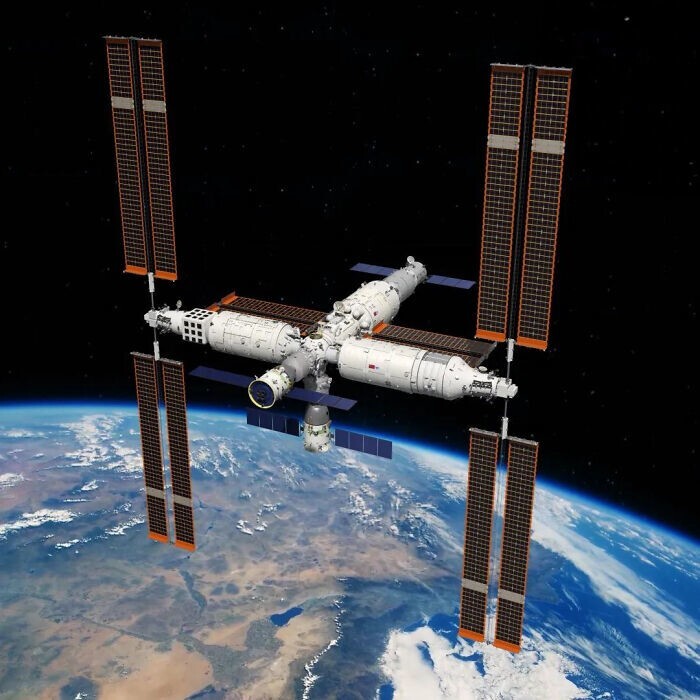
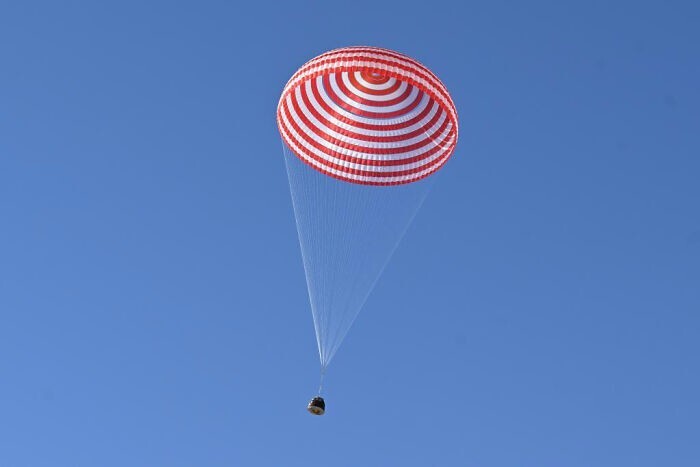
Chinese astronauts returned to Earth after the Shenzhou-17 mission (9 photos + 1 video)
The crew of the Chinese spacecraft Shenzhou 17 returned to Earth after six months in space. The astronauts spent all this time at the Chinese orbital station, conducting scientific experiments and various tests.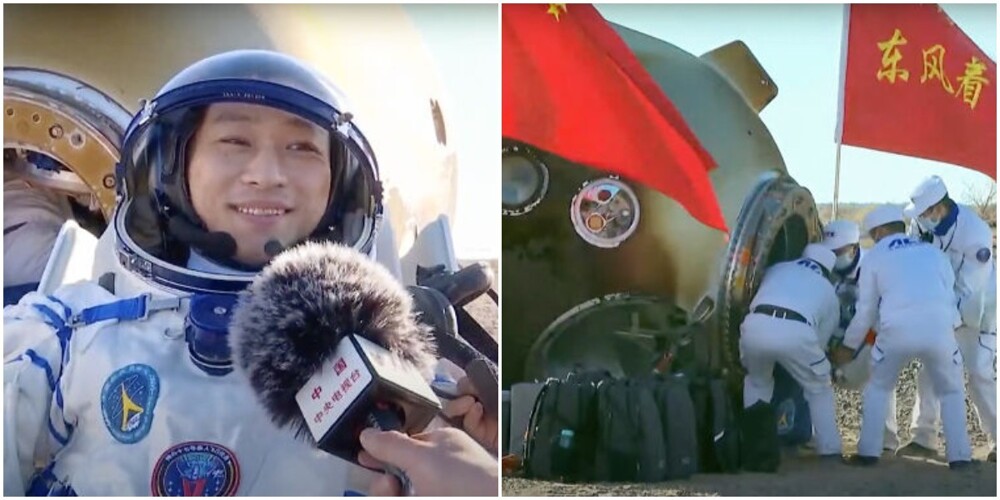 
The Shenzhou 17 spacecraft launched from China's Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on October 26, 2023, almost at the end of its previous mission. The Shenzhou-17 crew turned out to be the youngest in the history of flights to the Tiangong space station: commander Tang Hongbo was 48 years old, and cosmonauts Tang Shengjie and Jiang Xinlin were 34 and 35 years old at the time of the flight. This week, on April 30, three taikonauts successfully completed their mission and returned to Earth. The team landed in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in northern China.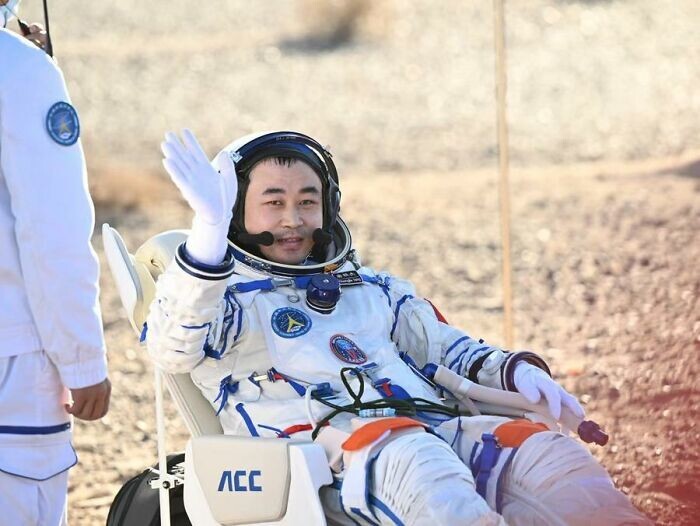 
The Shenzhou 17 mission was organized for various purposes, including conducting experiments and payload testing, performing extravehicular activities and tasks to remove cargo from the airlock module, repairing and maintaining the space station, and further improving the operational efficiency of the station. This mission was another step forward for China in space exploration: during their stay on board the Chinese space station, the team conducted a number of important experiments and scientific research. 
Currently, the ship's commander, Tang Hingbo, holds the record for the longest stay in orbit among Chinese astronauts. He spent 279 days in space during the Shenzhou 12 and Shenzhou 17 missions.
“During the mission, I missed my homeland, and my hometown in particular. Whenever the space station flew over China and I had free time, I looked out the window and looked for my hometown. I was filled with longing and pride,” - shared the commander after landing. 
After landing, all crew members were transported to Beijing, where they underwent a medical examination, recovered and summed up the results of the flight. By the way, the Chinese space program has made great progress since 2020, completing some of the most challenging missions in the history of space exploration. In the future, China plans to carry out more human space flights, as well as lunar and planetary missions. By 2030, Chinese astronauts are planned to land on the Moon.