How strong can an earthquake be? (4 photos)
The amount of energy released during an earthquake depends on on the degree of destruction of the earth's crust. The good news is that for our age we are unlikely to see the incredible magnitude of 10.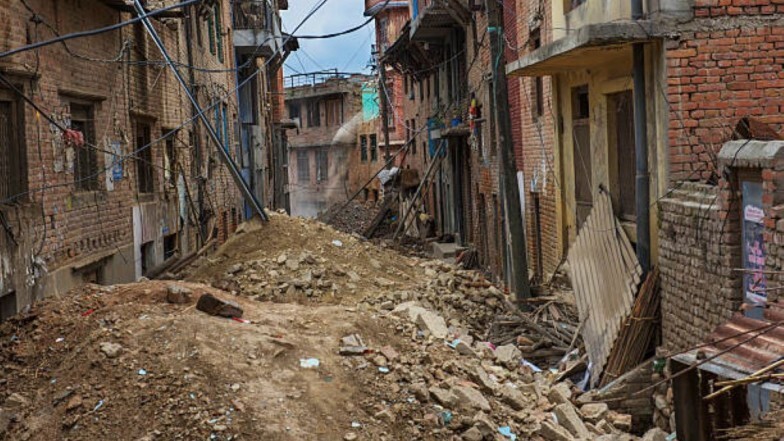 
May 22, 1960 in southern Chile happened destructive earthquake. Within 10 minutes the earth was shaking so hard that people could not stand on their feet. Cracks formed on the roads, and buildings collapsed one after another. One of the eyewitnesses who survived the earthquake and the tsunami that followed, decided that day that The Cold War escalated into nuclear Armageddon.
The Valdivia earthquake named after the city closest to its epicenter had a magnitude of approximately 9.5 points and became the strongest ever recorded for the whole history. But can earthquakes get even stronger?
earth power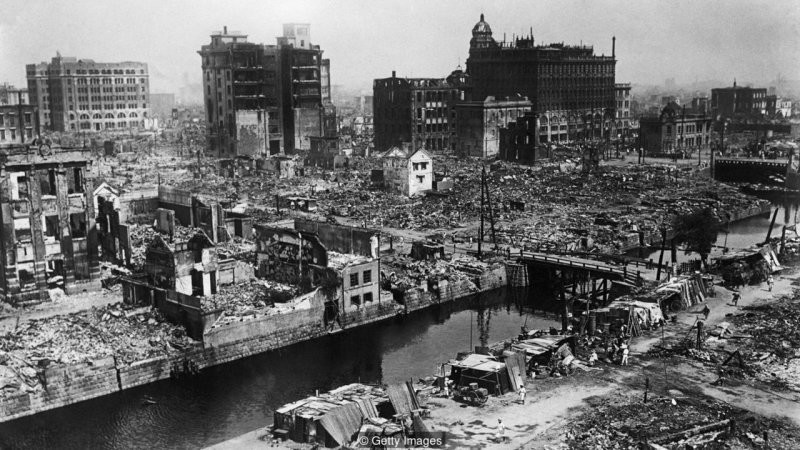 
Geologists say the answer is yes. Nevertheless the chances of a much larger earthquake are slim. Although underground points with a magnitude of more than 9.5 points may well occur and in our time, for the simultaneous destruction of a huge piece the earth's crust will require the movement of a fault as an emergency depth as well as extraordinary length. Not so on Earth there are many places where such a catastrophe is possible - at least so says Wendy Bohon, an earthquake geologist. She says that a magnitude 9.5 earthquake is likely near the upper limit what a planet can produce, and magnitude 10 is extremely unlikely.
Magnitude is a measure of the amount of energy released during an earthquake. It is slightly different from how an earthquake is felt strong, which can be affected by distance from the epicenter (to the observer, that is, to the person) and the condition of the earth itself. According to Bohon, the same the earthquake will be felt stronger for those who stand on loose soil and sand than for one who stands on solid rock.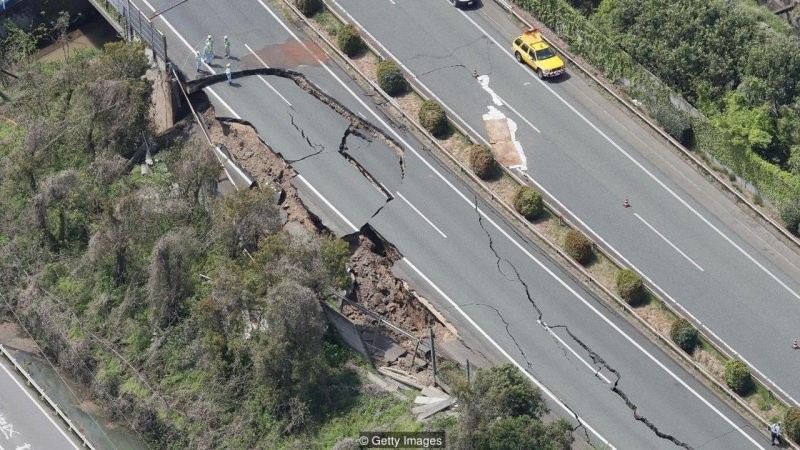 
The magnitude of an earthquake depends on the total area gap. It, in turn, depends on how the fault goes deep into the earth's crust and how long horizontally the segment that is being torn. There are physical limits on how large an area can collapse in progress. The deepest faults are in zones subduction, where one tectonic plate pushes another. If penetrate deep enough into the crust, then the rock turns into a hot and sticky melt; instead of break, rock masses will bend. Although earthquakes can sometimes occur at a depth of up to 800 kilometers below the Earth's surface, according to the US Geological Survey, most deep earthquakes do not produce large shaking on a surface; exactly those that are in the top ten kilometers of the earth's crust are the most dangerous for people.
The most dangerous earthquakes
According to Heidi Houston, earthquake geologist from the University of Southern California, faults, the most capable cause strong destructive earthquakes, these are inclined faults in subduction zones. They are so named because they are located at an oblique angle, and not vertically, and therefore have the most large areas of rocks that can get stuck in each other, accumulating tension and then finally collapsing.
“In fact, the size of the falling fault plane is the biggest factor determining the maximum size of an earthquake, and fault planes can be increased in zone settings subduction,” Houston said.
But there are also restrictions on segment length malfunctions that may break. According to Bohon, even subduction zone faults do not break immediately. Usually something interferes - possibly a seamount, a change in rock type or geometry rocks, due to which one segment of the fault is more resistant to loads, than the neighboring one.
Houston added that another factor influencing per earthquake magnitude is how strong the fault shifts or shifts. Typically smaller areas of collapse slip less than larger ones. Thus, at that time how a magnitude 5 earthquake can 'slip' a few centimeters - a distance that is unlikely to destroy ground higher, then a magnitude 9 earthquake could move 20 meters or more. So, the earthquake in Chile in 1960 year actually increased the territory of the country due to how stretched the earth itself!
Understanding the magnitude
An earthquake's magnitude scale can inadvertently hide the difference betweenDo very strong shocks. The scale is not linear, but logarithmic: per unit increase, ground movement increases by 10 times, and the released energy increases 32 times. Bohon likes to use the metaphor of breaking a pack. spaghetti. Breaking one stick of spaghetti is equivalent to magnitude 5 earthquake, you will have to break 32 pasta to release earthquake energy by force 6 points - that is, just a point higher. According to this "scale spaghetti "value 7 corresponds to the gap of 1024 sticks, the value 8 corresponds to 32,768 sticks, and the value 9 corresponds to an incredible 1,048,576 sticks! 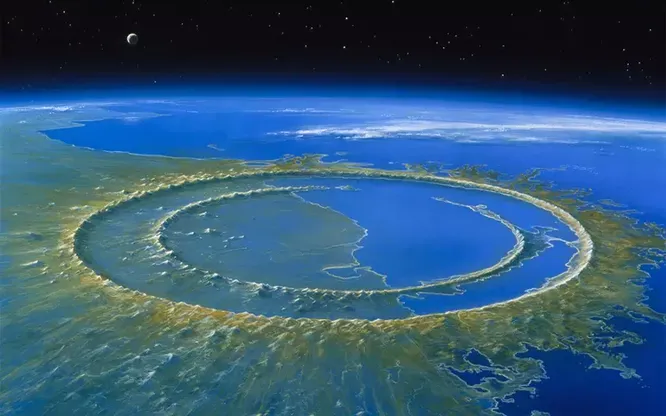
Chicxulub Crater is an impact crater believed to have been caused by a meteorite impact 66 million years ago.
There are, of course, planetary catastrophes, which theoretically can lead to much stronger earthquakes: for example, collision with an asteroid. Some scientists believe that the impact an asteroid at the end of the Cretaceous that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago, caused double-digit earthquakes magnitudes, although to accurately determine its power in our days is almost impossible. On a time scale (and for our planet this is billions of years) the Earth could certainly witness such disasters. But the chances that in the course of a human life something more than 9 on the Richter scale will happen, very small. According to 2022 research, the largest ancient an earthquake that was estimated based on geological data, also happened in Chile about 3800 years ago and probably also had a magnitude of about 9.5.
The Real Threat
Area or power is not always the most important factor in how deadly a disaster will be - at least not for humans. Small earthquakes caused many deaths simply because they hit populated areas and areas with buildings prone to collapse. While how a magnitude 9.5 earthquake in Chile claimed the lives of about 2000 people, it is believed that an earthquake with an estimated magnitude 8 claimed the lives of about 830,000 people in Shaanxi, China, in 1556. And in 2010, as a result An earthquake of magnitude 7.0 in Haiti killed about 220,000 Human. Even the Northridge earthquake in 1994, with a magnitude of only 6.7, which was due to a fault, which earlier no one even noticed, claimed the lives of 57 people, injured thousands and caused billions of dollars in damage because it affected Los Angeles.
"So many potential faults could lead to destructive earthquakes,” Bohon said. - but people think only of the biggest catastrophes when fearing in fact, we need sets of local ones.