8 delicious products that we risk losing forever (9 photos)
While many people still believe that climate change does not exist, we are already seeing its devastating effects in the form of heavy rains, hurricanes, floods, and droughts. 
But this is just one example of what global warming, changing weather patterns, and extreme temperatures are doing to our planet. Food is essential for our survival. Optimal weather conditions and temperatures, in turn, are critical for growing crops. When the climate changes and temperatures rise, food and its sustainability are affected. Here's why these 8 popular foods may not be as easy to come by in the future.
1. Grapes and Wine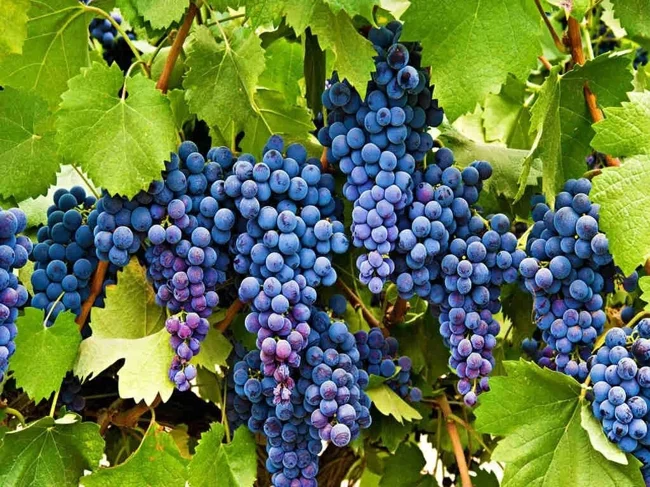 
Warmer temperatures in wine regions mean that grapes contain more sugar and less acid, and the bottle contains one to two percent more alcohol. This may not seem like a big deal, but earlier ripening due to these temperatures means that winemakers are cutting back on the time it takes to harvest grapes from the vine. This affects the quality of the product and the ability of some regions to produce popular wines.
2. Maple Syrup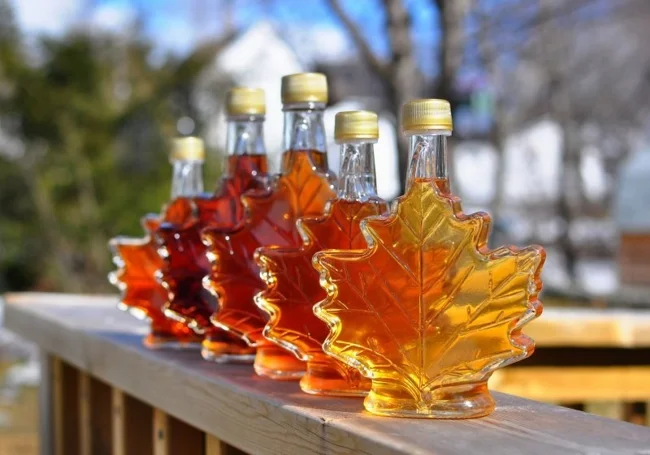 
Sugar maples need cold winter temperatures to produce the sap needed to make maple syrup. Maple trees won't necessarily disappear entirely, but they may be fewer in number and more stressed, further reducing the availability of maple syrup.
3. Seafood 
Climate change can cause ocean acidification by increasing CO2 levels. This changes the conditions that marine life needs to survive, and as a result, poses a direct threat to some species and the seafood industry.
4. Chocolate 
Rising temperatures and dwindling water supplies have made it harder for cacao trees to produce the same amount of cocoa beans, the raw ingredient for chocolate. Less chocolate and more demand mean that chocolate will become more expensive and less available in the future.
5. Cherry 
Cherry pits require exposure to cold to germinate, higher temperatures make pollination and growth more difficult. The pits are planted in the fall and seedlings begin to emerge in the spring, so warmer winters can lead to decreased germination.
6. Beans 
Beans do not like coolness and low temperatures, but they also suffer from heat, especially when it comes to flowering. Too frequent hurricanes and floods can also destroy the crop.
7. Coffee 
Coffee rust, or roya, is a fungus that destroys coffee trees by stopping photosynthesis, causing leaves to fall, and stopping growth. Rising temperatures caused by climate change allow the fungus to thrive at higher altitudes, which negatively affects coffee production.
8. Corn 
Scientists have calculated that a global temperature increase of just 1.8 degrees could slow corn growth by 7%. A drop in corn production could also mean less meat and even higher prices, since feed corn is used to produce green fodder suitable for cows, pigs, sheep and poultry.