China has become even closer to the creation of an “artificial sun” - a plasma with a current of 1 million amperes was obtained on a tokamak (2 photos + 1 video)
China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) has made a significant step towards the creation of an "artificial sun", that is, to controlled nuclear fusion reaction. Installation HL-2A type tokamak first generated plasma with a current of more than 1 million amperes or 1 MA in advanced hold mode (H-mode).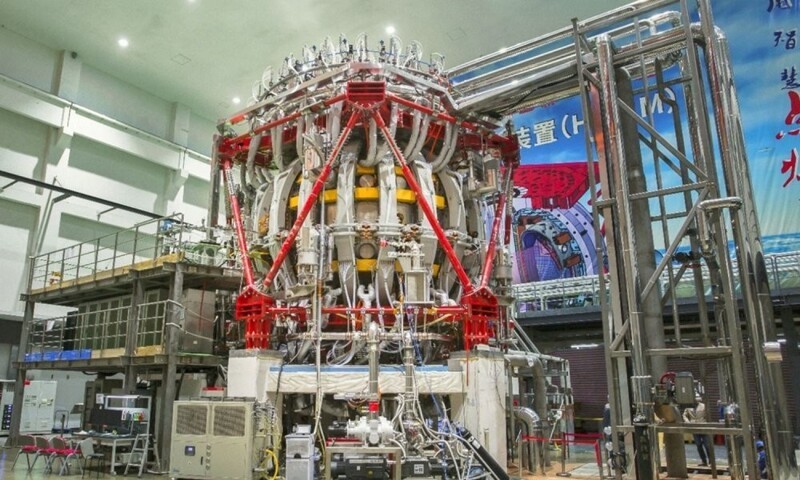 
CNNC confirmed the successful operation of the HL-2A installation in improved retention, in which significant growth can be achieved temperature and plasma density. This is a key step in development of controlled nuclear fusion, which, according to scientists, can provide the world with a safe, environmentally friendly and practical unlimited energy. Unlike nuclear fission, used in modern nuclear power plants, fusion produces less radioactive waste.
CNNC also noted that the new reactor has successfully overcome key technical difficulties associated with the use of a more powerful heating system and advanced diverting device. The device was developed at the Southwestern Institute of Physics in Chengdu (SWIP).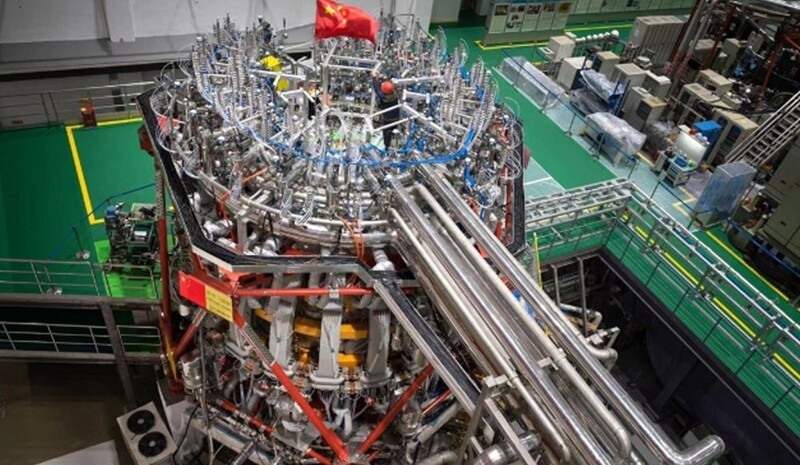 
China's next-generation 'artificial sun' shows amazing results in nuclear fusion
However, the HL-2A is not the first device capable of generate and maintain extremely hot plasma. In April Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak - Installation toroidal shape, designed to magnetically hold hot plasma in order to implement thermonuclear fusion - established a new record, maintaining the plasma for almost 7 minutes.
Scientists around the world are working to create similar "artificial suns" that generate energy by heating atoms hydrogen to temperatures above 100 million degrees Celsius, so that those connected with each other. The main problem is control this process so that the reactor does not melt.