25 almost unbelievable facts about the Milky Way (26 photos)
If you raise your head up on a starry night, you will see a myriad stars, and each of them will belong to our galaxy - the Milky Ways. The Milky Way is incredibly huge and just as amazing. Let's let's learn more about it!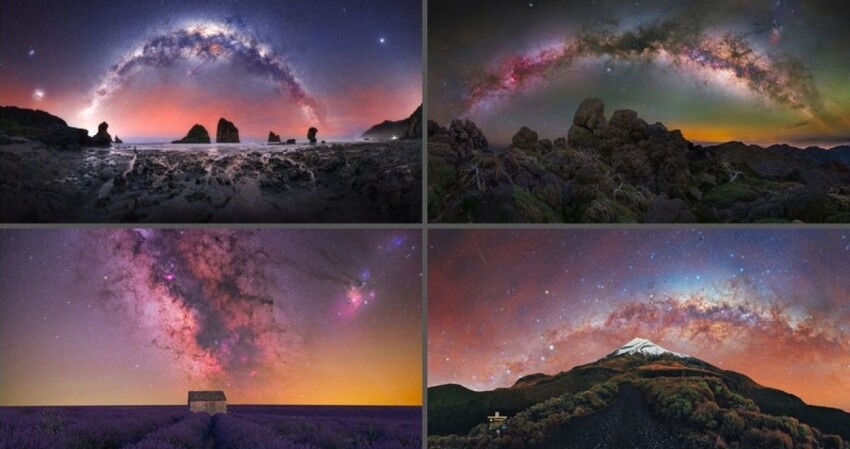 
The Milky Way is as old as the universe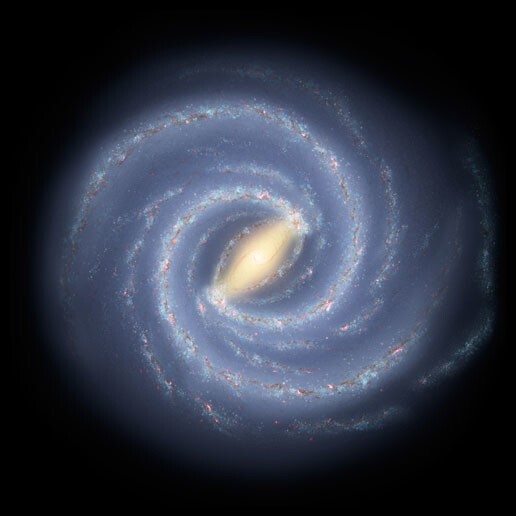 
Scientists believe that the Milky Way is one of the oldest galaxies in the universe. It formed about 13.6 billion years ago and almost as old as the universe itself, having formed around 13.7 billion years ago.
The Milky Way got its name a long time ago
According to Greek mythology, the Milky Way was created when Hera spilled her milk while breastfeeding Hercules. He was also described as the road to Mount Olympus or the path laid across the sky by a chariot Helios-sun.
The Milky Way is made up of other galaxies 
To reach their current size and shape, Throughout its history, the Milky Way has engulfed other galaxies. And in our galaxy is currently engulfing the dwarf galaxy of the Greater Psa, adding her stars to her own spiral.
A place of gigantic speeds 
Our solar system revolves around the center of the galaxy. a speed of about 827,000 km/ h. To understand what they really mean these numbers, and imagine: an object moving at that speed can circumnavigate the Earth's equator in less than three minutes.
Dust and gas 
The Milky Way is full of dust and gas. They make up 10-15% luminous visible matter in our galaxy, and the rest is stars. Our galaxy is about 100,000 light-years across. we can only see 6,000 light-years deep into the disk in the visible spectrum. However, when the light pollution is low, at night the sky can be seen dusty ring of the Milky Way.
Myriads of stars 
Even astronomers argue about how to calculate the number of stars in Milky Way. Modern telescopes can only see the brightest stars in the our galaxy, many of them are obscured by shading gas and dust. However, In addition to the visible ones, there are billions of invisible stars in the Milky Way. AND when we look at the Milky Way at night, we only see about 0.0000025% of the hundreds of billions of stars in the galaxy.
Red dwarfs are the most common 
The most common stars in our galaxy are red dwarfs. A red dwarf is a cold star which is one tenth of the mass of the Sun. red dwarfs still recently considered unsuitable for development of potentially suitable for life of planets, but now scientists believe that they can revolve and such planets.
Place of supernovae 
The Milky Way regularly loses stars due to explosions supernovae - moments when, at the end of a star's life cycle, a big explosion that takes away almost all of its mass.
different energies 
Visible light is only one form of energy. Our the galaxy is also made up of other types of energy such as infrared light, radio waves, gamma rays, dark matter and x-rays.
dark halo 
The Milky Way is surrounded by a halo of dark matter, which makes up more than 90% of its mass. This means that all we can see, even through telescopes, is less than 10% of the mass of our galaxy. The rest is darkness.
giant bubbles 
Recent observations of the center of the galaxy have allowed discover several giant bubbles at the center of the Milky Way, which emit radio waves. The bubbles are pulled outward from the black hole and into space in opposite directions. These bubbles look like two halves of an hourglass with a black hole at the "waist".
Mankind is new to the galaxy 
The sun and our solar system since its inception about 4.6 billion years ago, they orbited the galaxy in less than 20 once. However, since the advent of man
only 1/1250 of a revolution has been completed.
magellanic clouds 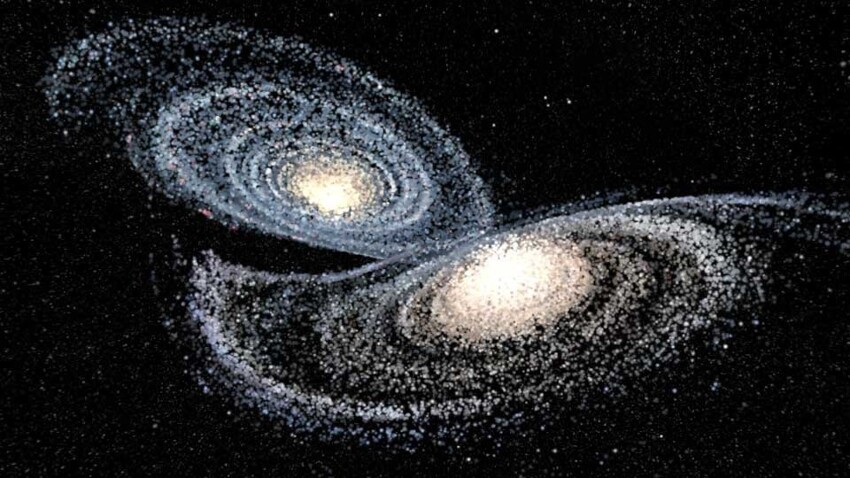
When the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan sailed to XVI century on the southern seas, he and his team are among the first Europeans reported round clusters of stars in the night sky.
These clusters are small galaxies that revolve around our Milky Way, just like the planets revolve around the star. Therefore, astronomers decided to call them Small and Large Magellanic Clouds in honor of Ferdinand Magellan.
Galaxy movement 
The Milky Way, like everything else in the universe, is moving in space. The earth moves around the sun, the sun moves around the milky way, and the Milky Way moves as part of the local group of galaxies. local the group, in turn, moves relative to the space microwave background radiation, also known as radiation, leftover from the Big Bang.
The Milky Way is full of toxic greasy dirt 
In the empty space between the stars of our galaxy a pile of dirty fat is spinning. Oily organic molecules aliphatic carbon compounds are produced in certain types stars and then seep into interstellar space.
Not so fat
If the Milky Way were reduced to the size of a frisbee, it would not be much thicker than a piece of paper.
Barred spiral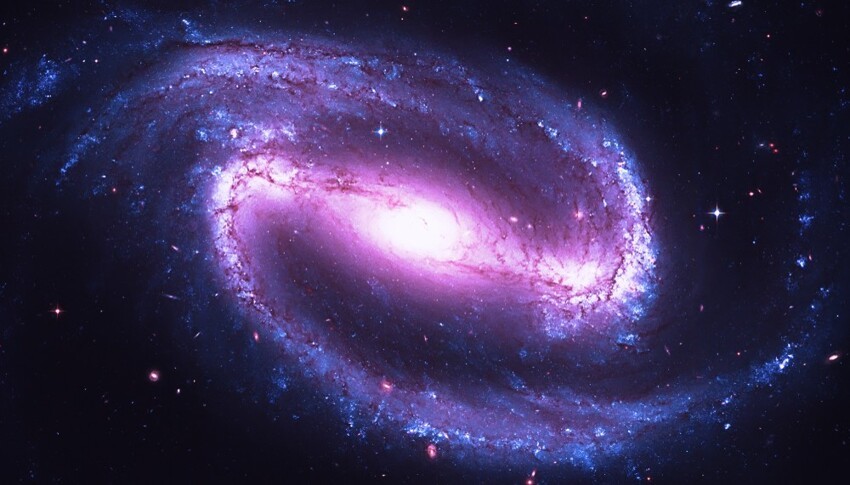 
Two-thirds of the galaxies in the known universe are spirals. Two-thirds of these spirals are barred. Since the Milky The path meets both of these criteria, it is one of the most common galaxy designs.
How much does a galaxy weigh? 
Astronomers still don't know exactly how much our galaxy. Estimates currently range from 700 billion to 2 trillion masses of our sun. Achieving a more accurate estimate is not easy task. Most of the mass of the Milky Way is perhaps 85 percent is in the form of dark matter, which is not emits light and is therefore inaccessible to traditional types of observations.
black hole in the center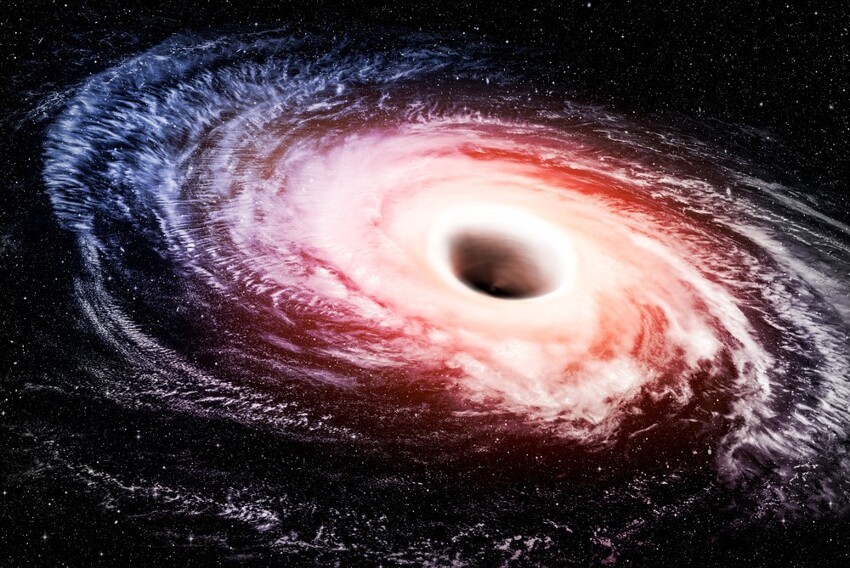 
At the very center of the Milky Way is a powerful gravitational a force that scientists believe is a black hole. They named her Sagittarius A. Astronomers believe that this black hole weighs as much as 4 a million of our suns combined.
From the Virgo Supercluster 
The Milky Way is part of an even larger galactic structures. Our nearest neighbors are Big and Small The Magellanic Clouds, as well as the Andromeda galaxy, are the closest to the Milky Spiral galaxy paths. Along with about 50 other galaxies The Milky Way and its immediate surroundings make up the local group galaxies, which, in turn, is part of an even larger clusters - the so-called Virgo supercluster.
Discovery of Democritus
The ancient Greek philosopher Democritus, who lived in 460 - 370. before AD, was the first to suggest that the Milky Way is made up of stars. Galileo Galileo (1564–1642) was the first to use his telescope in 1610 proved this assumption by seeing that the band of the Milky Way consists from many individual stars.
"Silver River" 
In China, the Milky Way is called the Silver River. IN Chinese myths say that the gods placed a river in the sky to to separate the weaver who wove their clothes from the shepherd who loved her.
Way of the dog
According to Cherokee legend, the Milky Way formed when the dog stole a bag of cornmeal. During the chase, the flour scattered on sky to form our galaxy. Thus, in Cherokee lore the galaxy is referred to as "The Way the Dog Escaped".
Just an inside look
img src="https://cn22.nevsedoma.com.ua/p/26/2636/142_files/e7b15666fe82f9409503772781652b00.jpg">
Any photo of the Milky Way from space that you ever seen is either a photograph of another galaxy, or piece of art. Since we are inside the galaxy, we just not being able to photograph her from the outside: before such a technique until it arrived.
Milky Way is not eternal 
In about four billion years, the Milky Way will collide with its nearest neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy. Two spiral galaxies are currently moving towards each other at a speed about 400,000 km/h. When they crash into each other, it will happen great cosmic disaster. The earth is most likely survive, but many of the galaxy's stars will either be destroyed or completely change their character and location. newly formed megagalaxy will completely change the night landscape, visible from the earth: the combination of stars in the earth's sky will be completely different from what we see today.