The most cruel and strange experiments on people in the history of mankind (19 photos)
There are cases in history when "in the name of science" experiments on people. These physical or psychological experiences could be cruel, illegal, unethical and just plain weird, but the researchers who conducted them believed that the goal justified facilities. 
1. Trade in a tea shop: a study of homosexual encounters in public places 
In the 1960s, sociologist Lod Humphreys pioneered a study called Tearoom Trade, in which focused on men who entered into an anonymous sexual intercourse with other men in public toilets (“tea rooms" in American gay slang).
Through observation and interviews, he sought to explore the social dynamics of this environment and the motives of its participants. Humphreys disguised as a voyeur, tracked test subjects on car numbers, interrogated them under the guise of a health officer. Today, his work is often cited as an example of unethical social research.
2. Malaria Study in Stateville Penitentiaries 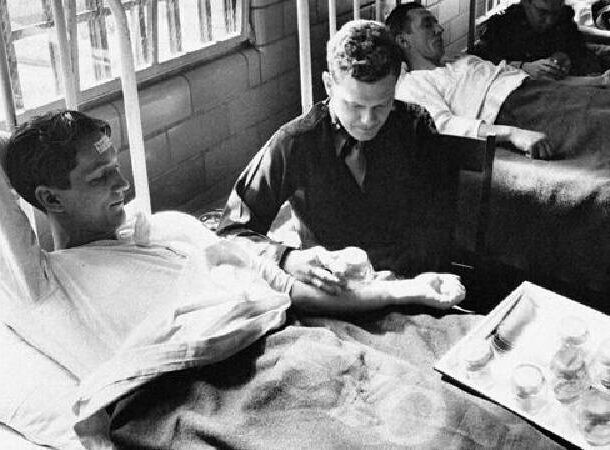
Malaria research in prisons Stateville, held in the 1940s, is one of the most controversial research in history. It took place in jail. "Stateville" in Illinois (USA) and was sent to test the impact malaria on prisoners by deliberately infecting them with malarial parasite.
The infected people were then injected with various drugs and measured their effectiveness in treating infection. The experiment expanded understanding of the mechanisms of malaria and methods of its treatment. However, the study caused a lot of debate on the subject of ethics.
3. Operation ARTICHOKE 
Operation ARTICHOKE, a CIA-led program was carried out from 1951 to 1961 and was aimed at research the use of hypnosis and other forms of psychological manipulation in intelligence gathering.
This program was part of the larger MKUltra project, initiated by the CIA to study the effects of psychological manipulation on people. Operation ARTICHOKE was aimed at evaluating the effectiveness hypnosis and other psychological methods in obtaining information from interrogated persons. The researchers also tried to understand how to use hypnosis to change the memory or behavior of the person involved in covert operations. The program has generated controversy over ethics and in was eventually discontinued.
4Monster Study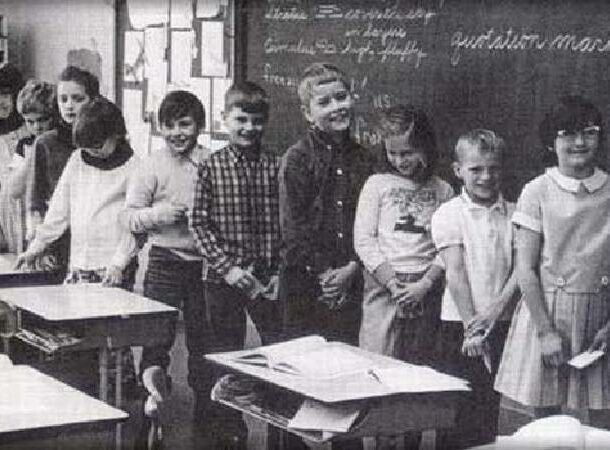 
In 1939, Wendell Johnson, a psychologist at the University of Iowa, conducted a psychological experiment called "The Monstrous experiment". Its purpose was to study the influence of value judgments on fluency in children.
22 subjects participated (children from an orphanage), randomly divided into two groups. children from the same group encouraged and praised for their ability to read and speak, and children from another groups were ridiculed and heavily criticized. As a result, some healthy children from the second group developed signs of stuttering.
The experiment was deemed unethical due to the psychological the injury he inflicted on these children and the lack of consent of their guardians or legal representatives.
5 Operation Midnight Climax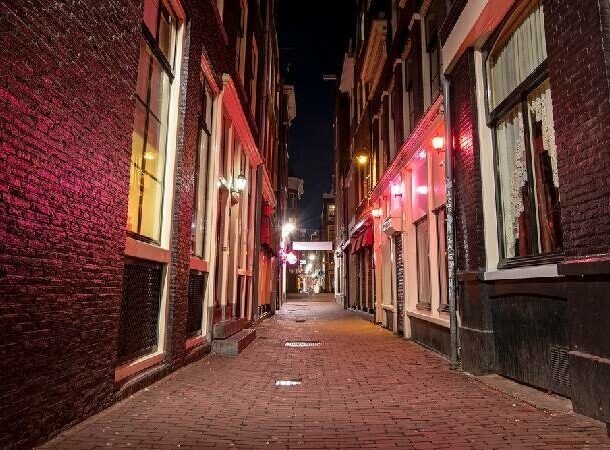 
Operation Midnight Climax was a covert CIA program carried out in the 1950s and 1960s as part of a larger project MKUltra. Agents set up safe houses in San Francisco and New York, where they lured nothing with the help of prostitutes suspicious men.
In a safe house, they were quietly injected hallucinogenic drugs such as LSD to observe and document the effect of these substances on behavior. This unethical the experiment continued until it was made public in the 1970s years, which led to its termination. During the years of this studies have tested many psychedelics on hundreds of nothing suspicious people.
6The Stanford Prison Experiment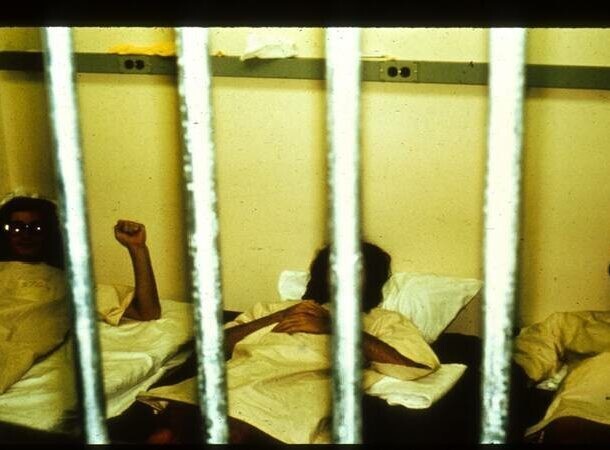 
This is a psychological experiment conducted in 1971 in Stanfordscom University in California. He was sent to study psychological impact of power and authority on people through reproduction of the prison environment. 24 male participants were arbitrarily appointed as either prisoners or guards, and placed in simulated prison environment for two weeks.
However, the experiment had to be terminated early due to severe psychological stress of the participants and unethical behavior guards.
The experiment showed that people begin to behave according to social roles and expectations, even if these roles offensive and harmful. The experiment is considered a classic example the dangers of obedience and conformity.
7. Project "Aversion" 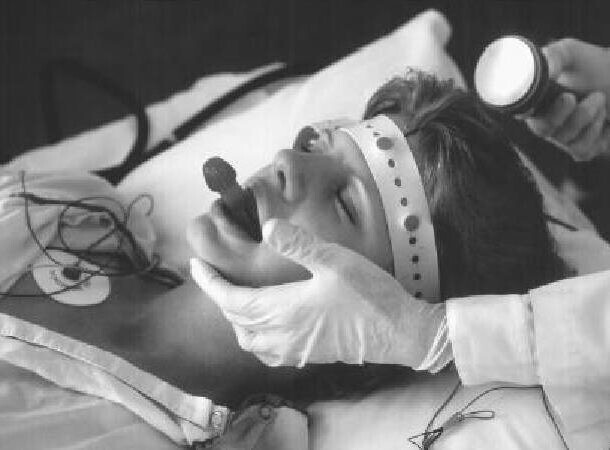
In the period from 1970 to 1989, a secret a program to purge the army of non-heterosexual soldiers. The project was a series of experiments led by a psychiatrist Aubrey Levin. These experiments, medical and psychiatric, were aimed at "treatment" of homosexuality of men and women in the South African army. The methods used in this experiment are today considered medical torture. Hormonal preparations, stun guns, chemical castration, gender reassignment surgery.
8. Experiments on people in Guatemala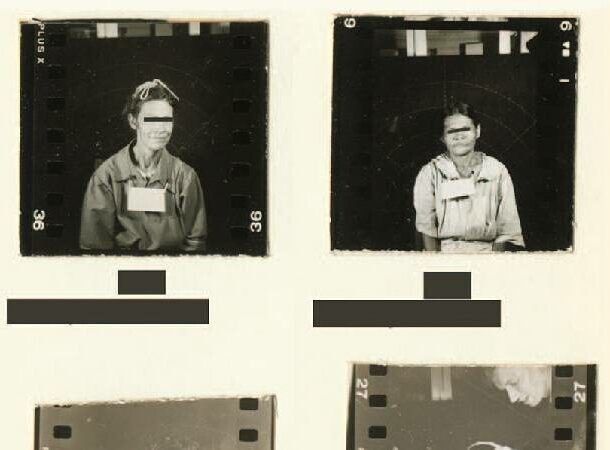 
The United States government has conducted medical experiments with sexually transmitted syphilis in Guatemala in 1940s. Subjects were intentionally infected without their knowledge or consent, and then tested the effectiveness of penicillin in the treatment. Experiments continued ten years, from 1946 to 1956, about 1.5 thousand people were infected, 83 test subjects have died.
9. Study of the effect of radiation on the testicles 
University of Washington on behalf of the US government conducted a series of experiments to test the effects of radiation on American prisoners in the 1960s and 70s. Impact test radiation on a person is unethical and illegal, because it harms the living organisms.
10 Milgram Experiments 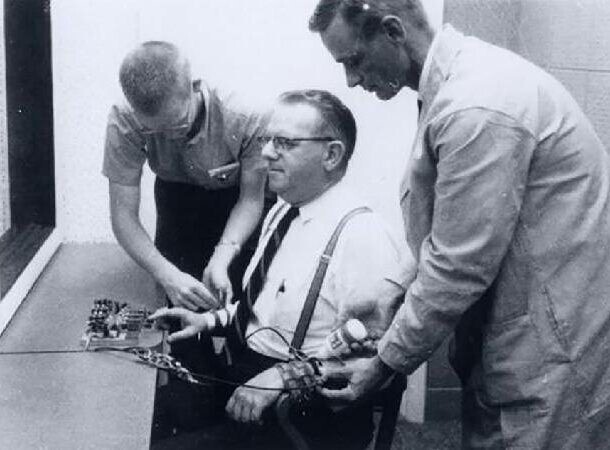
This is a series of experiments in the field of social psychology, conducted by Yale University psychologist Stanley Milgram in the 1960s years. Experiments were designed to test how far people will enter, obeying an authority figure, a leader who induces them to commit acts contrary to their conscience.
Some members were convinced that they would hit others electric current. They didn't know the electric shocks were fake, but, believing they were real, some of the participants were willing to apply these electric shocks to other people.
11. Detachment 731 
Detachment 731 was a biological and chemical weapons of the Imperial Japanese Army. Subdivision conducted experiments on humans during World War II and is responsible for some of the worst war crimes committed by Japan. Unit 731 conducted experiments on living prisoners, including Chinese, Korean, Russian and Mongolian civilians, and also by prisoners of war, for the development and testing of biological and chemical weapons.
The full scale of the atrocities committed by Unit 731 is not yet fully understood. known, but it is estimated that thousands of people were killed and subjected to cruel treatment.
12. Electric shock on children 
Dr. Lauretta Bender worked at a New York hospital Bellevue from 1942 to 1955. She performed electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or electroshock therapy to hundreds of infants and children aged three up to twelve years old.
ECT is a psychiatric treatment in which brain stimulation uses electrical currents, and it can be use to treat severe depression, bipolar disorder, and catatonia. While this form of therapy is known to be effective for some people, its use, particularly in children, is controversial. character and is considered unethical.
13. Infection of mentally retarded children with hepatitis 
In Staten Island, New York, a public school Willowbrook was a publicly funded institution for children with limited intellectual abilities. In the early 70s, the institution fell into disrepair. Reports and investigations have shown that it was overcrowded, unhygienic and lacking qualified personnel, which created conditions equivalent to inhuman treatment.
Strikingly, the reports showed that the staff of the institution deliberately infected children with hepatitis as part of an experiment to study the impact of the virus. This has led to numerous lawsuits and further investigations, which eventually ended closing the school in 1987.
14. Nazi experiments 
During World War II, the Nazis carried out brutal experiments on concentration camp prisoners. People were frozen, subjected experiments at high altitude, they tested the effects of chemical and biological products, and much more.
Those responsible for these inhuman experiments were later put on trial for war crimes.
15. Experiment with TGN1412 
In 2006, an immunomodulatory drug was tested drug TGN1412 to evaluate its effectiveness in the treatment of various autoimmune diseases and leukemia.
During the study, the drug was administered to six healthy volunteers, but in all of them he unexpectedly caused an acute systemic inflammatory response and multiple organ failure.
This has led to life-threatening conditions that demanded emergency medical attention and immediate cessation tests. Fortunately, thanks to prompt medical intervention the volunteers were able to recover without any long-term consequences.
16. Mustard gas test on soldiers 
Mustard gas (mustard gas) is a chemical warfare agent used during the First and Second World Wars. It calls severe irritation of the skin, eyes and respiratory tract and the formation of blisters. During World War I, mustard gas was tested on US soldiers to evaluate its effectiveness as a weapon.
Needless to say, soldiers exposed to mustard gas, often suffered serious injuries and long-term health consequences. No doubt these unfortunates had no idea what consequences await them.
17. Release of infected mosquitoes 
In the 1950s, the US Army released millions of mosquitoes, infected with dengue and yellow fever, in Avon Park, Florida, and Savannah, Georgia. This was done in order to check whether mosquitoes act as bioweapons by spreading contagious diseases.
Needless to say, as a result of the experiment, many people got sick and some died.
18. Radioactive pregnancy pills 
In a study conducted at the University Vanderbilt in the 1940s, pregnant women were given radioactive pills at the university's free prenatal clinic.
This experiment was carried out in the context of trials, conducted on humans to determine the effects of nuclear explosions and other types of radioactive exposure to people during the Cold War, following World War II.





















