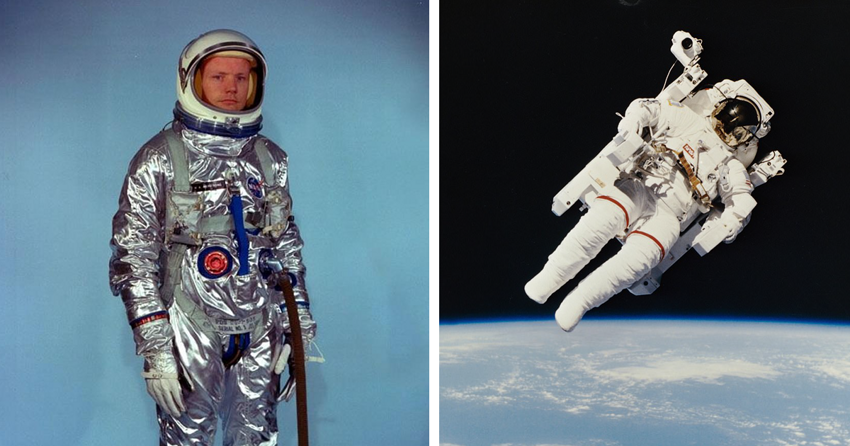
Space suit of the program "Mercury"
1959: Version 1
The first suit of the program "Mercury", outwardly resembling foil overalls, originally designed for high-altitude pilots fighters. However, NASA needed a spacesuit to protect the astronauts in case of a sudden depressurization of the cabin in the vacuum of space, therefore it has become an indispensable tool.
Each astronaut had three space suits: one for training sessions, one for the flight and one spare, with a total cost of 20,000 dollars. All of them have been individually adapted for each astronaut and eventually coped with their task, since not a single the suit did not fail during launch. The suit has also been used United States Navy from 1959 to the early 1970s.
Missions: Mercury-Redstone-3
Function: in-vehicle operation
Weight: 10 kg
Primary life support: from the Mercury spacecraft
Backup life support: from the Mercury spacecraft
Cons: Poor temperature control and astronauts couldn't turn their heads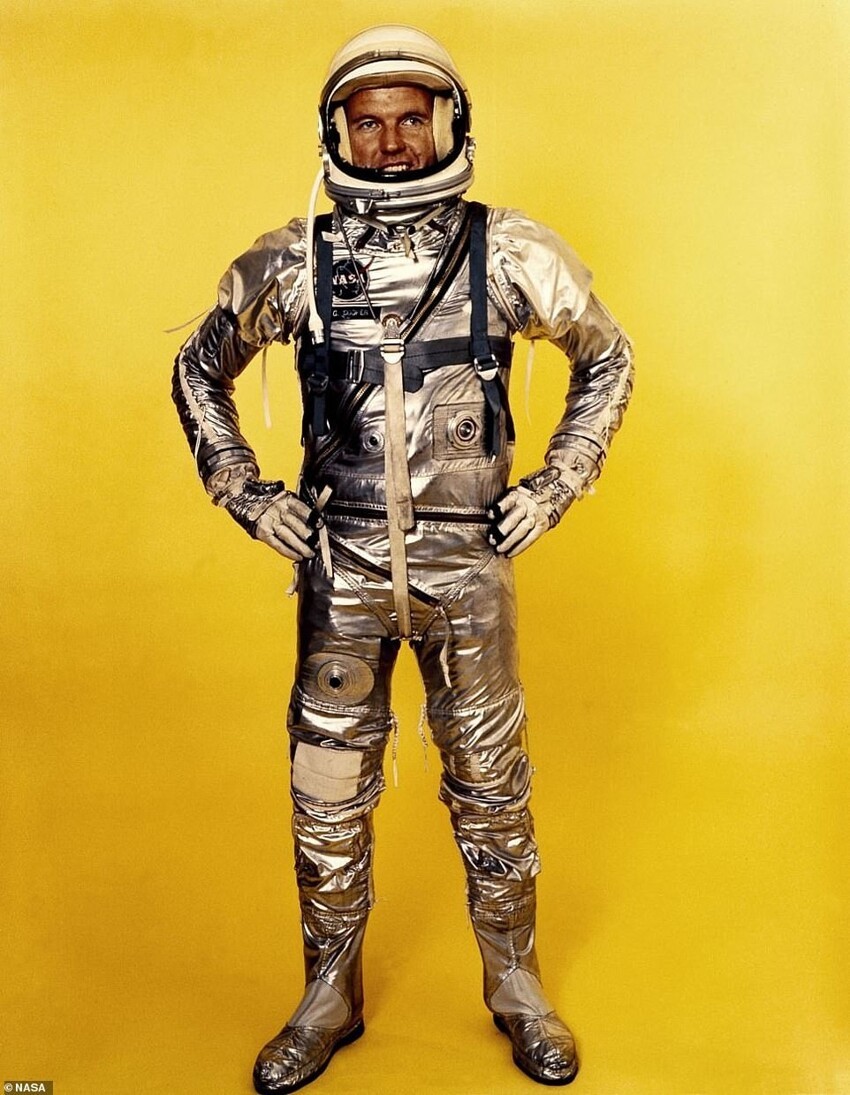 
1961: Version 2
Missions: "Mercury" from 4 to 9
Changes:
"Open circuit" breathing system replaced closed-loop system, whereby the rubber diaphragm around the user's face is eliminated.
Attempts to solve the problem of temperature control by replacing the dark gray nylon outer shell with a nylon outer shell aluminum coating, as well as new safety boots.
The introduction of special gloves with four curved fingers to help the astronauts better control the spacecraft. The middle finger has been made straight for pressing buttons and switching toggle switches.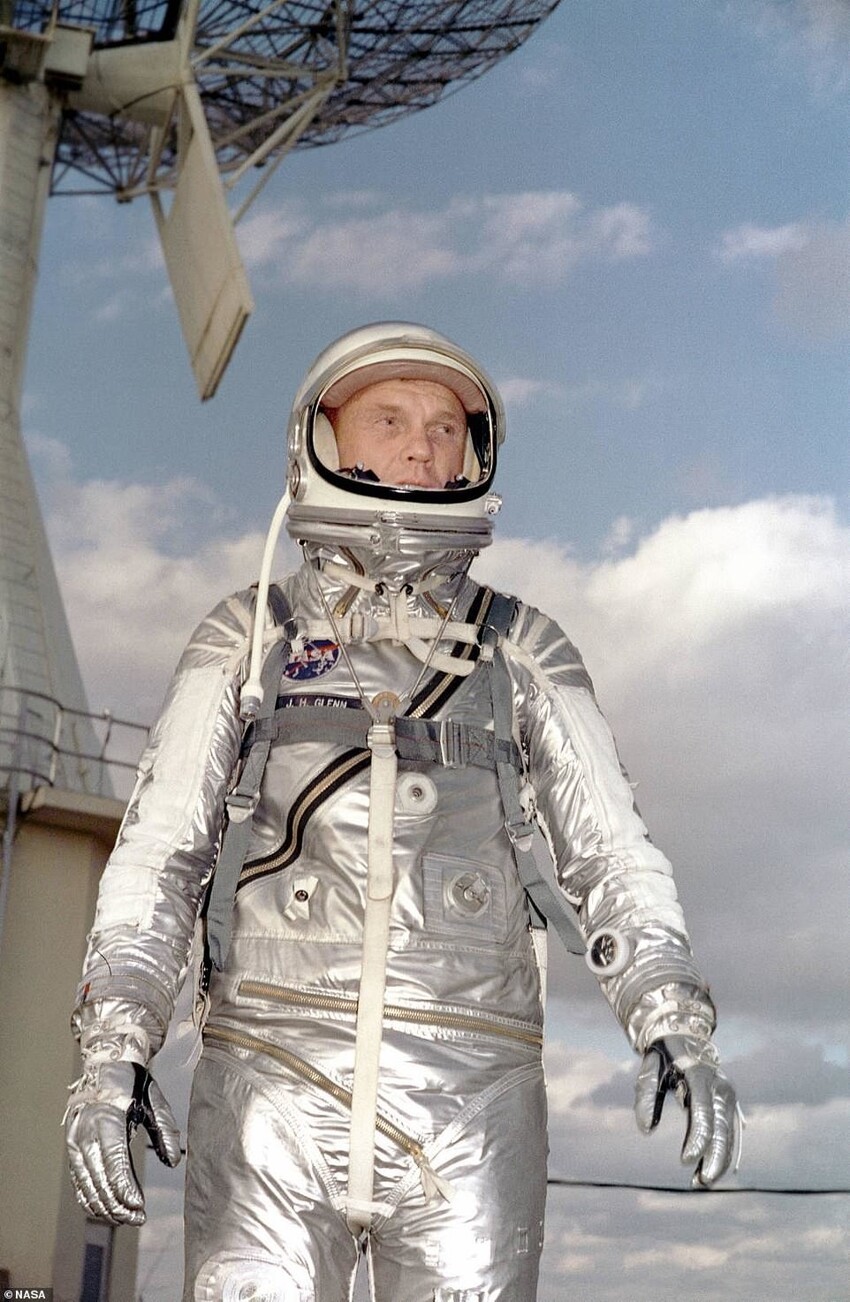 
Suit for the program "Gemini"
March 1965: Version 1
Designed by NASA based on the suit for high-altitude flight X-15, the Gemini suit was used by the astronauts to launch, in flight and landing. In contrast to the "soft" suit for the program Mercury, the entire Gemini suit was made flexible.
On the first Gemini mission, the astronauts had portable air conditioners that were connected to their space suits.
Missions: Gemini 3
Function: in-vehicle operation
Weight: 10.7 kg
Primary Life Support: From Space Shuttle Gemeni
Backup life support: from the Gemini spacecraft
Weaknesses: again poor temperature control, also a weaker helmet faceplate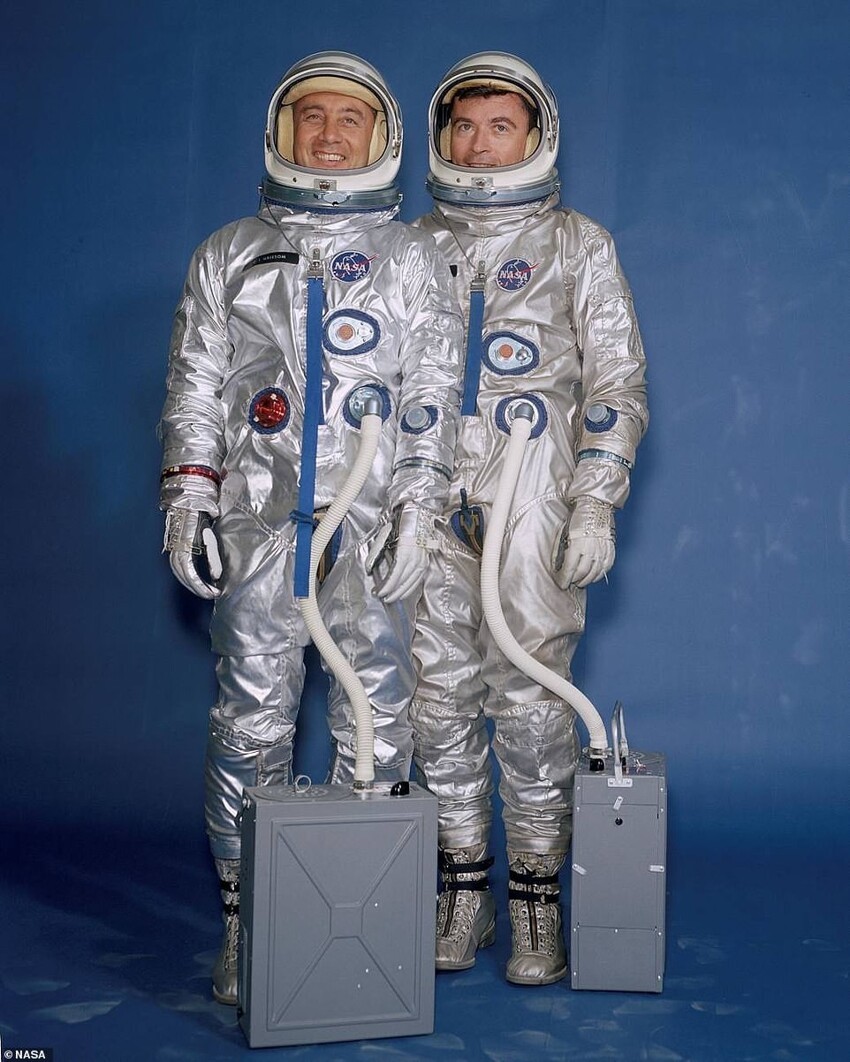 
June 1965: Version 2
Missions: Gemini 4-12 (except 7)
Changes:
Adding extra insulation to improve temperature control in direct sunlight and shade;
Built-in pilot boots and a removable sun visor that attaches to the helmet
The helmet's Plexiglas faceplate has been replaced with a more durable polycarbonate plastic plate.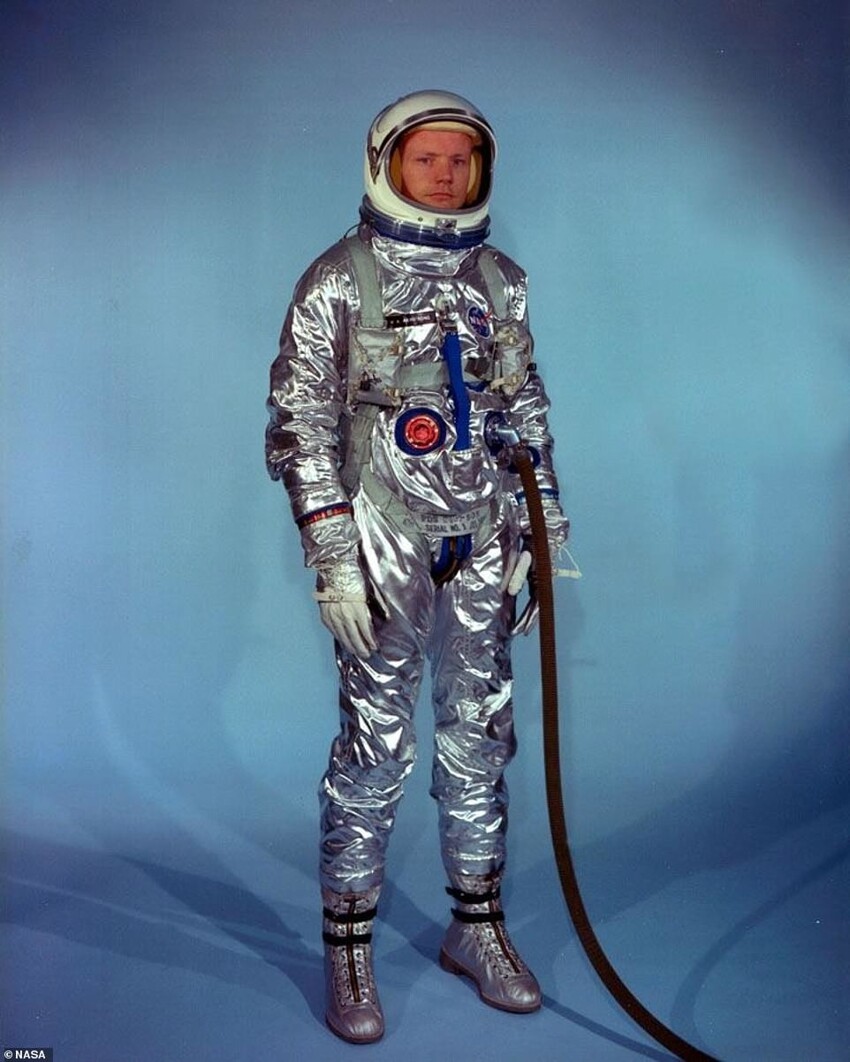 
December 1965: Version 3
Missions: Gemini 7
Changes:
The sealed helmet and neck ring were replaced with a zippered hood with a clear, fixed polycarbonate visor;
Introduction of modified US Navy-style crash helmets with microphones and headphones for communication;
Adding more lightning to the astronauts it was easier to adjust your suit in flight, including having the ability to completely remove it.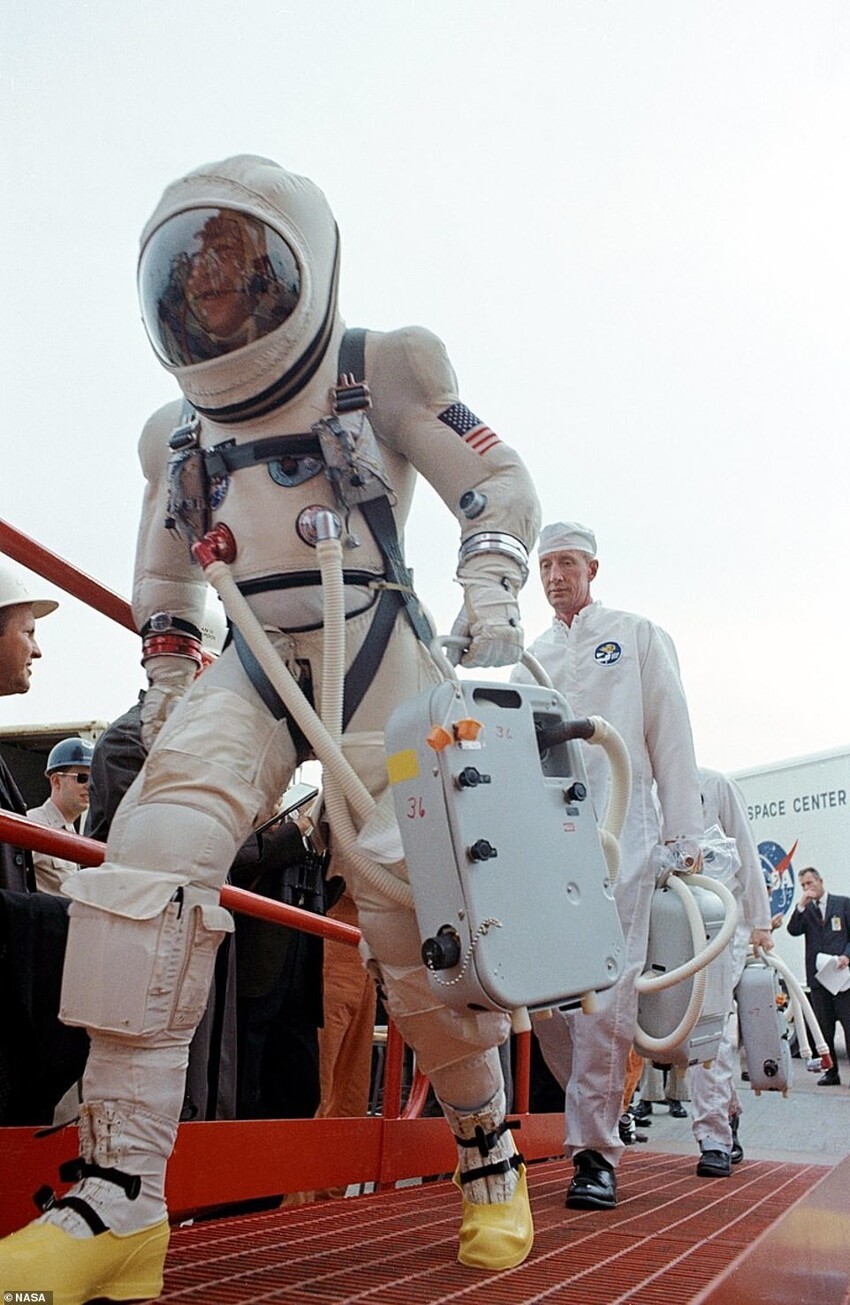 
Apollo space suit
Apollo suits with their famous "jet pack" - the most famous NASA spacesuits, because it was the Nile in it Armstrong when he became the first person to walk on the moon in 1969.
The suit consisted of the suit itself and a portable life support systems in the form of the same "jetpack, which used on the Apollo 7-14 missions.
1967: Version 1
Missions: Apollo 1
The suit was updated after the tragic fire on the ship Apollo 1, which killed all three crew members in January 1967.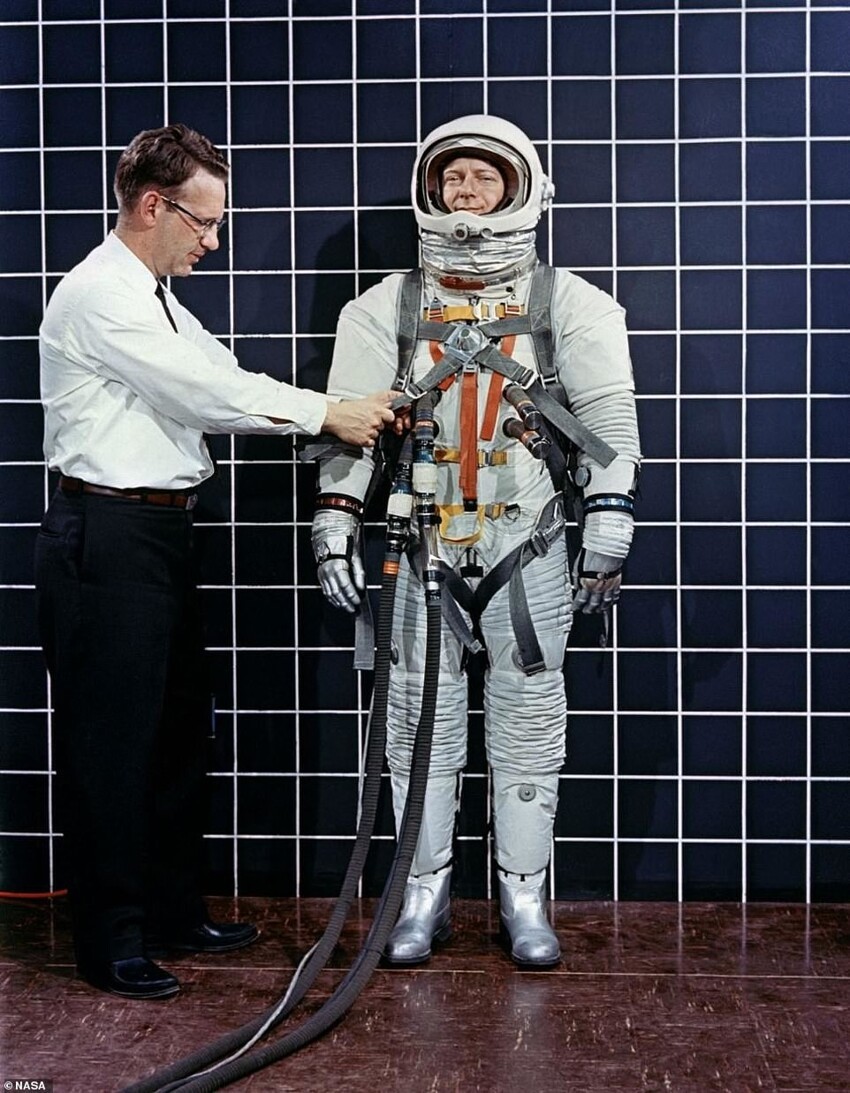 
1968: Version 2
Missions: Apollo 7-14
Function: in-vehicle and extra-vehicular activities, landing on the moon.
Weight: 96.2 kg
Basic life support: 7 hours (420 minutes)
Backup life support: 30 minutes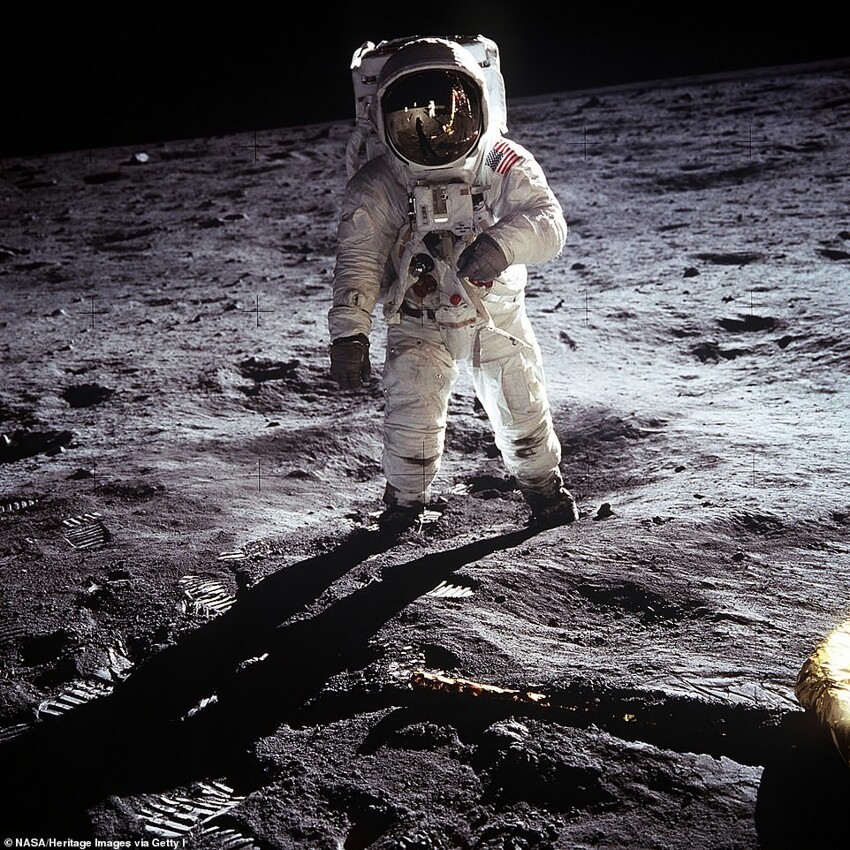 
1971: Version 3
Missions: Apollo 15-17
Changes:
Changes made for longer lunar missions and for the first use of the lunar rover (LRV);
The backpacks have been modified to carry more oxygen, power, and cooling water.
Small energy bars were placed in special pouches under the inner part of the spacesuit helmet ring, and drinking water was stored in a "collar" under the outer suit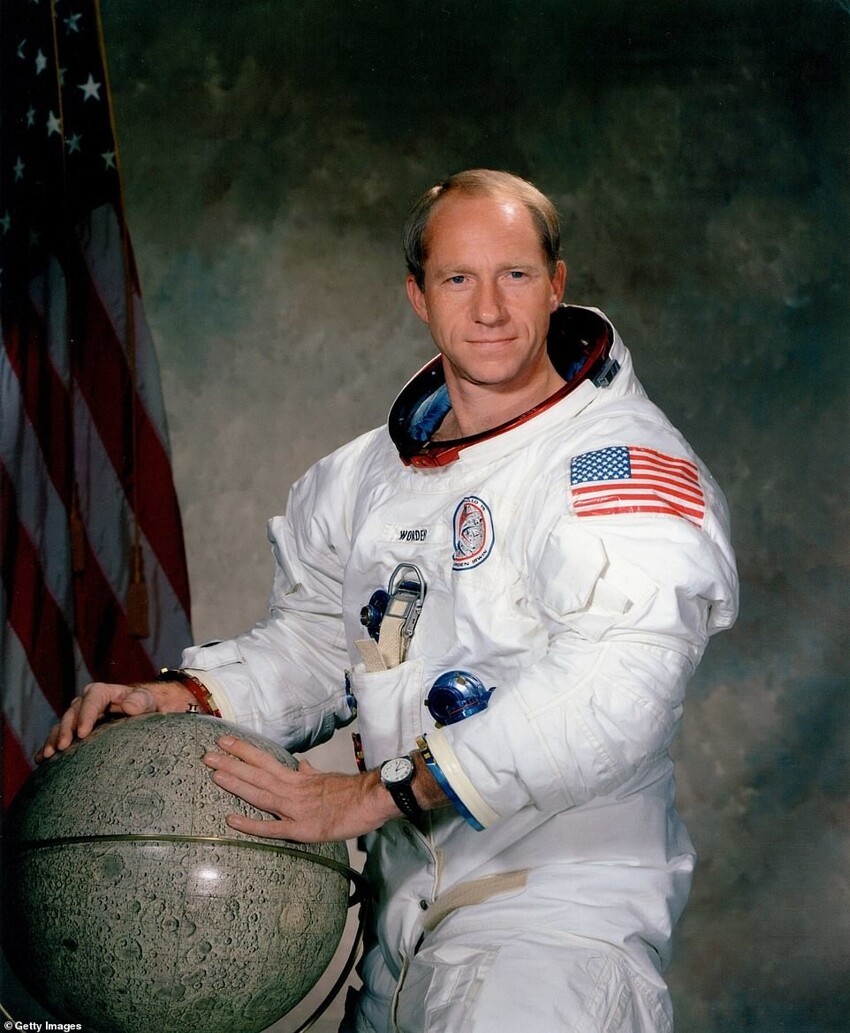 
Suits for the "Shuttle"
The shuttle crews are famous for their iconic orange "space suits-pumpkins." A bright color was chosen so that rescuers could it is easy to spot astronauts if they have to escape in the ocean. But when the Shuttle first lifted off on April 12, 1981, astronauts John Young and Robert Crippen were actually dressed somewhat differently. It was due to the fact that the crew of two did not go outside, so they put on only a life suit for emergency ejection, and not the Launch Entry Suit (LES), which only appeared in 1988. That, in turn, replaced the Advanced Crew Escape Suit in 1994.
1981: Version 1
Missions: STS-1 to STS-4
Function: inboard and ejection
Weight: 18 kg
Primary life support: from the Space Shuttle
Backup life support: from the Space Shuttle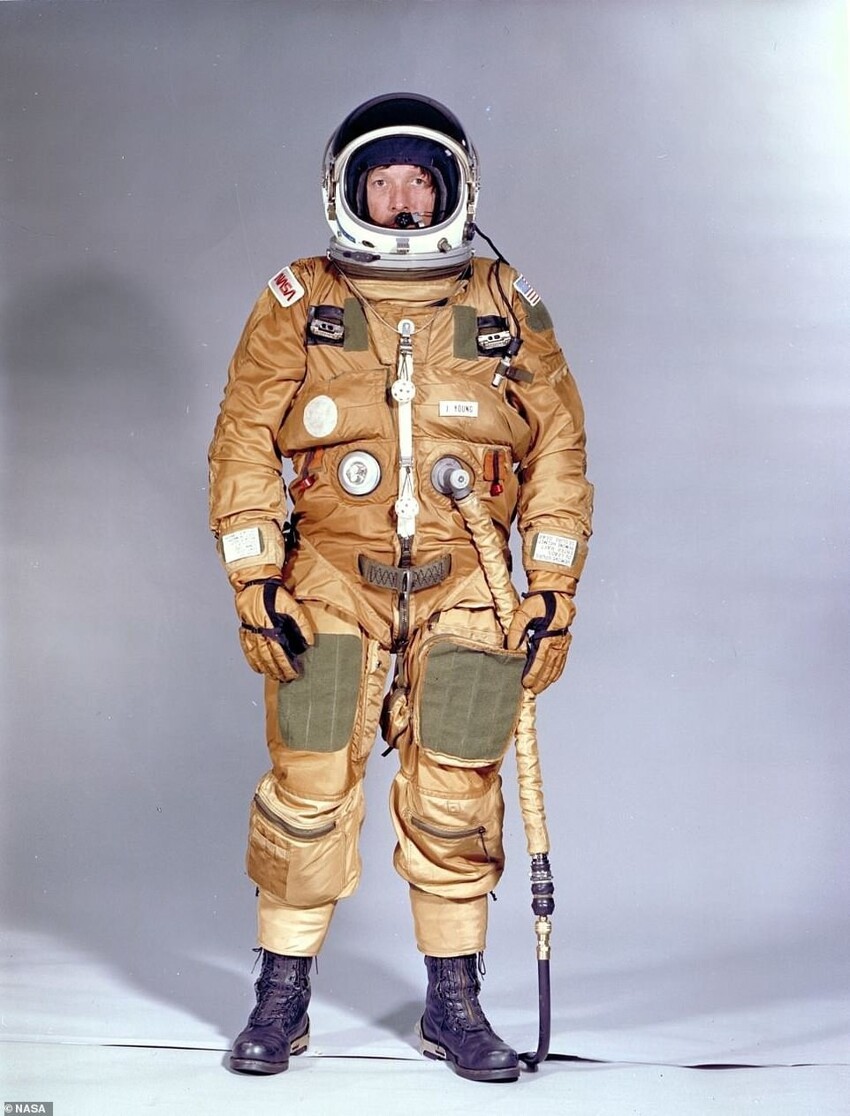 
Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU)
1984: Version 1
This is not so much a spacesuit as the iconic "jet satchel that NASA used on three Shuttle missions in 1984. The system allowed astronauts to perform spacewalks without bindings to the distance from the shuttle.
However, after the Challenger disaster, NASA decided that using an MMU is too risky. The space agency came to conclusion that many of the activities planned for the MMU are in fact can be performed just as efficiently with robotic arms or traditional tethered spacewalks.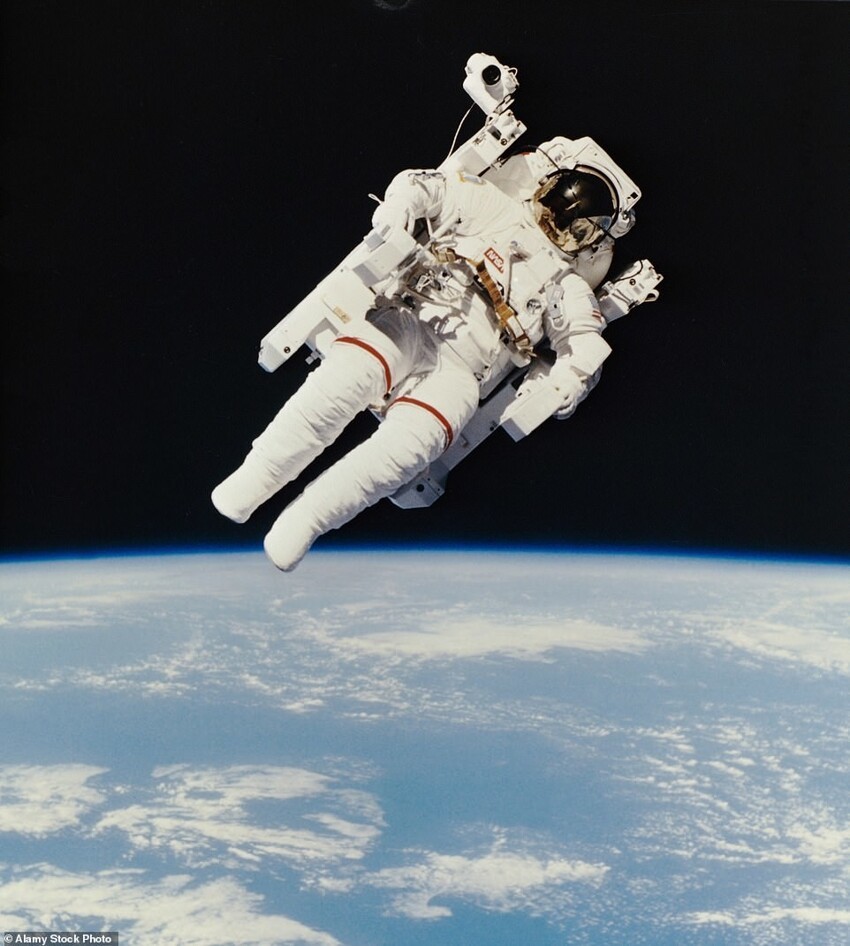 
"Spacesuit-pumpkin"
The first "pumpkin suit" for the crew of the "Shuttle" was Launch Entry Suit (LES). It was a semi-hermetic suit, which put on the takeoff and landing parts of the flight from the STS-26 mission in 1988 to STS-65 in 1994. It was later replaced by the Advanced Crew Escape Suit.
1988: Version 1
Missions: STS-26 to STS-65
Function: in-vehicle operation
Weight: 13.6 kg
Primary life support: from the Space Shuttle
Backup life support: 10 minutes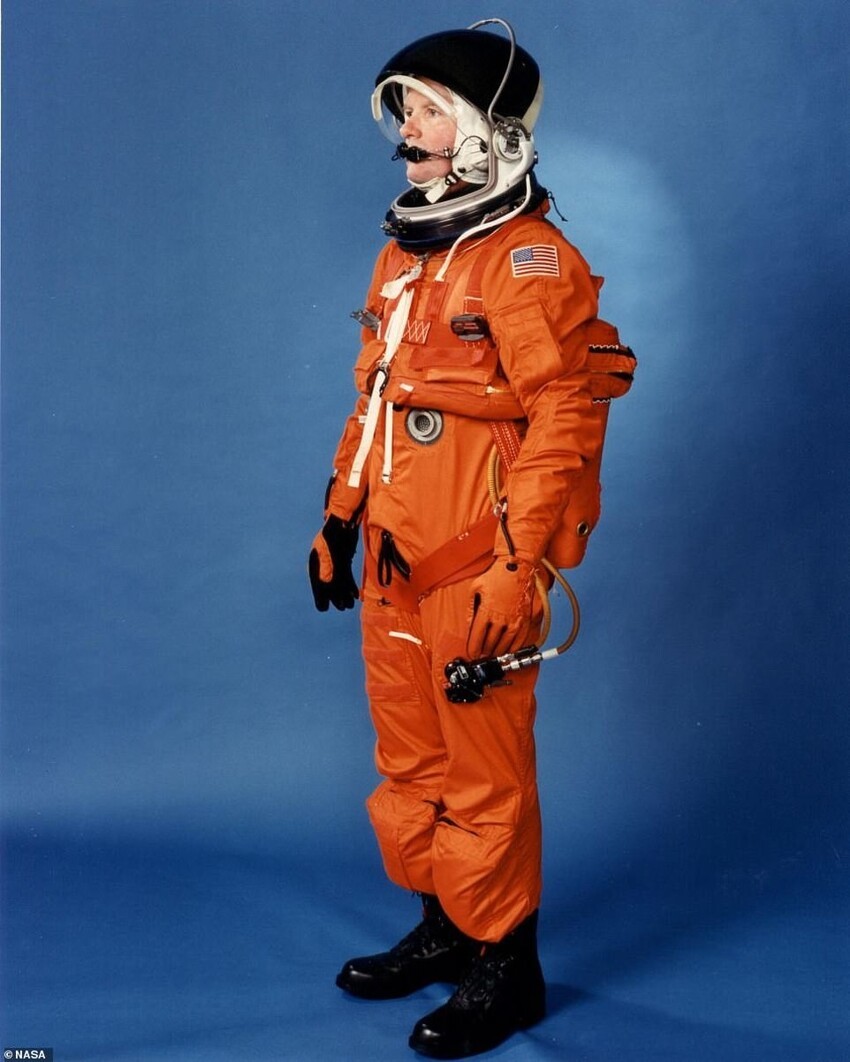 
1994: Version 2
Missions: STS-64 to STS-135
Function: in-vehicle operation
Weight: 13 kg
Primary Life Support: Externally, from the Space Shuttle
Backup life support: 10 minutes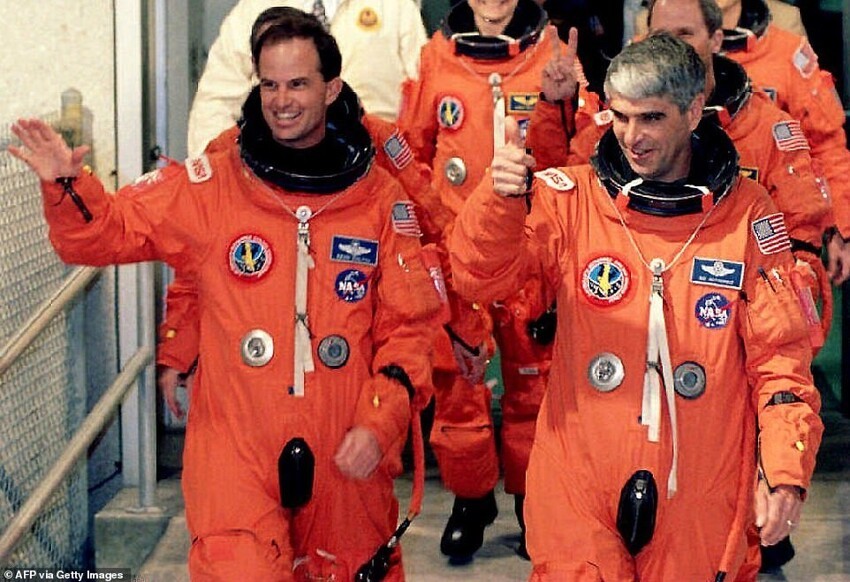 
Space suit for the Artemis program
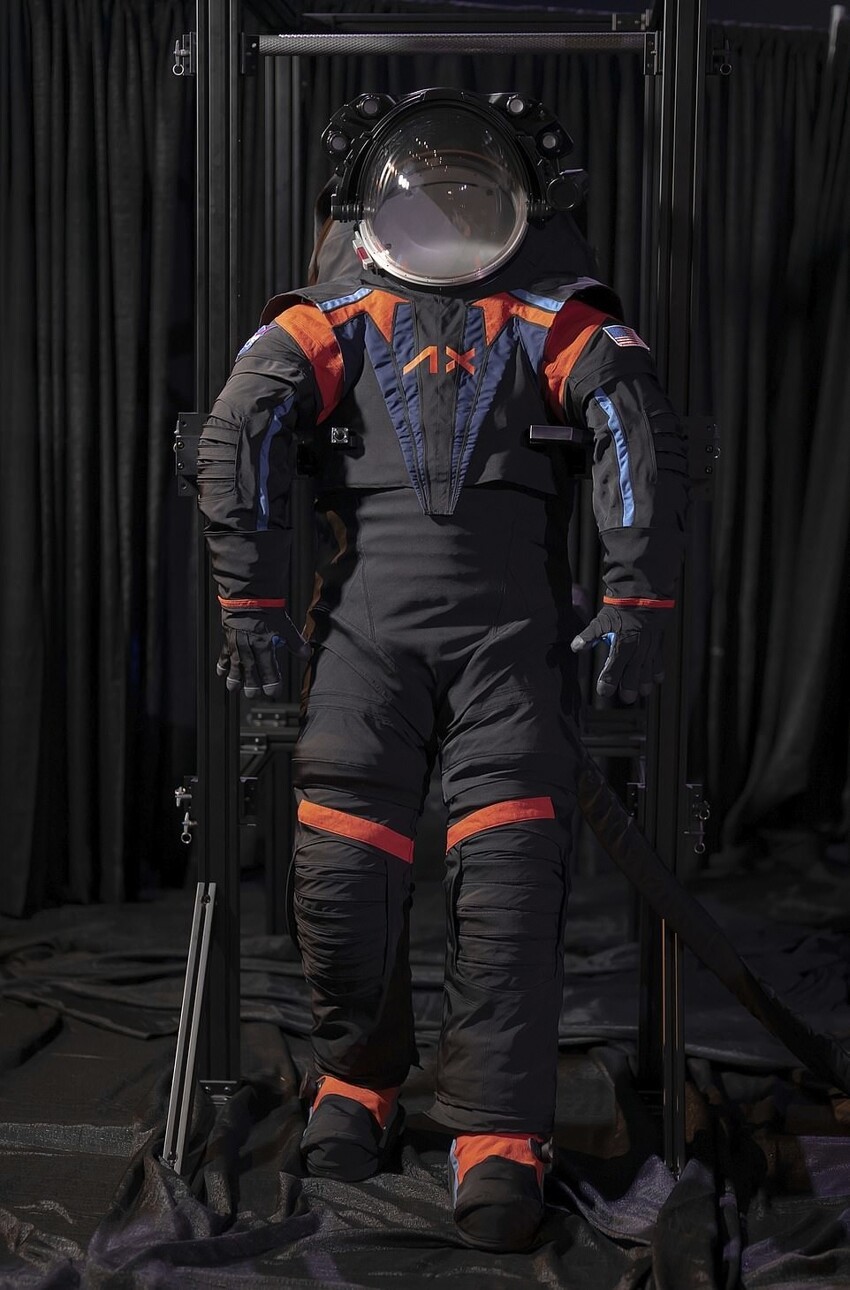
Earlier this week, NASA unveiled its new space suit, which in 202 will land on the moon, including the first woman and the first non-white person.
US space agency in partnership with aerospace Axiom has developed a new equipment with improved mobility compared to the bulky Apollo suits that made the astronauts fell while walking on the lunar surface.
Astronauts will be able to walk in the new Axiom spacesuit Extravehicular Mobility Unit (AxEMU), instead of skipping like theirs predecessors, which allows them to bend and lift objects above head.
Innovative spacesuit made from Mylar and Kevlar includes a new "bubble helmet"boots specially designed for moon trips, and a portable life support system that "looks like a weird mixture of scuba gear and air conditioning." It's sealed suit with built-in HD camera.
2023: Version 1
Missions: Artemis III and Beyond
Function: in-vehicle operation
Weight: 13 kg
Primary Life Support: Externally, from the Space Shuttle
Backup life support: 10 minutes