On Mars noticed an unusual stone, similar to the ridge of a fish (9 photos)
NASA's Curiosity rover photographed on the Red Planet a bizarre geological formation that looks like a fish bone, spruce branch or stone with thorns. The find was made on 1 April base of Gale crater. It is considered an ancient dry lake, age which is 3.5–3.8 billion years.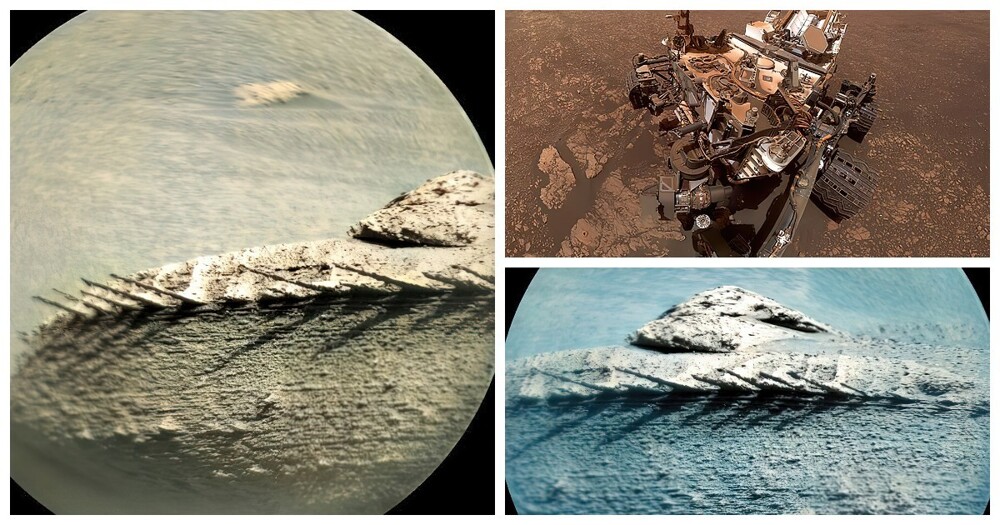 
Curiosity rover has been moving around Gale Crater since August 2012 as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. The objectives of the mission are to study the climate and geology of the Red Planet, as well as preparation for its development by man. The device constantly sends images of strange things he encounters - for example, here it is a spiked rock formation. 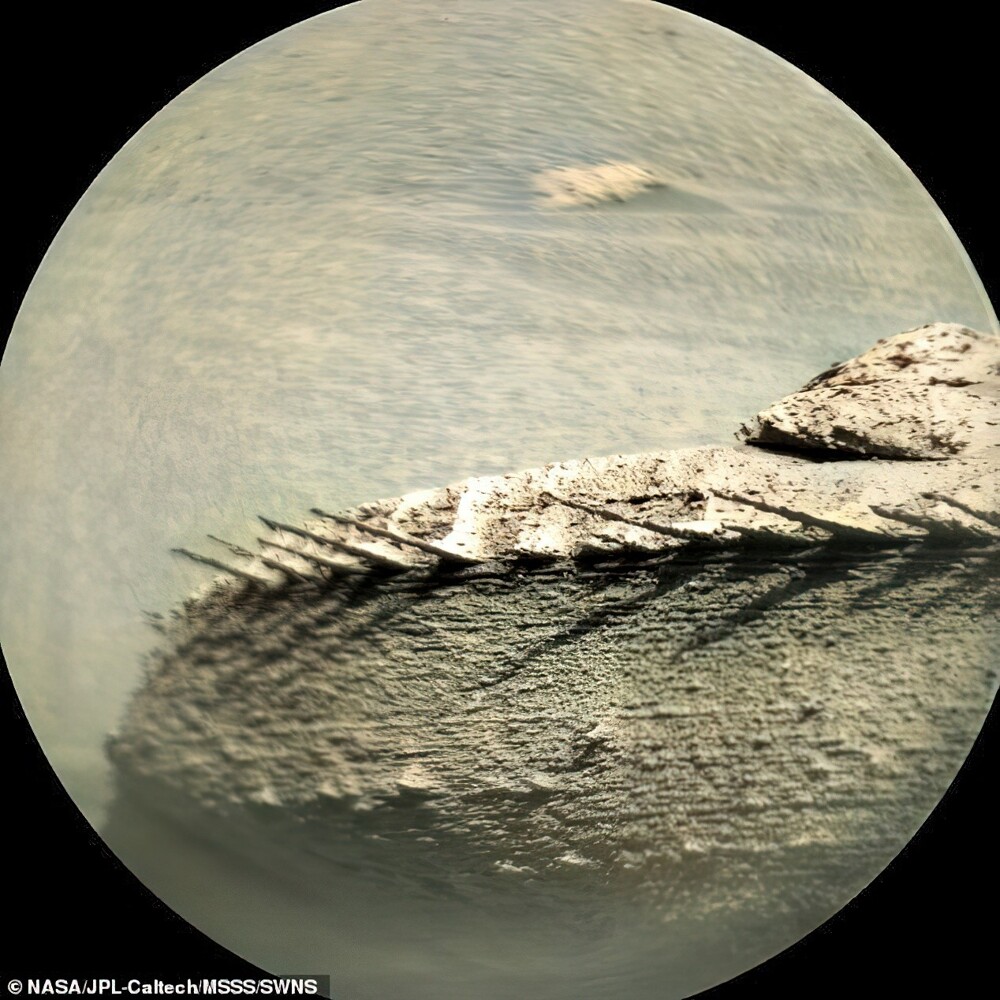
Astrobiologist Natalie Cabrol shared a photo of the find in Twitter, noting that in 20 years of studying Mars, this is the strangest stone she had ever seen. "I'm looking forward to detailed image of this object,” she added.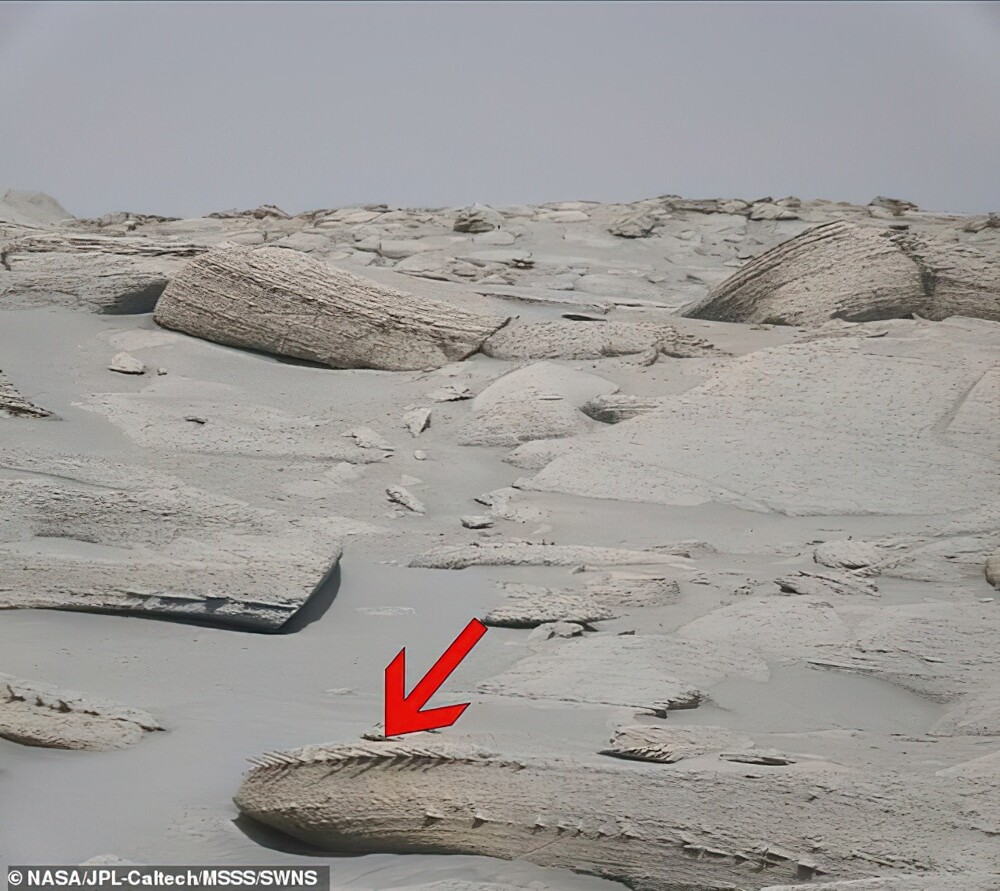 
So far, experts are inclined to believe that the strange formation is the result of severe erosion.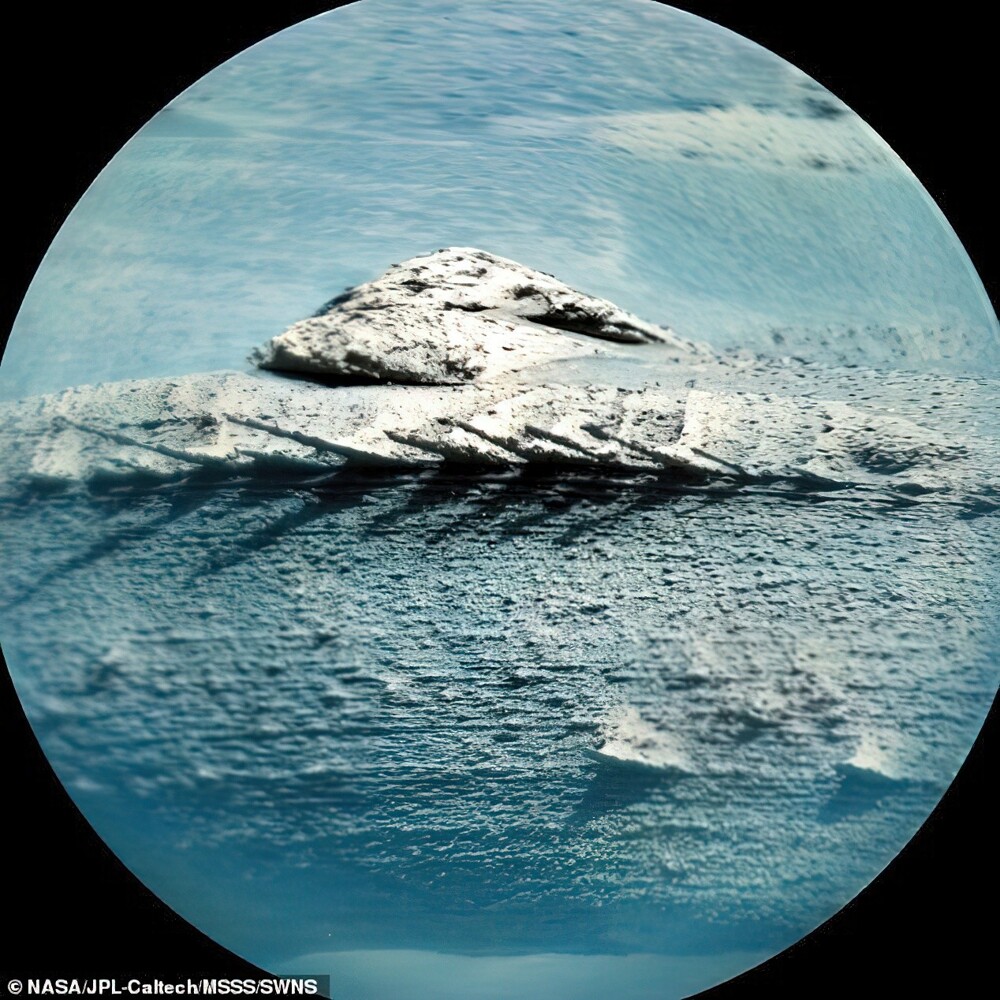 
Well, the rest build a variety of guesses, the most popular of which - the backbone of a fish, the skeleton of a fossilized Martian dragon or artificial object. 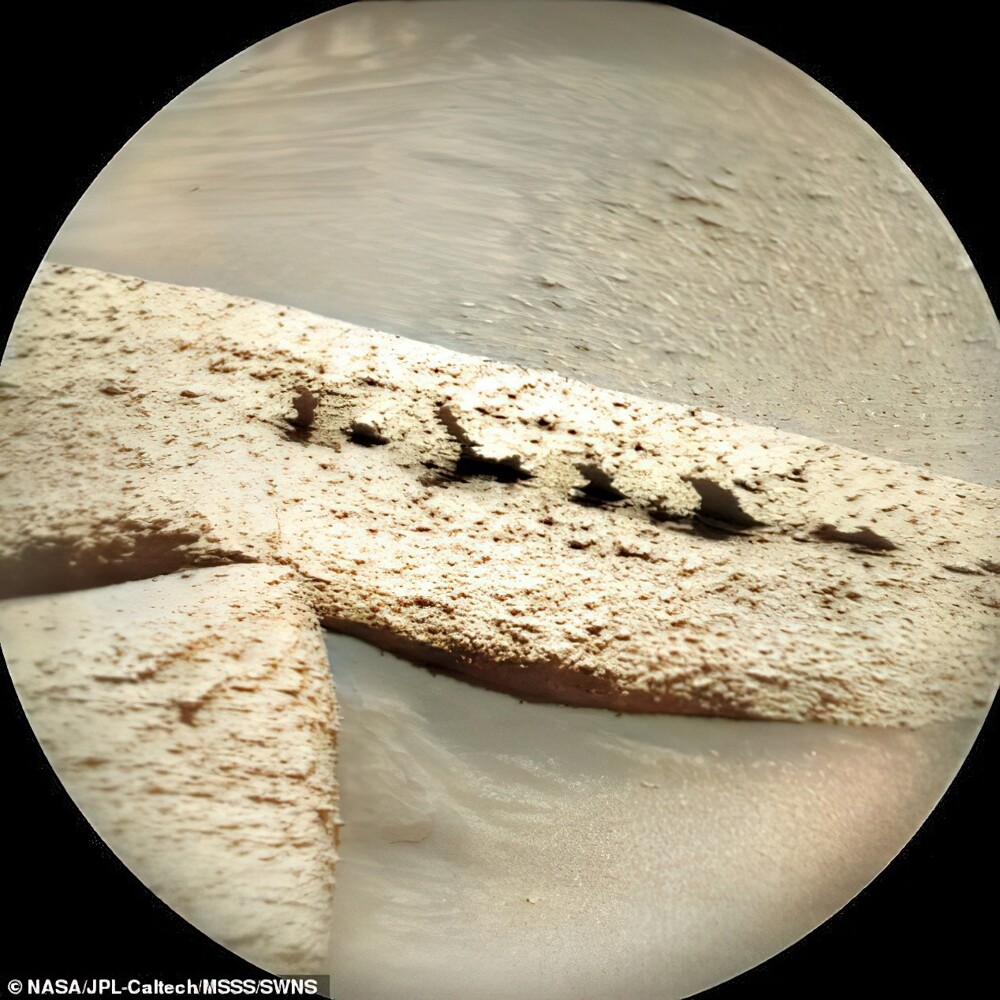
This isn't the first strange formation photographed by the Curiosity rover that has puzzled scientists.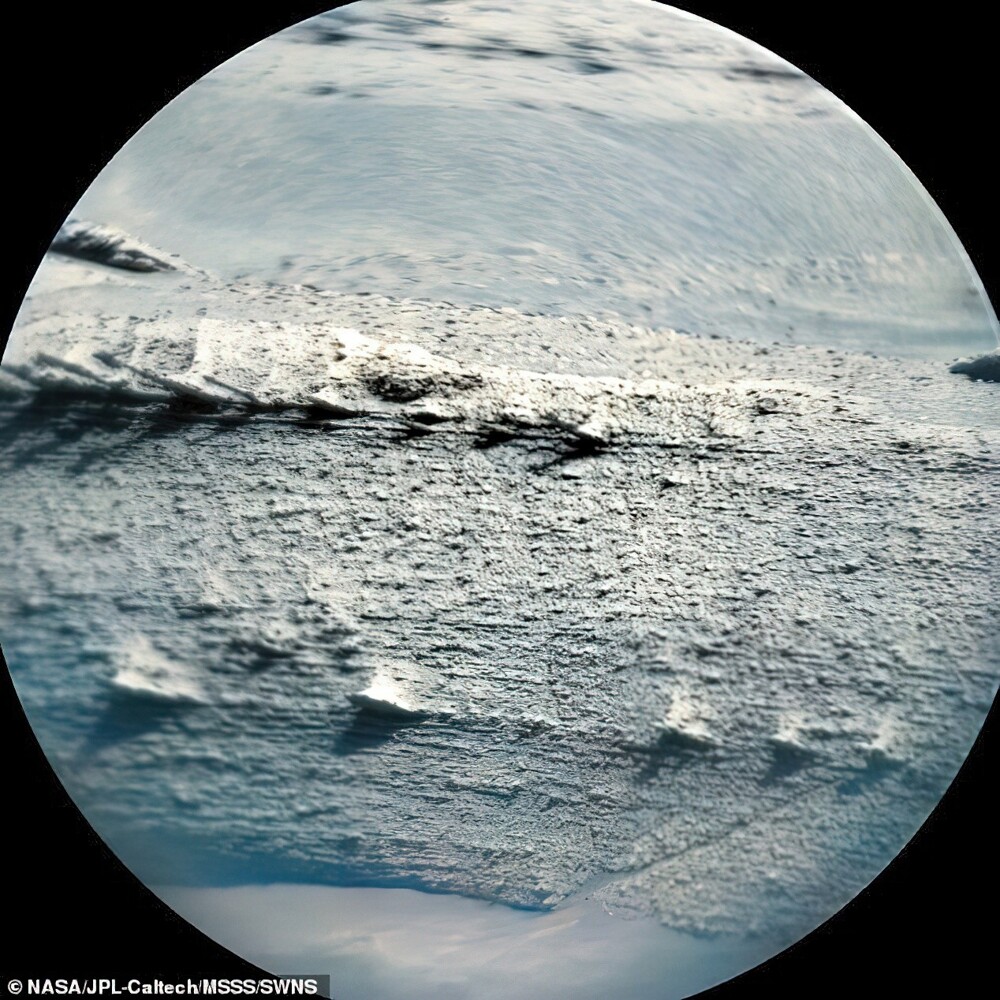 
Last June, he discovered several strange twisting structures sticking out of the surface of Mars.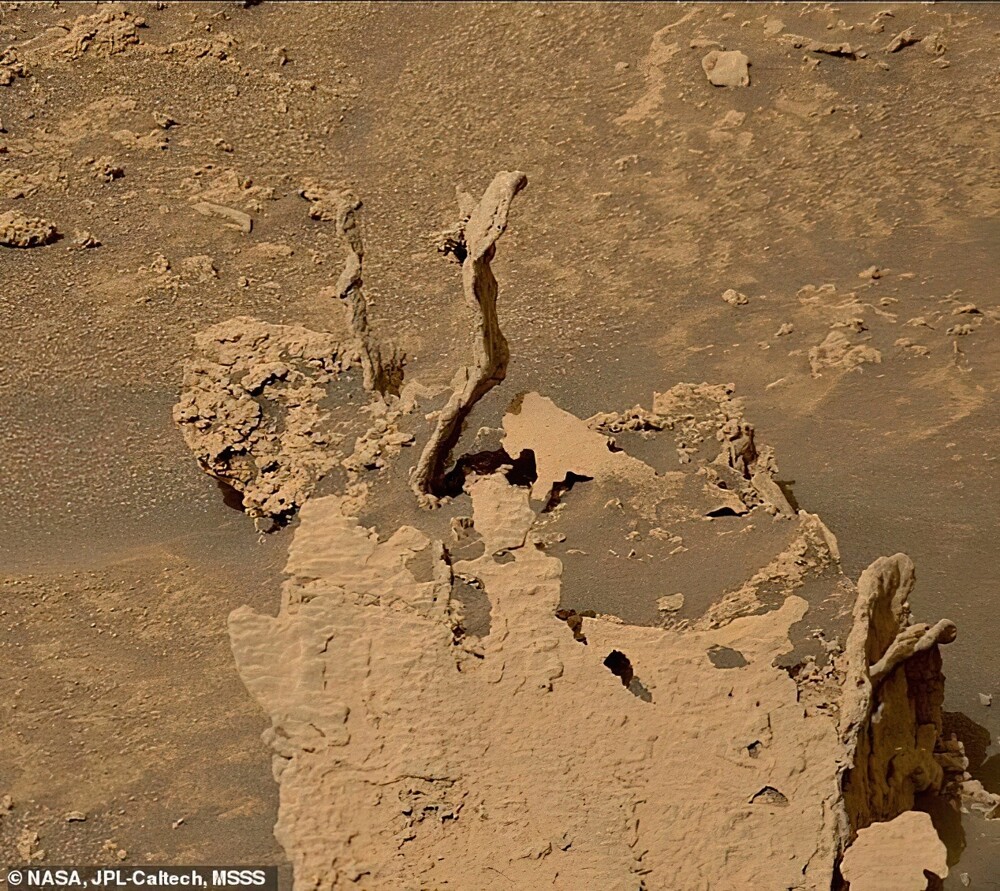 
Experts say the columns were probably created from cement-like substances that once filled ancient cracks in martian breed.
But over time, the softer rock eroded away, leaving only winding towers of dense material sticking out of the sand in the crater.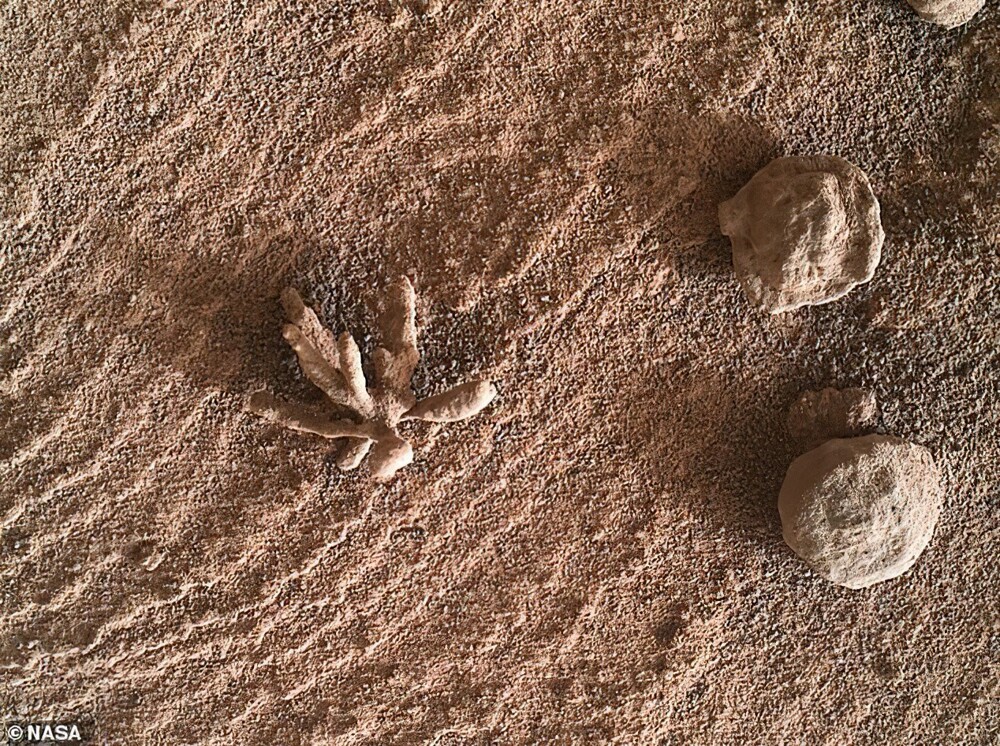 
In February 2022, the rover took a picture of what seemed like a coral "flower" in Gale Crater, but in fact was a microscopic mineral formation. Scientists confirmed that this is a miniature cluster of crystals, which could be formed by minerals that precipitate from water.
Studies have shown that minerals growing in different directions were probably built into the rock, which over time collapsed. However, it appears that these minerals were resistant to erosion, therefore, they remained on the dusty surface of the Red Planet.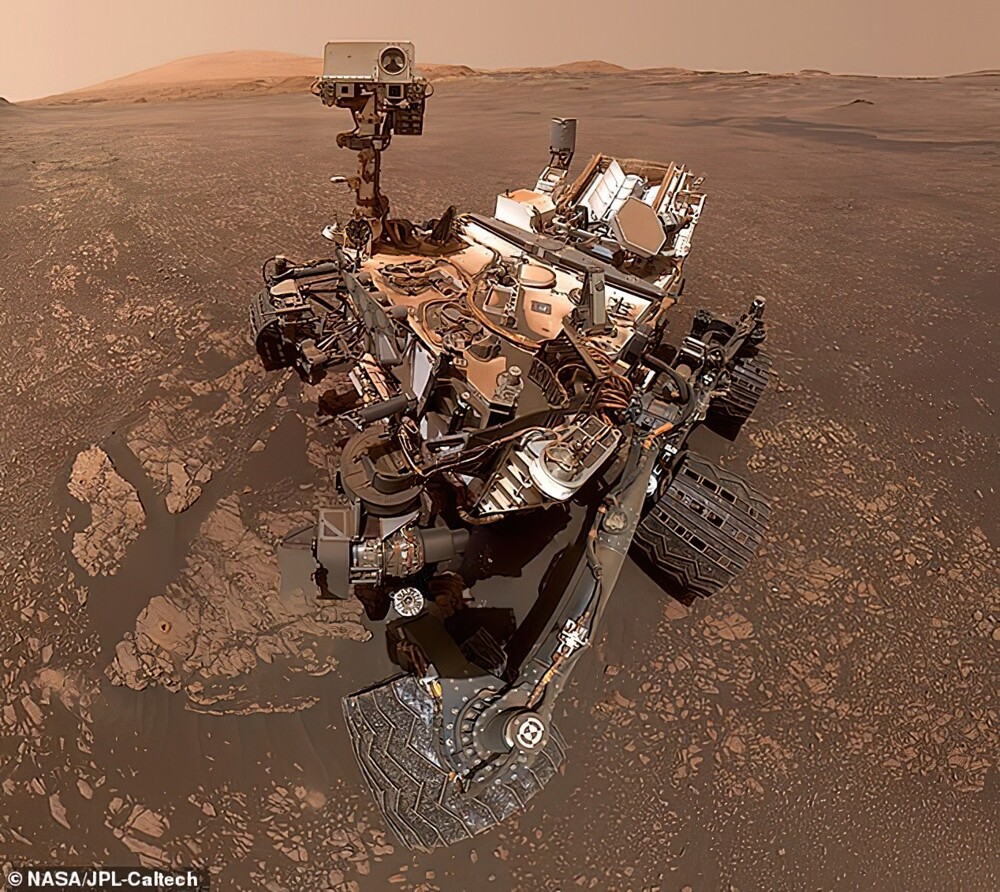 
The Curiosity rover has been on Mars for over 10 years. He traveled more than 29 kilometers, climbed to a height of more than 625 meters, exploring Gale Crater and the foothills of Mount Sharp within it. Apparatus analyzed about 40 rock and soil samples. rover also studied the sky of the Red Planet, taking pictures of glowing clouds and drifting moons, and measured the radiation with a special sensor. He manages with its task so successfully that it was planned for two years the mission was extended indefinitely.
But most importantly, Curiosity determined that liquid water, and See also the chemical building blocks and nutrients needed to sustain life, were in Gale Crater for at least tens of millions of years.