NASA scientists have found the cause of the solar superheat (6 photos)
NASA experts have discovered the latent ultraviolet and x-rays from the sun. According to experts, the find help explain why the temperature of our star's outer layer exceeds the grandiose figure of a million degrees. 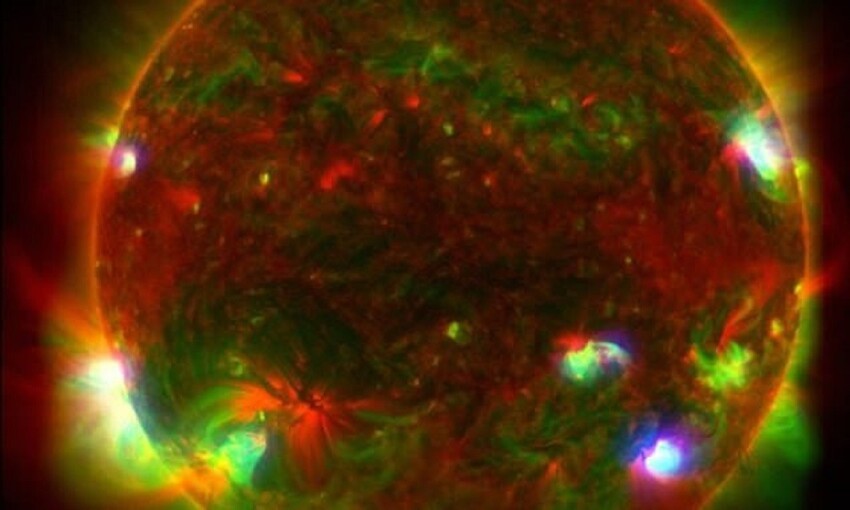
NASA scientists have discovered new types of radiation emanating from sun, which may help explain the features of our star. Using the NuSTAR Deep Space Observatory, the US space agency recorded x-rays, emitted by the hottest matter in our star's atmosphere. High-energy X-rays were observed only in several places, but low-energy X-rays and ultraviolet light was detected over the entire surface of the gaseous sphere. Scientists hope that new findings will help them solve one of the most big mysteries of the Sun: why the temperature of its outer atmosphere reaches over a million degrees - at least 100 times hotter, what is its surface? 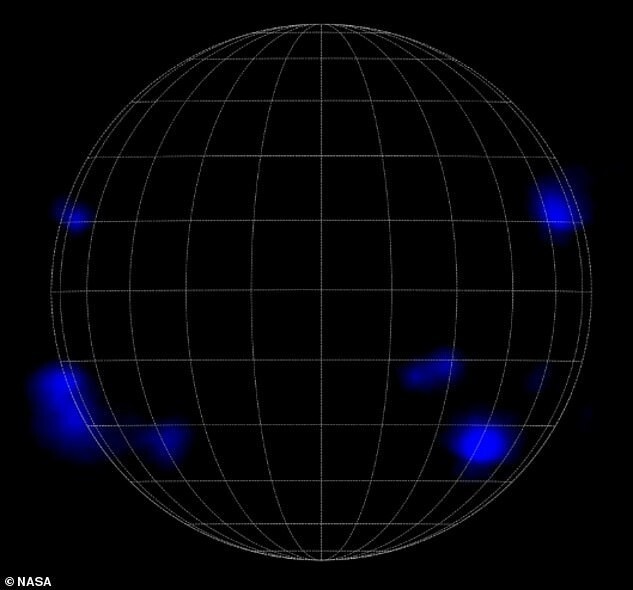
NuSTAR is usually involved in the study of black holes, supernovae and other high-energy objects in space. Now with his help It was decided to study our Sun. The result of the study can be seen in picture. The high energy X-rays observed by NuSTAR are indicated in blue, x-rays shown in green lower energy, imaged with X-ray telescope installed on the Hinode spacecraft, named after the Japanese word for sunrise. Red colors, in turn, show ultraviolet light: these photos provided by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory.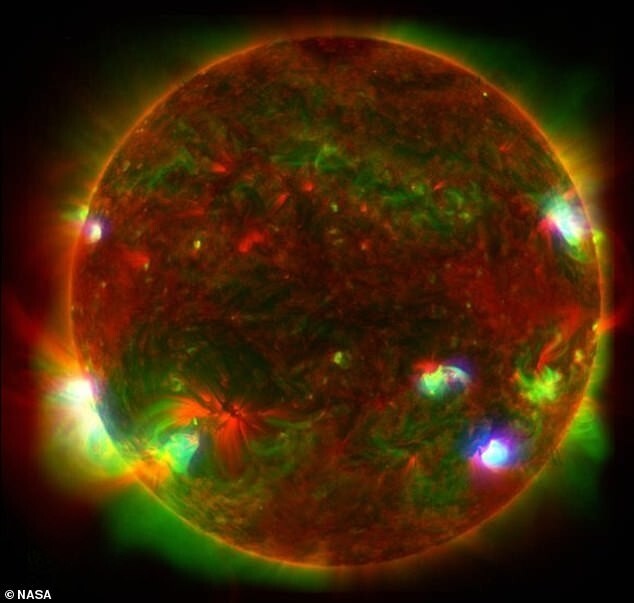 
Last June, NuSTAR took 25 photographic images Sun, which allowed NASA to put together a picture that shows rays of different colors emanating from the surface of a star. NASA also collected Observation mission Hinode Japan Aerospace Agency research, shown in green, and the Solar Observatory speakers that captured ultraviolet light, designated in red.
Now astronomers are puzzled by the source of the corona's heat, itself outer layer of the sun. They speculate that the cause is small eruptions in the solar atmosphere - the so-called nanoflares. Normal solar flares are large ejections of heat, light, and particles visible to numerous solar observatories. Although nanoflares much less, both types of flares lead to ejections of matter, which hotter than the average corona temperature. 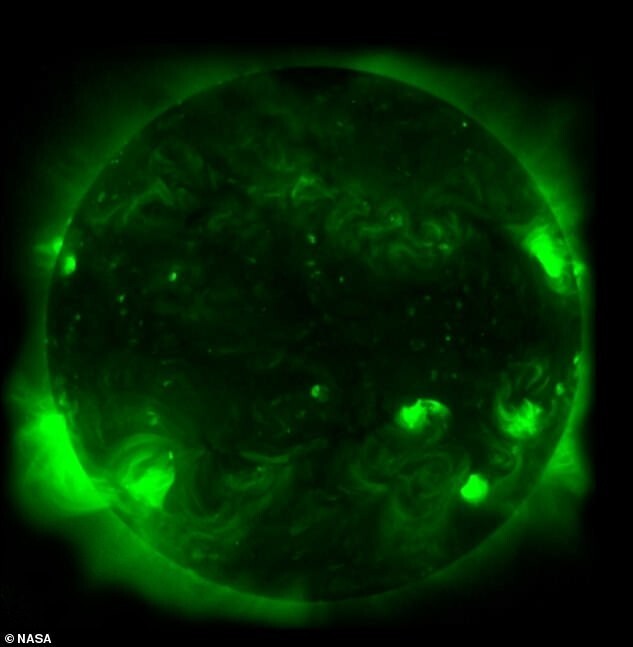
According to NASA officials, regular outbreaks not frequent enough to keep the heat of the corona, observed by scientists, but nanoflares can occur much more often - perhaps often enough to collectively heat up the corona. Individual nanoflares go unnoticed due to the bright solar light, but NuSTAR can detect light from super-hot matter, which, as the researchers believe, is formed when a large the number of nanoflares occurs close to each other. This ability allows physicists to see how often nanoflares occur and how they release energy. 
This month, NASA also made another exciting discovery by observing how a piece of northern poles of the sun. Space weather forecaster Tamita Skov on social media shared information, saying that the video was shot by the Observatory NASA Solar Dynamics. “Let's talk about the polar vortex! northern material the prominence has just detached from the main filament and is now circulating in a massive polar vortex around the north pole of our star, shared Skov NASA describes solar filaments as clouds of charged particles that float above the sun, bound to it by magnetic forces. They look like elongated uneven strands that break out with the surface of the star. The prominences mentioned by Skov appear exactly on 55 degrees latitude around the sun's polar corona every 11 years. "One once every solar cycle it forms at 55 degrees latitude and starts moving towards the solar poles,” says solar physicist Scott McIntosh, Associate Director of the National Center for Atmospheric research in Boulder, Colorado.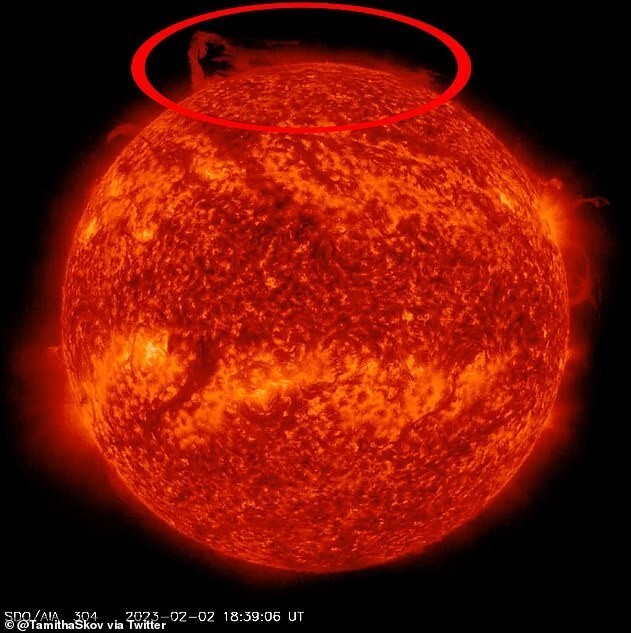 
“This is a very curious phenomenon, and yet incomprehensible,” says Mac. - Why does it move towards the pole only once, then disappear, and again, as if by magic, returns after three or four years exactly in the same area? Although astronomers have previously observed how the filaments break away from the Sun, they first managed to fix how a whirlwind circulates throughout the region. This observation may be of great importance for science, scientists say.