An iceberg the size of London broke off the Antarctic shelf (7 photos + 1 video)
A huge iceberg the size of Greater London has broken off Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica. Now it's starting to fall apart into smaller pieces and, as experts warn, can cause damage transport courts.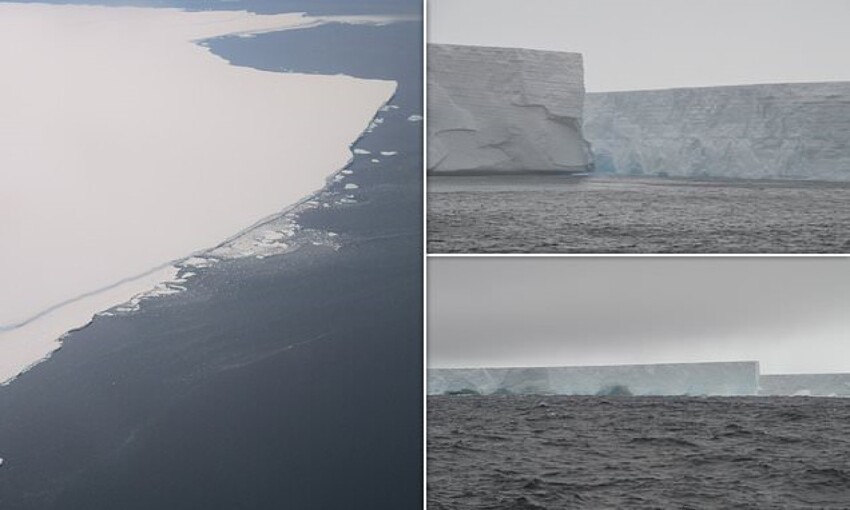 
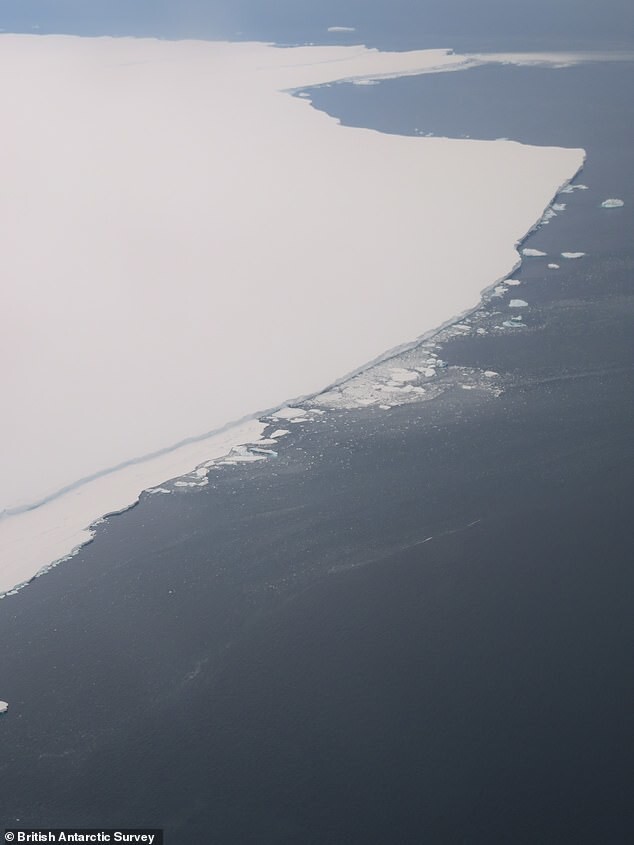

Scientists observe two of the world's largest icebergs including one size for Greater London and another size for Cornwall, which broke away from the shelf of Antarctica. Experts have fears that frozen giants are drifting into areas where they can adversely affect shipping, fisheries and wildlife.
A huge iceberg, the size of the capital of England, broke away from Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica at the end of January and only quite was recently photographed from the air.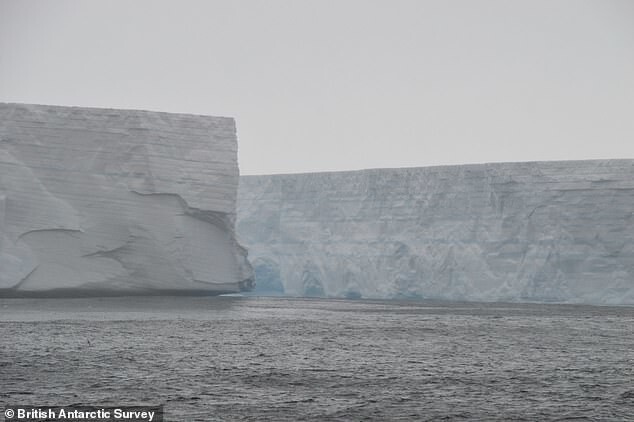 
Glaciologist Dr. Oliver Marsh, who returned from Halley Research Station, British Antarctic Survey, stated:
“We knew that this iceberg would break off soon. Our the station monitors the Brunt Ice Shelf and breaking off from it icebergs for more than a decade."
“Glaciologists first noticed the beginning of the breaking off of the iceberg back in 2012, Marsh says. - We were looking forward to this event. To monitor the expansion of the split, high-precision GPS tools; and satellite data. In 2016, BAS adopted precautions by moving Halley's research station inland to protect her."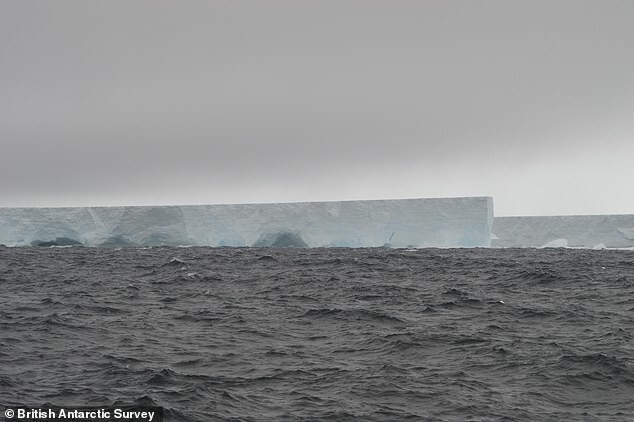 
A team of British explorers even made a swim around iceberg A76A, part of iceberg A76 that broke off offshore Filchner-Ronne glacier in mid-May 2021. On the way north A76 fell apart into three parts, the largest of which is called A76A and It is shaped like a giant ironing board. Its dimensions are 135 km long and 25 km wide. This is the largest floating iceberg on the planet as big as the English county of Cornwall. Now he is moving to direction between the Falkland Islands and South Georgia. Eat fears that it might move east towards South Georgia and get stuck in the shallow waters of the continental shelf, or possibly head to the nearby islets known as Shag Rocks. In both these areas, its appearance can cause problems for local wildlife nature and people.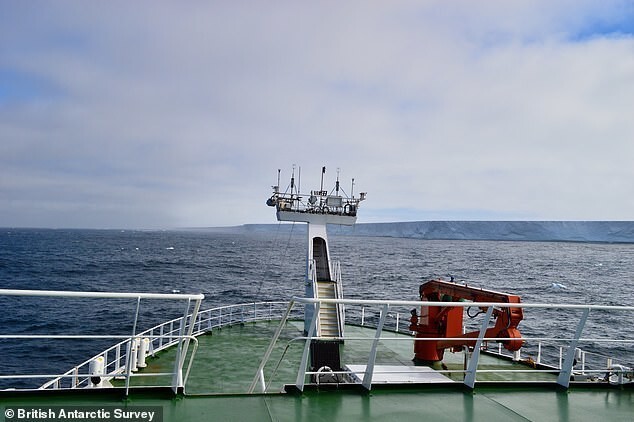 
If an iceberg gets stuck in shallow water in this region, it can destroy the fauna on the seabed and disrupt ocean currents and feeding routes for local wildlife.
In addition to the environmental impact, icebergs in the area South Georgia can pose a great danger to local courts. 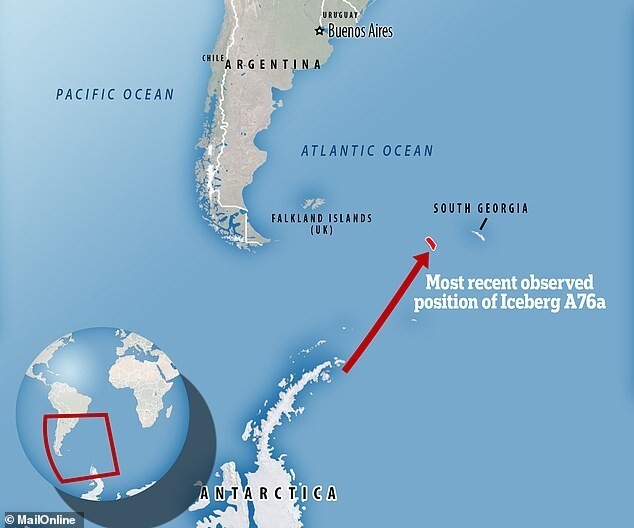
Huge icebergs can take decades to melt and disappear, so for a while they will represent potential threat.
Iceberg A81 the size of Greater London has broken off the shelf, when a large crack in the ice went through the entire ice shelf. He headed south and is now sailing about 150 km from the place of separation. 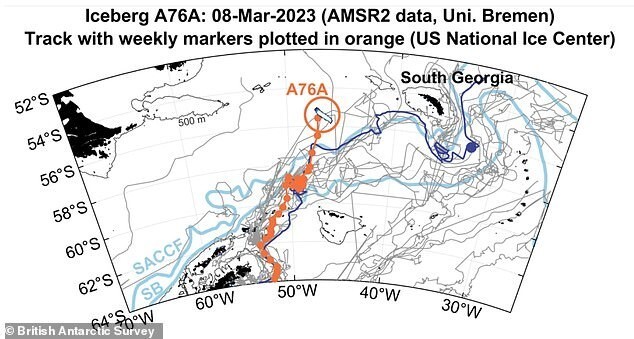
The Brunt Ice Shelf is one of the most carefully observed ice shelves on the planet. It is here that British research station Halley.
British scientists are now saying that the research station and the territory adjacent to it are practically not hit by an iceberg break.
A81 is the second major iceberg in the region in two years. It is expected to follow in the footsteps of previous icebergs blown strong Antarctic coastal current to the west.
In January, a team of BAS scientists aboard the science vessel Discovery rounded part of it - iceberg A76A. Researchers took water samples around the iceberg to better understand its potential impact on environment.
Professor Geraint Tarling, Head of the BAS Ecosystems Group, was on board the Discovery. Here is what he said:
"Iceberg of this size would have a major impact on ocean ecosystems that maintain a rich diversity of marine life in this Antarctic region. This impact can be both positive, as well as negative. On the one hand, as the iceberg melts vysvExpect many nutrients that can help the growth of microscopic plants such as phytoplankton lying in basis of ocean food chains. The negative side is that this same melting on such a large scale dumps into the ocean plenty of fresh water, which reduces salinity and makes the water unsuitable for many species of phytoplankton and zooplankton that they eats. These effects can then spread down the food chain to fish, birds, seals and whales. In addition, if the A76A continues on trajectories to the rocks Step, disturbance of the shallow seabed can have catastrophic consequences for diverse biocommunities seabed, including in areas where valuable species of fish feed.